|
Faraday Effect
The Faraday effect or Faraday rotation, sometimes referred to as the magneto-optic Faraday effect (MOFE), is a physical magneto-optical phenomenon. The Faraday effect causes a polarization rotation which is proportional to the projection of the magnetic field along the direction of the light propagation. Formally, it is a special case of gyroelectromagnetism obtained when the dielectric permittivity tensor is diagonal. This effect occurs in most optically transparent dielectric materials (including liquids) under the influence of magnetic fields. Discovered by Michael Faraday in 1845, the Faraday effect was the first experimental evidence that light and electromagnetism are related. The theoretical basis of electromagnetic radiation (which includes visible light) was completed by James Clerk Maxwell in the 1860s. Maxwell's equations were rewritten in their current form in the 1870s by Oliver Heaviside. The Faraday effect is caused by left and right circularly polarized wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superposition Principle
The superposition principle, also known as superposition property, states that, for all linear systems, the net response caused by two or more stimuli is the sum of the responses that would have been caused by each stimulus individually. So that if input ''A'' produces response ''X'', and input ''B'' produces response ''Y'', then input (''A'' + ''B'') produces response (''X'' + ''Y''). A function F(x) that satisfies the superposition principle is called a linear function. Superposition can be defined by two simpler properties: additivity F(x_1 + x_2) = F(x_1) + F(x_2) and homogeneity F(ax) = a F(x) for scalar . This principle has many applications in physics and engineering because many physical systems can be modeled as linear systems. For example, a beam can be modeled as a linear system where the input stimulus is the load on the beam and the output response is the deflection of the beam. The importance of linear systems is that they are easier to analyze mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electro-optic Effect
Electro–optics is a branch of electrical engineering, electronic engineering, materials science, and material physics involving components, electronic devices such as lasers, laser diodes, LEDs, waveguides, etc. which operate by the propagation and interaction of light with various tailored materials. It is closely related to photonics, the branch of optics that involves the application of the generation of photons. It is not only concerned with the " electro–optic effect", since it deals with the interaction between the electromagnetic (optical) and the electrical ( electronic) states of materials. Electro-optical devices The electro-optic effect is a change in the optical properties of an optically active material in response to changes in an electric field. This interaction usually results in a change in the birefringence Birefringence, also called double refraction, is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Étienne-Louis Malus
Étienne-Louis Malus (; ; 23 July 1775 – 23 February 1812) was a French officer, engineer, physicist, and mathematician. Malus was born in Paris, France and studied at the military engineering school at Mezires where he was taught by Gaspard Monge. He participated in Napoleon's expedition into Egypt (1798 to 1801). He was also a member of the mathematics section of the Institut d'Égypte. Malus became a member of the Académie des Sciences in 1810. In 1810 the Royal Society of London awarded him the Rumford Medal. His mathematical work was almost entirely concerned with the study of light. He studied geometric systems called ''ray systems'', closely connected to Julius Plücker's '' line geometry''. He conducted experiments to verify Christiaan Huygens's theories of light and rewrote the theory in analytical form. His discovery of the polarization of light by reflection was published in 1809 and his theory of double refraction of light in crystals, in 1810. Malus at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustin-Jean Fresnel
Augustin-Jean Fresnel (10 May 1788 – 14 July 1827) was a French civil engineer and physicist whose research in optics led to the almost unanimous acceptance of the wave theory of light, excluding any remnant of Isaac Newton, Newton's corpuscular theory of light, corpuscular theory, from the late 1830s until the end of the 19th century. He is perhaps better known for inventing the Catadioptric system, catadioptric (reflective/refractive) Fresnel lens and for pioneering the use of "stepped" lenses to extend the visibility of lighthouses, saving countless lives at sea. The simpler Dioptrics, dioptric (purely refractive) stepped lens, first proposed by Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon, Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel, is used in screen magnifying glass, magnifiers and in condenser lenses for overhead projectors. By expressing Christiaan Huygens, Huygens's principle of secondary waves and Thomas Young (scientist), Young's principle of interference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday With Glass Bar Crop2
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the study of electrochemistry and electromagnetism. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis. Although Faraday received little formal education, as a self-made man, he was one of the most influential scientists in history. It was by his research on the magnetic field around a Electrical conductor, conductor carrying a direct current that Faraday established the concept of the electromagnetic field in physics. Faraday also established that magnetism could Faraday effect, affect rays of light and that there was an underlying relationship between the two phenomena. the 1911 ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. He similarly discovered the principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and the Faraday's laws of electrolysis, laws of electrolysis. His inventions of electric motor, electromagnetic rotar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Circulators
An optical circulator is a three- or four-port optical device designed such that light entering any port exits from the next. This means that if light enters port 1 it is emitted from port 2, but if some of the emitted light is reflected back to the circulator, it does not come out of port 1 but instead exits from port 3. This is analogous to the operation of an electronic circulator. Fiber-optic circulators are used to separate optical signals that travel in opposite directions in an optical fiber, for example to achieve bi-directional transmission over a single fiber. Because of their high isolation of the input and reflected optical powers and their low insertion loss, optical circulators are widely used in advanced fiber-optic communications and fiber-optic sensor applications. Optical circulators are ''non-reciprocal'' optics, which means that changes in the properties of light passing through the device are not reversed when the light passes through in the opposite direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
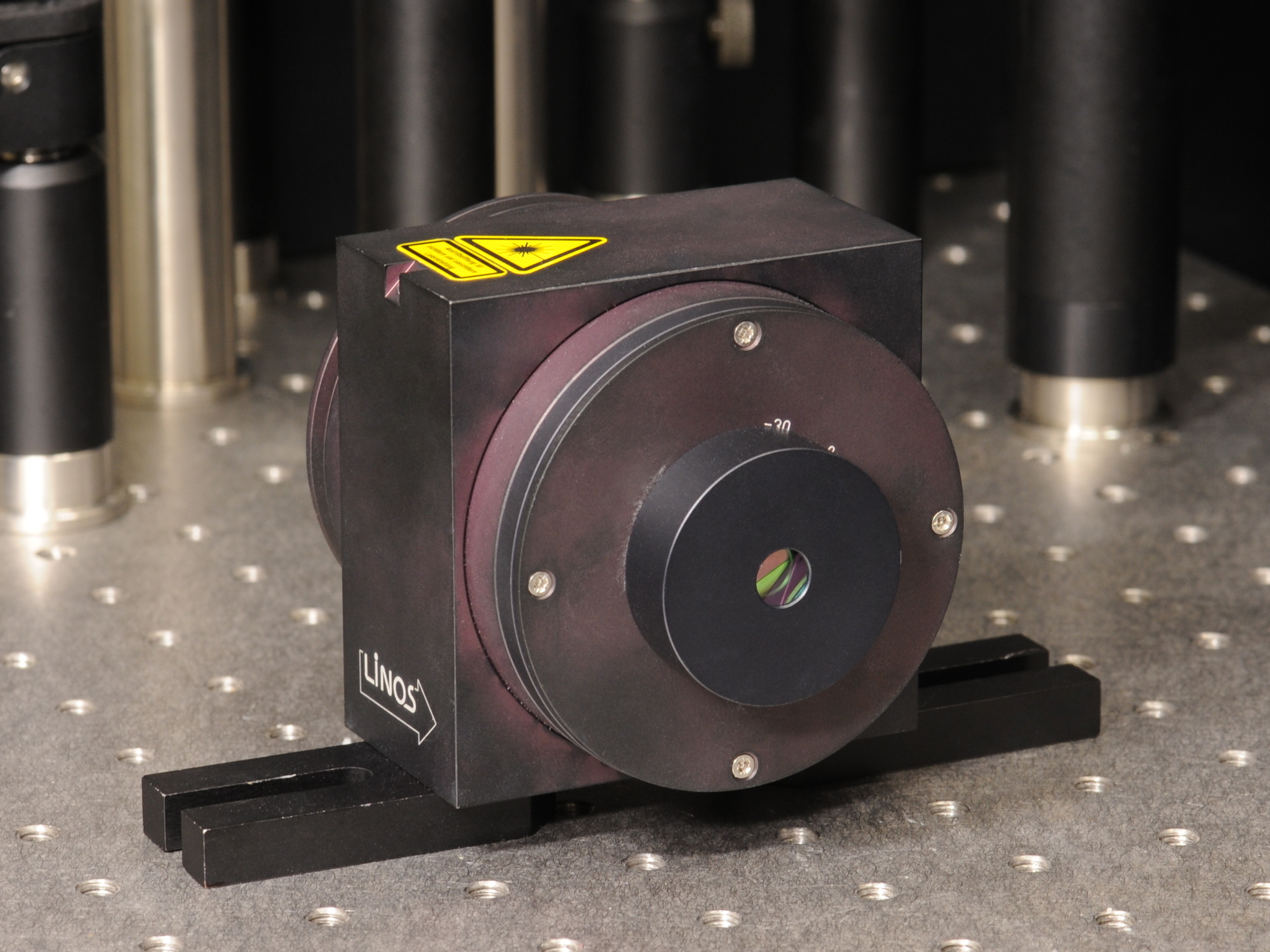
Optical Isolator
An optical isolator, or optical diode, is an optical component which allows the transmission of light in only one direction. It is typically used to prevent unwanted feedback into an optical oscillator, such as a laser cavity. The operation of conventional optical isolators relies on the Faraday effect (which in turn is produced by magneto-optic effect), which is used in the main component, the Faraday rotator. However, integrated isolators which do not rely on magnetism have been made in recent years too. Theory The main component of the optical isolator is the Faraday rotator. The magnetic field, B, applied to the Faraday rotator causes a rotation in the polarization of the light due to the Faraday effect. The angle of rotation, \beta, is given by, :\beta=\nu B d\,, where, \nu is the Verdet constant of the material (amorphous or crystalline solid, or liquid, or crystalline liquid, or vaprous, or gaseous) of which the rotator is made, and d is the length of the rotato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Rotator
A Faraday rotator is a polarization rotator based on the Faraday effect, a magneto-optic effect involving transmission of light through a material when a longitudinal static magnetic field is present. The state of polarization (such as the axis of linear polarization or the orientation of elliptical polarization) is rotated as the wave traverses the device, which is explained by a slight difference in the phase velocity between the left and right circular polarizations. Thus it is an example of circular birefringence, as is optical activity, but involves a material only having this property in the presence of a magnetic field. Mechanism Circular birefringence, involving a difference in propagation between opposite circular polarizations, is distinct from linear birefringence (or simply birefringence, when the term is not further specified) which also transforms a wave's polarization but not through a simple rotation. The polarization state is rotated in proportion to the applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluxon
In physics, a fluxon is a quantum of electromagnetic flux. The term may have any of several related meanings. Superconductivity In the context of superconductivity, in type II superconductors fluxons (also known as Abrikosov vortices) can form when the applied field lies between B_ and B_. The fluxon is a small whisker of normal phase surrounded by superconducting phase, and Supercurrents circulate around the normal core. The magnetic field through such a whisker and its neighborhood, which has size of the order of London penetration depth \lambda_L (~100 nm), is quantized because of the phase properties of the magnetic vector potential in quantum electrodynamics, see magnetic flux quantum for details. In the context of long Superconductor-Insulator-Superconductor Josephson tunnel junctions, a fluxon (aka Josephson vortex) is made of circulating supercurrents and has ''no'' normal core in the tunneling barrier. Supercurrents circulate just around the mathematical center of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where Electrical resistance and conductance, electrical resistance vanishes and Magnetic field, magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic Electrical conductor, conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic Phase transition, critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and Atomic spectral line, atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete cancellation of the magnetic field in the interior of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spintronics
Spintronics (a portmanteau meaning spin transport electronics), also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-state devices. The field of spintronics concerns spin-charge coupling in metallic systems; the analogous effects in insulators fall into the field of multiferroics. Spintronics fundamentally differs from traditional electronics in that, in addition to charge state, electron spins are used as a further degree of freedom, with implications in the efficiency of data storage and transfer. Spintronic systems are most often realised in dilute magnetic semiconductors (DMS) and Heusler alloys and are of particular interest in the field of quantum computing and neuromorphic computing, upon which leads to integrated research requirements around Hyperdimensional Computation. History Spintronics emerged from discoveries in the 1980s concerning spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |