|
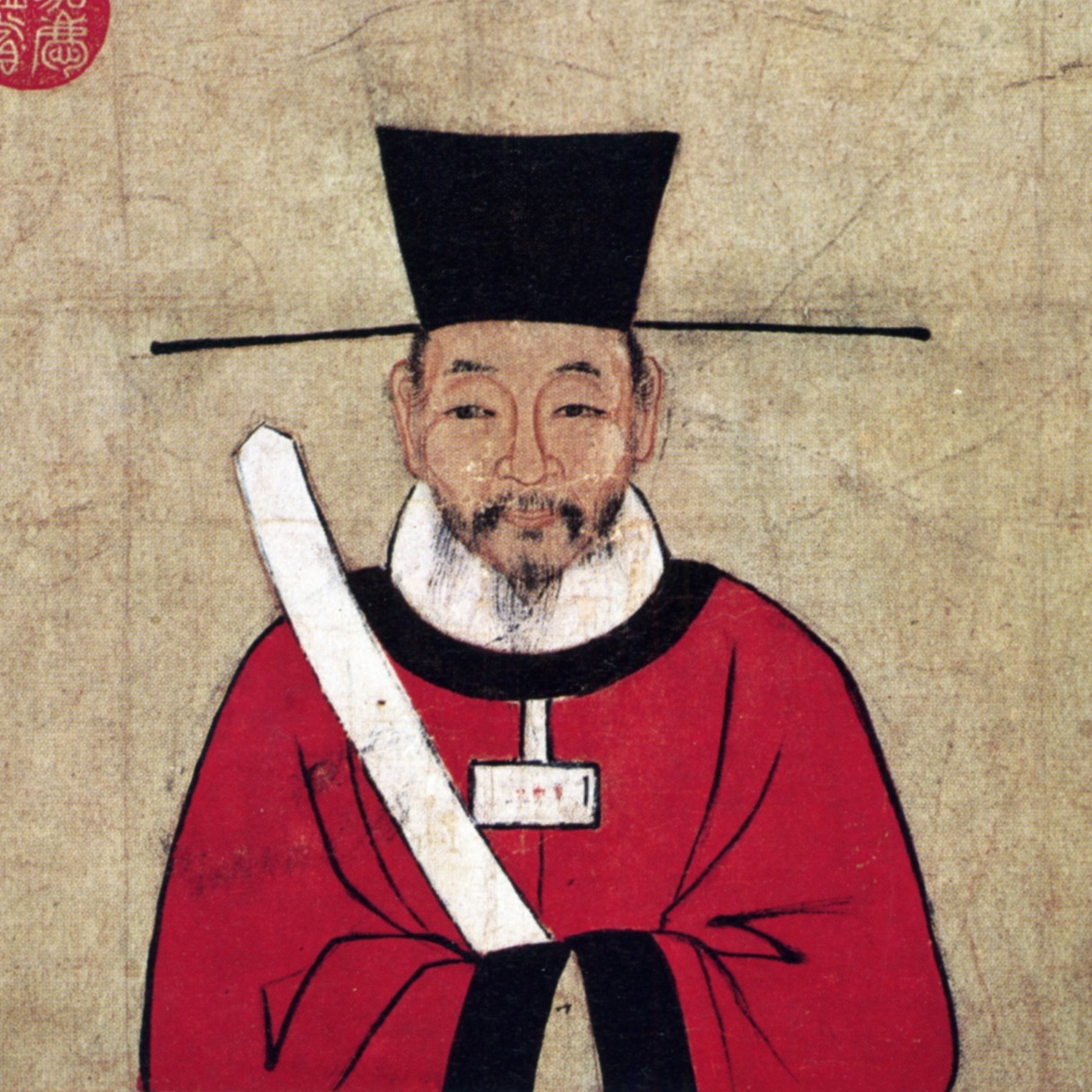
Feng Ba
Feng Ba (; died 430), courtesy name Wenqi (文起), nickname Qizhifa (乞直伐), also known by his posthumous name as the Emperor Wencheng of Northern Yan (北燕文成帝), was either the founding or second Chinese sovereign, ruler of the Northern Yan, Northern Yan dynasty of China. He became monarch after Gao Yun (emperor), Gao Yun (Emperor Huiyi), whom he supported in a 407 coup that overthrew Murong Xi (Emperor Zhaowen), was assassinated in 409. During his reign, the Northern Yan largely maintained its territorial integrity but made no headway against the much stronger rival Northern Wei, Northern Wei dynasty. He was said to have had more than 100 sons, but after his death in 430, his brother and successor Feng Hong (Emperor Zhaocheng) had them all executed. Family background and early life Feng Ba's grandfather Feng He (馮和) was ethnically Han Chinese and was said to have settled down in Shangdang Commandery (上黨, roughly modern Changzhi, Shanxi) in the aftermaths of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavenly King
Heavenly King or Tian Wang (), also translated as Heavenly Prince, is a Chinese language, Chinese title for various religious deities and divine leaders throughout history, as well as an alternate form of the term ''Son of Heaven'', referring to the Emperor of China, emperor. The Chinese term for Heavenly King consists of two Chinese characters: 天 (''tiān''), meaning Tian, "heaven" or "sky", and 王 (''wáng''), which could mean either "king" or "prince" depending on the context. The term was most notably used in its most recent sense as the title of the kings of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom, but is also used in religious (particularly Buddhism, Buddhist) contexts as well. Historical uses Spring and Autumn period In the Spring and Autumn period, the term ''Heavenly King'' was used to at least some extent to refer to the kings of the various Chinese states of the time. On the second page of the first text of the Spring and Autumn Annals, the term ''Heavenly King'' is used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
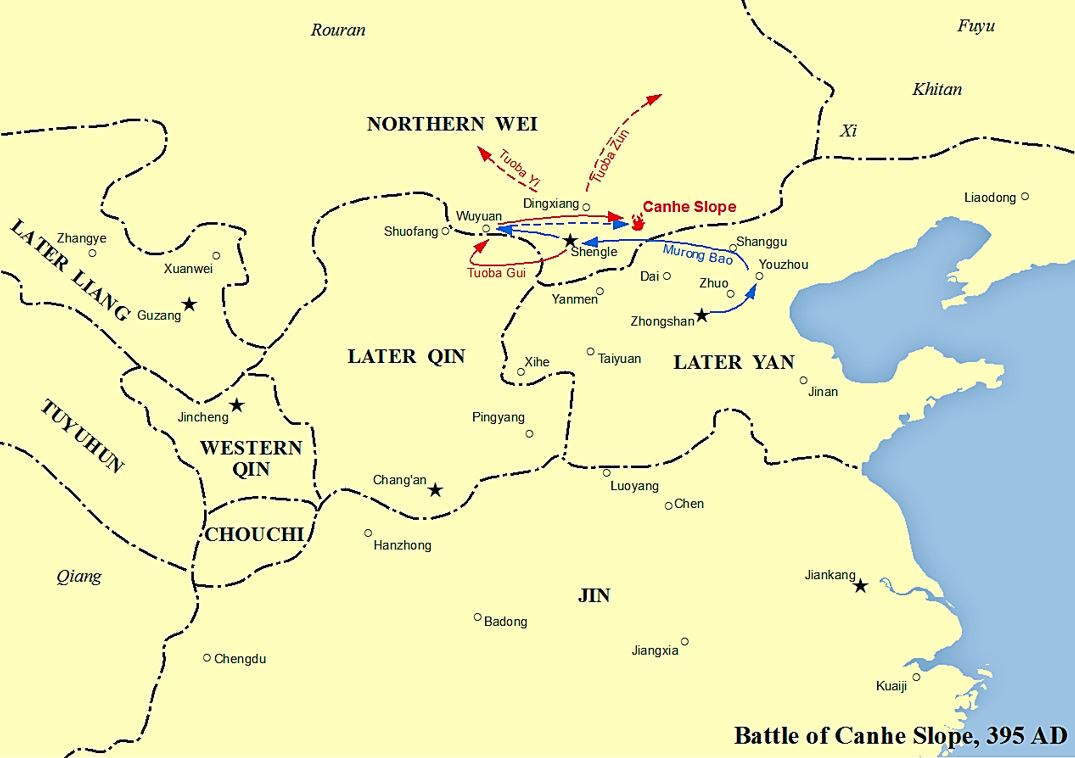
Later Yan
Yan, known in historiography as the Later Yan (; 384 – 407 or 409), was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Xianbei people during the era of Sixteen Kingdoms. The prefix "Later" to distinguish them from the Former Yan before them and other Yan states from the period. Historiographers also consider the Former Yan and Later Yan as separate states despite both being ruled by the same imperial family, and the Later Yan's founder, Murong Chui, had intended his state to be a restoration. Due to the devastation inflicted on the old Yan capital, Ye, the city of Zhongshan (中山, in modern Baoding, Hebei) became the first capital of the Later Yan. The Later Yan managed to recover most of their old territory in Liaoning, Hebei, Shaanxi, Shandong and Henan by 394. However, after the Northern Wei invasion in 396, they were reduced to Liaoning and parts of northeastern Hebei, where they made Longcheng their new capital. Their territory was further reduced during their war with Gogu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Sun
Princess Sun (; personal name unknown) was a princess consort of the Chinese Northern Yan dynasty. Her husband was Feng Ba Feng Ba (; died 430), courtesy name Wenqi (文起), nickname Qizhifa (乞直伐), also known by his posthumous name as the Emperor Wencheng of Northern Yan (北燕文成帝), was either the founding or second Chinese sovereign, ruler of the Norther ... (Emperor Wencheng). When Feng Ba took the throne in 409 after the death of Gao Yun (Emperor Huiyi), he took the title "Heavenly King" (''Tian Wang''), but whereas most owners of that title during the Sixteen Kingdoms period treated themselves and were treated as emperors in all respects, including creating their wives as empresses, Feng Ba only gave her the title of princess. No further historical reference was made to her, although she was in all likelihood the mother of his daughter Princess Lelang. At the time of Feng Ba's death in 430, his favorite concubine was Consort Song, and nothing was mentioned a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixteen Kingdoms
The Sixteen Kingdoms (), less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439 when northern China fragmented into a series of short-lived dynastic states. The majority of these states were founded by the "Five Barbarians", non- Han peoples who had settled in northern and western China during the preceding centuries, and had launched a series of rebellions against the Western Jin dynasty in the early 4th century. However, several of the states were founded by the Han people, and all of the states—whether ruled by Xiongnu, Xianbei, Di, Jie, Qiang, Han, or others—took on Han-style dynastic names. The states frequently fought against both one another and the Eastern Jin dynasty, which succeeded the Western Jin in 317 and ruled southern China. The period ended with the unification of northern China in 439 by the Northern Wei, a dynasty established by the Xianbei Tuoba clan. This occurred 19 years after the Eastern Jin collapsed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Dowager
Empress dowager (also dowager empress or empress mother; ) is the English language translation of the title given to the mother or widow of a monarch, especially in regards to Chinese, Japanese, Korean, or Vietnamese monarchs in the Chinese cultural sphere. The term however, is applied well beyond just East Asia. The title was also given occasionally to another woman of the same generation, while a woman from the previous generation was sometimes given the title of grand empress dowager (). An empress dowager wielded power over the harem and imperial family. Numerous empress dowagers held regency during the reign of underage emperors. Many of the most prominent empress dowagers also extended their control for long periods after the emperor was old enough to govern. This was a source of political turmoil according to the traditional view of Chinese history. In Europe, the title dowager empress was given to the wife of a deceased Emperor of Russia or Holy Roman Emperor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Dowager Zhang
Feng Ba (; died 430), courtesy name Wenqi (文起), nickname Qizhifa (乞直伐), also known by his posthumous name as the Emperor Wencheng of Northern Yan (北燕文成帝), was either the founding or second ruler of the Northern Yan dynasty of China. He became monarch after Gao Yun (Emperor Huiyi), whom he supported in a 407 coup that overthrew Murong Xi (Emperor Zhaowen), was assassinated in 409. During his reign, the Northern Yan largely maintained its territorial integrity but made no headway against the much stronger rival Northern Wei dynasty. He was said to have had more than 100 sons, but after his death in 430, his brother and successor Feng Hong (Emperor Zhaocheng) had them all executed. Family background and early life Feng Ba's grandfather Feng He (馮和) was ethnically Han Chinese and was said to have settled down in Shangdang Commandery (上黨, roughly modern Changzhi, Shanxi) in the aftermaths of the conquest of the northern half of Jin during the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zizhi Tongjian
The ''Zizhi Tongjian'' (1084) is a chronicle published during the Northern Song dynasty (960–1127) that provides a record of Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynasties and spanning almost 1400 years. The main text is arranged into 294 scrolls (), each equivalent to a chapter—totaling around 3 million Chinese characters. In 1065, Emperor Yingzong of Song commissioned his official, Sima Guang (1019–1086), to lead a project to compile a Universal history (genre), universal history of China, and granted him funding and the authority to appoint his own staff. His team took 19 years to complete the work and in 1084 it was presented to Emperor Yingzong's successor Emperor Shenzong of Song. It was well-received and has proved to be immensely influential among both scholars and the general public. Endymion Wilkinson regards it as reference quality: "It had an enormous influence on later Chinese historical writing, either directly or through its many a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Shu
The ''Book of Jin'' is an official Chinese historical text covering the history of the Jin dynasty from 266 to 420. It was compiled in 648 by a number of officials commissioned by the imperial court of the Tang dynasty, with chancellor Fang Xuanling as the lead editor, drawing mostly from official documents left from earlier archives. A few essays in volumes 1, 3, 54 and 80 were composed by the Tang dynasty's Emperor Taizong himself. However, the contents of the ''Book of Jin'' included not only the history of the Jin dynasty, but also that of the Sixteen Kingdoms period, which was contemporaneous with the Eastern Jin dynasty. Compilation Over 20 histories of the Jin had been written during the Jin era itself and the subsequent Northern and Southern dynasties, of which 18 were still extant at the beginning of the Tang dynasty. Yet Emperor Taizong deemed them all to be deficient and ordered the compilation of a new standard history for the period,Fang, Xuanling ''ed.''(2002) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Fu Xunying
Fu Xunying (苻訓英) (died 407 AD) was an empress of the Xianbei-led Chinese Later Yan dynasty. Her husband was Murong Xi (Emperor Zhaowen). Life Fu Xunying was a daughter of Fu Mo (苻謨), a member of Former Qin's imperial house before he surrendered to Later Yan under military pressure. As of 397, he was the mayor of Later Yan's capital Zhongshan (中山, in modern Baoding, Hebei) when the Later Yan emperor Murong Bao (Emperor Huimin) abandoned Zhongshan in face of Northern Wei military attacks, and he was subsequently killed by Murong Bao's nephew Murong Xiang (慕容詳) the Duke of Kaifeng, who wanted to be emperor himself. His family was slaughtered. Somehow, however, Fu Xunying and her older sister Fu Song'e were not killed—perhaps they escaped the slaughter, or perhaps they were no longer in Zhongshan at that point. After Murong Xi became emperor in 401 after succeeding his nephew Murong Sheng (Emperor Zhaowu), he took Fu Song'e and Fu Xunying as imperial con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gao Yun (Northern Yan)
Gao Yun () (died 409), at one time Murong Yun (慕容雲), courtesy name Ziyu (子雨), also known by his posthumous name as the Emperor Huiyi of Later/Northern Yan (後/北燕惠懿帝), was either the last monarch of China's Later Yan dynasty or the founding monarch of China's Northern Yan dynasty, depending on the historian's characterization. He was a descendant of the royal house of Goguryeo (Gaogouli), whose ancestors were captured by the Former Yan dynasty. He was adopted into the Later Yan imperial house after helping Murong Bao (Emperor Huimin) put down a rebellion by Murong Bao's son Murong Hui. Gao Yun became emperor after the people rebelled against the despotic rule of his adoptive uncle Murong Xi (Emperor Zhaowen), and during his reign, he used the title "Heavenly King". In 409, he was assassinated, and after a disturbance, was replaced by his ethnic Han general Feng Ba (Emperor Wencheng). Original from the University of California Early life Gao Yun's ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murong Bao
Murong Bao (; 355–398), courtesy name Daoyou (道佑), Xianbei name Kugou (庫勾), also known by his posthumous name as the Emperor Huimin of Later Yan (後燕惠愍帝), was an Emperor of China, emperor of the Xianbei-led Chinese Later Yan, Later Yan dynasty. He inherited from his father Murong Chui (Emperor Wucheng) a sizable empire but lost most of it within a span of a year, and would be dead in less than three, a victim of a rebellion by his granduncle Lan Han. Historians largely attributed this to his irresolution and inability to judge military and political decisions. While the Later Yan would last for one more decade after his death, it would never regain the power it had under Murong Chui. Prior to Later Yan's establishment Murong Bao was Murong Chui's fourth son, by his first wife Princess Duan (Murong Chui's wife), Princess Duan while he was the Prince of Wu under his brother Murong Jun (Emperor Jingzhao of Former Yan). He was initially not his father's heir apparen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multilingual, multi-ethnic confederation consisting of mainly Proto-Mongols (who spoke either pre-Proto-Mongolic,, quote: "The Xianbei confederation appears to have contained speakers of Pre-Proto-Mongolic, perhaps the largest constituent linguistic group, as well as former Xiongnu subjects, who spoke other languages, Turkic almost certainly being one of them."Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Pressp. 452of pp. 411–466. or Para-Mongolic languages), and, to a minor degree, Tungusic and Turkic peoples. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the Wuhuan and Xianbei when they were defeated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |