|
Ferdinand Hérold
Louis Joseph Ferdinand Herold (28 January 1791 – 19 January 1833), better known as Ferdinand Hérold (), was a French composer. He was celebrated in his lifetime for his operas, of which he composed more than twenty, but he also wrote ballet music, works for piano and choral pieces. He is best known today for the ballet ''La fille mal gardée#Jean-Pierre Aumer's new version taddo the music of Hérold, La Fille mal gardée'' and the overture to the opera ''Zampa''. Born in Paris to a musical family, Hérold trained at the Paris Conservatoire and won France's premier musical prize, the Prix de Rome in 1812. After a time in Italy he returned to Paris and worked first at the Comédie-Italienne, Théâtre Italien and then at the Paris Opéra, Opéra. He wrote several ballets for the latter, but was best known as a composer of ''opéra comique''. Some of them, particularly in his early days, were hampered by poor librettos, but later he had more successes than failures, and his last tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, essayist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most opera composers, Wagner wrote both the libretto and the music for each of his stage works. Initially establishing his reputation as a composer of works in the romantic vein of Carl Maria von Weber and Giacomo Meyerbeer, Wagner revolutionised opera through his concept of the ''Gesamtkunstwerk'' ("total work of art"), whereby he sought to synthesise the poetic, visual, musical and dramatic arts, with music subsidiary to drama. The drama was to be presented as a continuously sung narrative, without conventional operatic structures like Aria, arias and Recitative, recitatives. He described this vision in a List of prose works by Richard Wagner, series of essays published between 1849 and 1852. Wagner realised these ideas most fully in the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodolphe Kreutzer
Rodolphe Kreutzer (15 November 1766 – 6 January 1831) was a French violinist, teacher, conductor, and composer of forty French operas, including '' La mort d'Abel'' (1810). He is probably best known as the dedicatee of Beethoven's Violin Sonata No. 9, Op. 47 (1803), known as the ''Kreutzer Sonata'', though he never played the work. Kreutzer made the acquaintance of Beethoven in 1798, when at Vienna in the service of the French ambassador, Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte (later King of Sweden and Norway). Beethoven originally dedicated the sonata to George Bridgetower, the violinist at its first performance, but after a quarrel he revised the dedication in favour of Kreutzer. Biography Kreutzer was born in Versailles, and was initially taught by his German father, who was a musician in the royal chapel, with later lessons from Anton Stamitz. He became one of the foremost violin virtuosos of his day, appearing as a soloist until 1810. He embedded with the Army of Italy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles-Simon Catel
Charles-Simon Catel (; 10 June 1773 – 29 November 1830) was a French composer and educator born at L'Aigle, Orne. Biography Catel studied at the Royal School of Singing in Paris. He studied composition with François-Joseph Gossec and by the age of 16 became his chief assistant at the orchestra of the National Guard in 1790. A member of the Institute, he jointly composed pieces of military music for official state ceremonies, including ''L'Hymne à la Victoire'' (Victory Hymn), with words by Ponce-Denis Écouchard-Lebrun. He was appointed inaugural professor of harmony at the Conservatoire de Paris, but was relieved of his duties in 1814. Amongst his students were the Prix de Rome winning composers Joseph Daussoigne-Méhul and Victor Dourlen, the Belgian composer Martin-Joseph Mengal, and the famous, if eccentric, harpist Nicolas-Charles Bochsa. Catel died in Paris. His works include a ''Treatise on Harmony'' (1802), which was used by the young Berlioz, several concert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Adam
Louis Adam or Jean-Louis Adam (born Johann Ludwig Adam) (3 December 1758 – 8 April 1848) was a French composer, music teacher, and piano virtuoso.Baker, Theodore"Adam, Louis in ''Baker's Biographical Dictionary of Musicians, A Biographical Dictionary of Musicians'', p. 3 (New York: G. Schirmer, 1905). Life and career Born in Muttersholtz, Alsace, the son of Mathias Adam and Marie-Dorothée Meyer, Adam went to Paris in 1775 to study piano and harpsichord with Jean-Frédéric Edelmann. He spent over four decades, from 1797 through 1842, as Professor of Pianoforte at the Conservatoire de Paris, retiring in 1842 (at age 84), and died in the city, aged 89. As professor, he was the teacher of a number of notable students, including Joseph Daussoigne-Méhul, Friedrich Kalkbrenner, Ferdinand Hérold,Brubaker, Bruce and Gottlieb, Jane (eds), ''Pianist, Scholar, Connoisseur: Essays in Honor of Jacob Lateiner'' (Stuyvesant, N.Y.: Pendragon Press, 2000), p. 39, . and Henry Lemoine. In addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François-Joseph Fétis
François-Joseph Fétis (; 25 March 1784 – 26 March 1871) was a Belgian musicologist, critic, teacher and composer. He was among the most influential music intellectuals in continental Europe. His enormous compilation of biographical data in the ''Biographie universelle des musiciens'' remains an important source of information today. Family Fétis was born in Mons, Hainaut, eldest son of Antoine-Joseph Fétis and Élisabeth Desprets, daughter of a noted surgeon. He had nine brothers and sisters. His father was titular organist of the noble chapter of Saint-Waltrude. His grandfather was an organ manufacturer. He was trained as a musician by his father and played at young age on the choir organ of Saint Waltrude. In October 1806 he married Adélaïde Robert, daughter of the French politician Pierre-François-Joseph Robert and Louise-Félicité de Kéralio, friend of Robespierre. They had two sons: the elder son helped his father with the editions of '' Revue Musicale'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
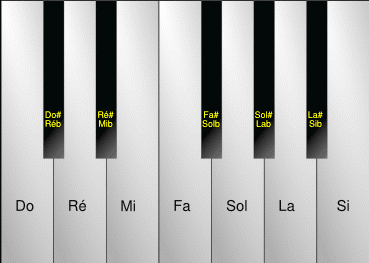
Solfège
In music, solfège (British English or American English , ) or solfeggio (; ), also called sol-fa, solfa, solfeo, among many names, is a mnemonic used in teaching aural skills, Pitch (music), pitch and sight-reading of Western classical music, Western music. Solfège is a form of solmization, though the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Syllables are assigned to the notes of the Scale (music), scale and assist the musician in Gordon music learning theory#Audiation, audiating, or mentally hearing, the pitches of a piece of music, often for the purpose of singing them aloud. Through the Renaissance music, Renaissance (and much later in some shapenote publications) various interlocking four-, five- and six-note systems were employed to cover the octave. The tonic sol-fa method popularized the seven syllables commonly used in English-speaking countries: ''do'' (spelled ''doh'' in tonic sol-fa),''Oxford English Dictionary'' 2nd Ed. (1998) ''re'', ''mi'', ''fa'', ''so(l)'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champs-Élysées
The Avenue des Champs-Élysées (, ; ) is an Avenue (landscape), avenue in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France, long and wide, running between the Place de la Concorde in the east and the Place Charles de Gaulle in the west, where the Arc de Triomphe is located. It is known for its theatres, cafés, and luxury shops; as the finish of the Tour de France cycling race; and for its annual Bastille Day military parade. The name is French for the Elysium, Elysian Fields, the place for dead heroes in Greek mythology. It has been described as the "most beautiful avenue in the whole world". Description The avenue runs for through the 8th arrondissement of Paris, 8th arrondissement in northwestern Paris, from the Place de la Concorde in the east, with the Luxor Obelisks, Obelisk of Luxor, to the Place Charles de Gaulle (formerly the ''Place de l'Étoile'') in the west, location of the Arc de Triomphe. The Champs-Élysées forms part of the ''Axe historique''. The lower part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Arrondissement Of Paris
The 1st arrondissement of Paris (''Ier arrondissement'') is one of the 20 Arrondissements of Paris, arrondissements of the capital city of France. In spoken French, this arrondissement is colloquially referred to as ''le premier'' (the first). It is governed locally together with the 2nd arrondissement of Paris, 2nd, 3rd arrondissement of Paris, 3rd and 4th arrondissement of Paris, 4th arrondissement, with which it forms the 1st sector of Paris (Paris Centre, Paris-Centre). Also known as ''Louvre'', the arrondissement is situated principally on the Rive Droite, right bank of the River Seine. It also includes the west end of the Île de la Cité. The locality is one of the oldest areas in Paris, the Île de la Cité having been the heart of the city of Lutetia, conquered by the Ancient Rome, Romans in 52 BC, while some parts on the right bank (including Les Halles) date back to the early Middle Ages. It is the least populated of the city's arrondissements and one of the smallest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-largest in the European Union with a population of over 1.9 million. The Hamburg Metropolitan Region has a population of over 5.1 million and is the List of EU metropolitan areas by GDP, eighth-largest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. At the southern tip of the Jutland Peninsula, Hamburg stands on the branching River Elbe at the head of a estuary to the North Sea, on the mouth of the Alster and Bille (Elbe), Bille. Hamburg is one of Germany's three city-states alongside Berlin and Bremen (state), Bremen, and is surrounded by Schleswig-Holstein to the north and Lower Saxony to the south. The Port of Hamburg is Germany's largest and Europe's List of busiest ports in Europe, third-largest, after Port of Rotterdam, Rotterda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach
Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach (8 March 1714 – 14 December 1788), also formerly spelled Karl Philipp Emmanuel Bach, and commonly abbreviated C. P. E. Bach, was a German composer and musician of the Baroque and Classical period. He was the fifth child and second surviving son of Johann Sebastian Bach and Maria Barbara Bach. Bach was an influential composer working at a time of transition between his father's Baroque style and the Classical style that followed it. He was the principal representative of the ' or 'sensitive style'. The qualities of his keyboard music are forerunners of the expressiveness of Romantic music, in deliberate contrast to the statuesque forms of Baroque music. His organ sonatas mainly come from the galant style. To distinguish him from his brother Johann Christian, the "London Bach", who at this time was music master to Queen Charlotte of Great Britain,Hubeart Jr., T. L. (14 July 2006"A Tribute to Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach" Bach was known as the "Berlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seltz
Seltz (; ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department of the Grand Est region in north-eastern France. It is located on the Sauer River near its confluence with the Rhine, opposite the German town of Rastatt. History The former Celtic settlement of ''Saliso'' near a crossing of the Rhine river was mentioned as the Roman '' castrum Saletio'' in the '' Notitia Dignitatum'' about 425. Later a part of the German stem duchy of Swabia, Emperor Otto I granted the area to his wife Adelaide of Burgundy in 968. Saint Adelaide established Selz Abbey in 991 and died here eight years later. In 1357 Emperor Charles IV of Luxembourg raised Selz to an Imperial city, after which the town joined the Alsatian Décapole league. It however lost its immediate status in 1414, when it was mediatised by Elector Palatine Louis III of Wittelsbach. Seltz finally was annexed by France in 1680. Population Landmarks Église Saint-Étienne de Seltz was last built in 1954–6. Ferry Seltz - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |