|
Ătienne-Louis Malus
Ătienne-Louis Malus (; ; 23 July 1775 – 23 February 1812) was a French officer, engineer, physicist, and mathematician. Malus was born in Paris, France and studied at the military engineering school at Mezires where he was taught by Gaspard Monge. He participated in Napoleon's expedition into Egypt (1798 to 1801). He was also a member of the mathematics section of the Institut d'Ăgypte. Malus became a member of the AcadĂŠmie des Sciences in 1810. In 1810 the Royal Society of London awarded him the Rumford Medal. His mathematical work was almost entirely concerned with the study of light. He studied geometric systems called ''ray systems'', closely connected to Julius PlĂźcker's '' line geometry''. He conducted experiments to verify Christiaan Huygens's theories of light and rewrote the theory in analytical form. His discovery of the polarization of light by reflection was published in 1809 and his theory of double refraction of light in crystals, in 1810. Malus at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-LĂŠopold Boilly
Louis-LĂŠopold Boilly (; 5 July 1761 â 4 January 1845) was a French painter and draftsman. A creator of popular portrait paintings, he also produced a vast number of genre paintings documenting French middle-class social life. His life and work spanned the eras of Ancien RĂŠgime, monarchical France, the French Revolution, the First French Empire, Napoleonic Empire, the Bourbon Restoration in France, Bourbon Restoration and the July Monarchy. His 1800 painting ''Un Trompe-l'Ĺil'' introduced the term ''trompe-l'Ĺil'' ("trick the eye"), applied to the technique that uses realistic imagery to create the optical illusion that the depicted objects exist in three dimensions, though the "unnamed" technique itself had existed in Greek and Roman times. Life and career Boilly was born in La BassĂŠe in northern France, the son of a local wood sculptor. A self-taught painter, Boilly began his career at a very young age, producing his first works at the age of twelve or thirteen. In 1774 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AcadĂŠmie Des Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (, ) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific method, scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, and is one of the earliest Academy of Sciences, Academies of Sciences. Currently headed by Patrick Flandrin (President of the academy), it is one of the five Academies of the . __TOC__ History The Academy of Sciences traces its origin to Colbert's plan to create a general academy. He chose a small group of scholars who met on 22 December 1666 in the King's library, near the present-day Bibliothèque nationale de France, Bibliothèque Nationale, and thereafter held twice-weekly working meetings there in the two rooms assigned to the group. The first 30 years of the academy's existence were relatively informal, since no statutes had as yet been laid down for the ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewster's Law
Brewster's angle (also known as the polarization angle) is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with ''no reflection''. When ''unpolarized'' light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. The angle is named after the Scottish physicist Sir David Brewster (1781â1868). Explanation When light encounters a boundary between two media with different refractive indices, some of it is usually reflected as shown in the figure above. The fraction that is reflected is described by the Fresnel equations, and depends on the incoming light's polarization and angle of incidence. The Fresnel equations predict that light with the ''p'' polarization (electric field polarized in the same plane as the incident ray and the surface normal at the point of incidence) will not be reflected if the angle of incidence is :\theta_\mathrm = \arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir David Brewster
Sir David Brewster KH PRSE FRS FSA Scot FSSA MICE (11 December 178110 February 1868) was a British scientist, inventor, author, and academic administrator. In science he is principally remembered for his experimental work in physical optics, mostly concerned with the study of the polarization of light and including the discovery of Brewster's angle. He studied the birefringence of crystals under compression and discovered photoelasticity, thereby creating the field of optical mineralogy.A. D. Morrison-Low (2004) "Brewster, Sir David (1781â1868)" in ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' For this work, William Whewell dubbed him the "father of modern experimental optics" and "the Johannes Kepler of optics." Brewster was a pioneer in photography. He invented an improved stereoscope, which he called "lenticular stereoscope" and which became the first portable 3D-viewing device. He also invented the stereoscopic camera, two types of polarimeters, the polyzonal lens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refraction, refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflectivity, reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
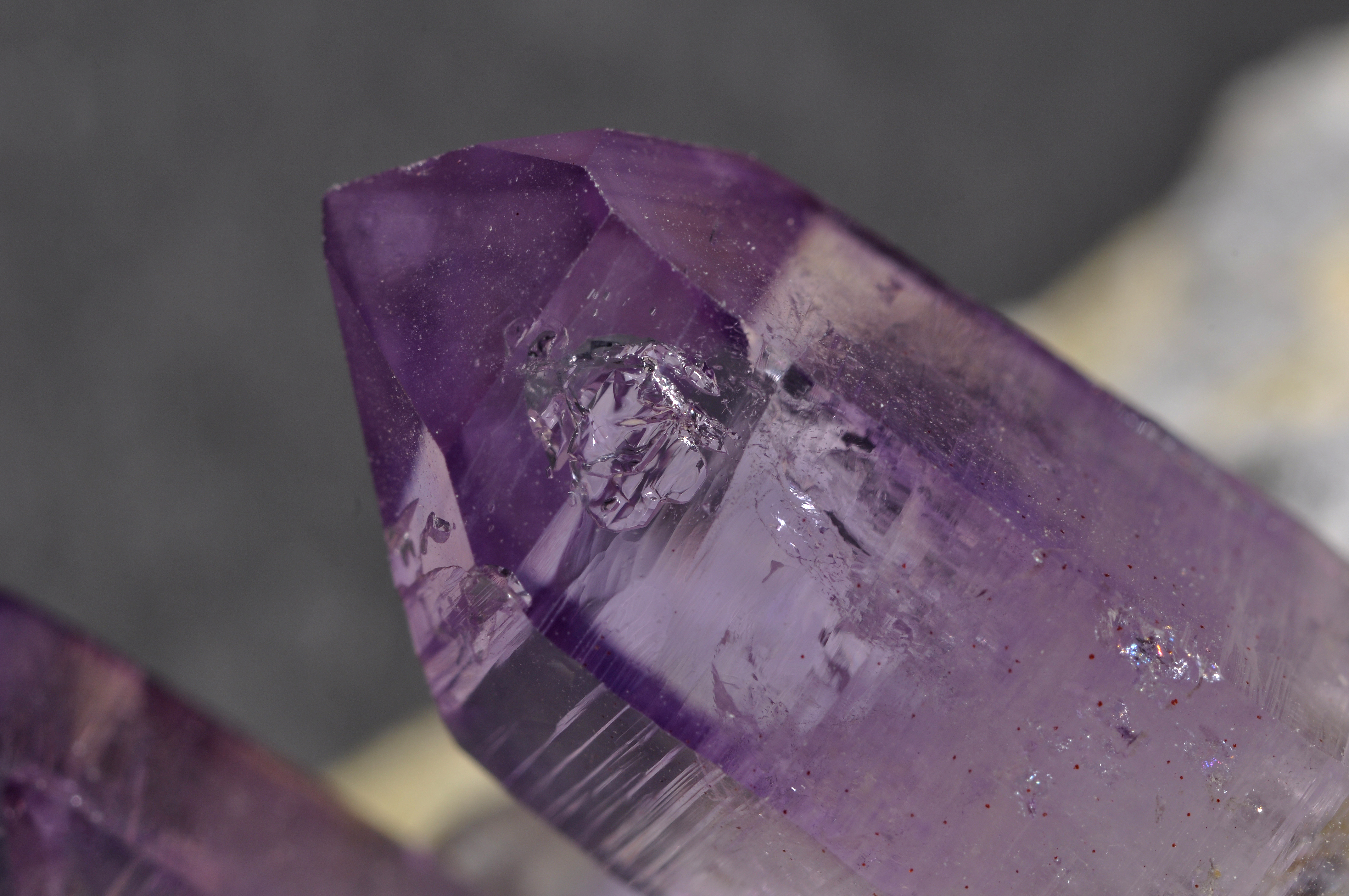
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and " rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Refraction
Birefringence, also called double refraction, is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are described as birefringent or birefractive. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in Iceland spar (calcite) crystals which have one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. The ''law of reflection'' says that for specular reflection (for example at a mirror) the angle at which the wave is incident on the surface equals the angle at which it is reflected. In acoustics, reflection causes echoes and is used in sonar. In geology, it is important in the study of seismic waves. Reflection is observed with surface waves in bodies of water. Reflection is observed with many types of electromagnetic wave, besides visible light. Reflection of VHF and higher frequencies is important for radio transmission and for radar. Even hard X-rays and gamma rays can be reflected at shallow angles with special "grazing" mirrors. Reflection of light Reflection of light is either '' specular'' (mirror-like) or '' diffuse'' (retai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 â 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution. In physics, Huygens made seminal contributions to optics and mechanics, while as an astronomer he studied the rings of Saturn and discovered its largest moon, Titan (moon), Titan. As an engineer and inventor, he improved the design of telescopes and invented the pendulum clock, the most accurate timekeeper for almost 300 years. A talented mathematician and physicist, his works contain the first idealization of a physical problem by a set of Mathematical model, mathematical parameters, and the first mathematical and mechanistic explanation of an unobservable physical phenomenon.Dijksterhuis, F.J. (2008) Stevin, Huygens and the Dutch republic. ''Nieuw archief voor wiskunde'', ''5'', pp. 100â10/ref> Huygens first identified the correct la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Geometry
In geometry, line coordinates are used to specify the position of a line just as point coordinates (or simply coordinates) are used to specify the position of a point. Lines in the plane There are several possible ways to specify the position of a line in the plane. A simple way is by the pair where the equation of the line is ''y'' = ''mx'' + ''b''. Here ''m'' is the slope and ''b'' is the ''y''-intercept. This system specifies coordinates for all lines that are not vertical. However, it is more common and simpler algebraically to use coordinates where the equation of the line is ''lx'' + ''my'' + 1 = 0. This system specifies coordinates for all lines except those that pass through the origin. The geometrical interpretations of ''l'' and ''m'' are the negative reciprocals of the ''x'' and ''y''-intercept respectively. The exclusion of lines passing through the origin can be resolved by using a system of three coordinates to speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius PlĂźcker
Julius PlĂźcker (16 June 1801 â 22 May 1868) was a German mathematician and physicist. He made fundamental contributions to the field of analytical geometry and was a pioneer in the investigations of cathode rays that led eventually to the discovery of the electron. He also vastly extended the study of LamĂŠ curves. Biography Early years PlĂźcker was born at Elberfeld (now part of Wuppertal). After being educated at DĂźsseldorf and at the universities of Bonn, Heidelberg and Berlin he went to Paris in 1823, where he came under the influence of the great school of French geometers, whose founder, Gaspard Monge, had only recently died. In 1825 he returned to Bonn, and in 1828 was made professor of mathematics. In the same year he published the first volume of his ''Analytisch-geometrische Entwicklungen'', which introduced the method of "abridged notation". In 1831 he published the second volume, in which he clearly established on a firm and independent basis projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |