|
Fabrizio Ruffo
Fabrizio Dionigi Ruffo (16 September 1744 – 13 December 1827) was an Italian cardinal and politician, who led the popular anti-Jacobin '' Sanfedismo'' movement (whose members were known as the ''Sanfedisti''). Biography Ruffo was born at San Lucido, in Calabria Citra (today in province of Cosenza), then part of the Kingdom of Naples. His father, Litterio Ruffo, was a Calabrian aristocrat, holder of the title of duke of Baranello, while his mother, Giustiniana, was of the Roman family of Colonna. Fabrizio owed his education to his uncle, cardinal Tommaso Ruffo, then dean of the College of Cardinals. In early life he secured the favour of Giovanni Angelo Braschi, who in 1775 became Pope Pius VI. Ruffo was placed by the pope among the ''chierici di camera'', the clerks who formed the papal civil and financial service. He was later promoted to treasurer-general, a post which carried with it the ministry of war. Ruffo's conduct in office was diversely judged. Pietro Colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
His Eminence
His Eminence (abbreviation H.Em. or HE) is a style (manner of address), style of reference for high nobility, still in use in various religious contexts. Catholicism The style remains in use as the official style or standard form of address in reference to a cardinal (Catholicism), cardinal of the Catholic Church, reflecting his status as a Prince of the Church. A longer, and more formal, title is "His [or Your when addressing the cardinal directly] Most Reverend Eminence". Patriarchs of Eastern Catholic Churches who are also cardinals may be addressed as "His Eminence" or by the style particular to Catholic patriarchs, His Beatitude. When the Grand master (order), Grand Master of the Sovereign Military Order of Malta, the head of state of their sovereign territorial state comprising the island of Malta until 1797, who had already been made a Reichsfürst (i.e., prince of the Holy Roman Empire) in 1607, became (in terms of honorary order of precedence, not in the actual churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Cosenza
The province of Cosenza () is a province in the Calabria region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Cosenza. It contains 150 ''comuni'' (: ''comune''), listed at list of ''comuni'' of the province of Cosenza. The province of Cosenza contains a community of Occitan language (also known as Langue d'oc) speakers in Guardia Piemontese: it was formed by Vaudoi or Waldensian movement members, who moved to Cosenza to avoid religious persecution, in the 13th and 14th centuries. Many of the Arbëreshë Albanians of Italy live in the province, since arriving in the 16th century to flee the religious persecution undertaken by the Ottoman Empire. History The first traces of human settlement in the area date from the early Palaeolithic period. These sites include the Romito Cave at Papasidero, including wall paintings of bovidae. Cosenza began as a settlement of the Italic Bruttii tribe, and became their capital before the Romans invaded the area. The town was conquered by the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sant'Angelo In Pescheria
Sant'Angelo in Pescheria or in Piscaria is a churches of Rome, church in Rome. Dating from the 8th century, it is now used as the conventual church of the General Curia of the Clerics Regular Minor, the orders global headquarters. "In Pescheria" refers to its location close to the fish market built in the ruins of the ancient Porticus Octaviae. History The relics of St. Symphorosa and her seven sons were transferred to the Church of Sant'Angelo in Pescheria at Rome by Pope Stephen II in 752. A sarcophagus was found here in 1610, bearing the inscription: ''Hic requiescunt corpora SS. Martyrum Simforosae, viri sui Zotici (Getulii) et Filiorum ejus a Stephano Papa translata''. This inscription refers to Saint Getulius and Saint Symphorosa, purported to be husband and wife, who had seven sons, who were also martyred. The remains of these saints were transferred to Sant'Angelo by Pope Stephen II in 752. The revolutionary "tribune" Cola di Rienzo was born near Sant'Angelo. He launc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commendam
In canon law, commenda (or ''in commendam'') was a form of transferring an ecclesiastical benefice ''in trust'' to the ''custody'' of a patron. The phrase ''in commendam'' was originally applied to the provisional occupation of an ecclesiastical benefice, which was temporarily without an actual occupant, in contrast to the conferral of a title, '' in titulum'', which was applied to the regular and unconditional occupation of a benefice.Ott, Michael. "In Commendam". ''The Catholic Encyclopedia'' Vol. 7. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1910. 25 July 2015 The word ''commendam'' is the accusative singular of the |
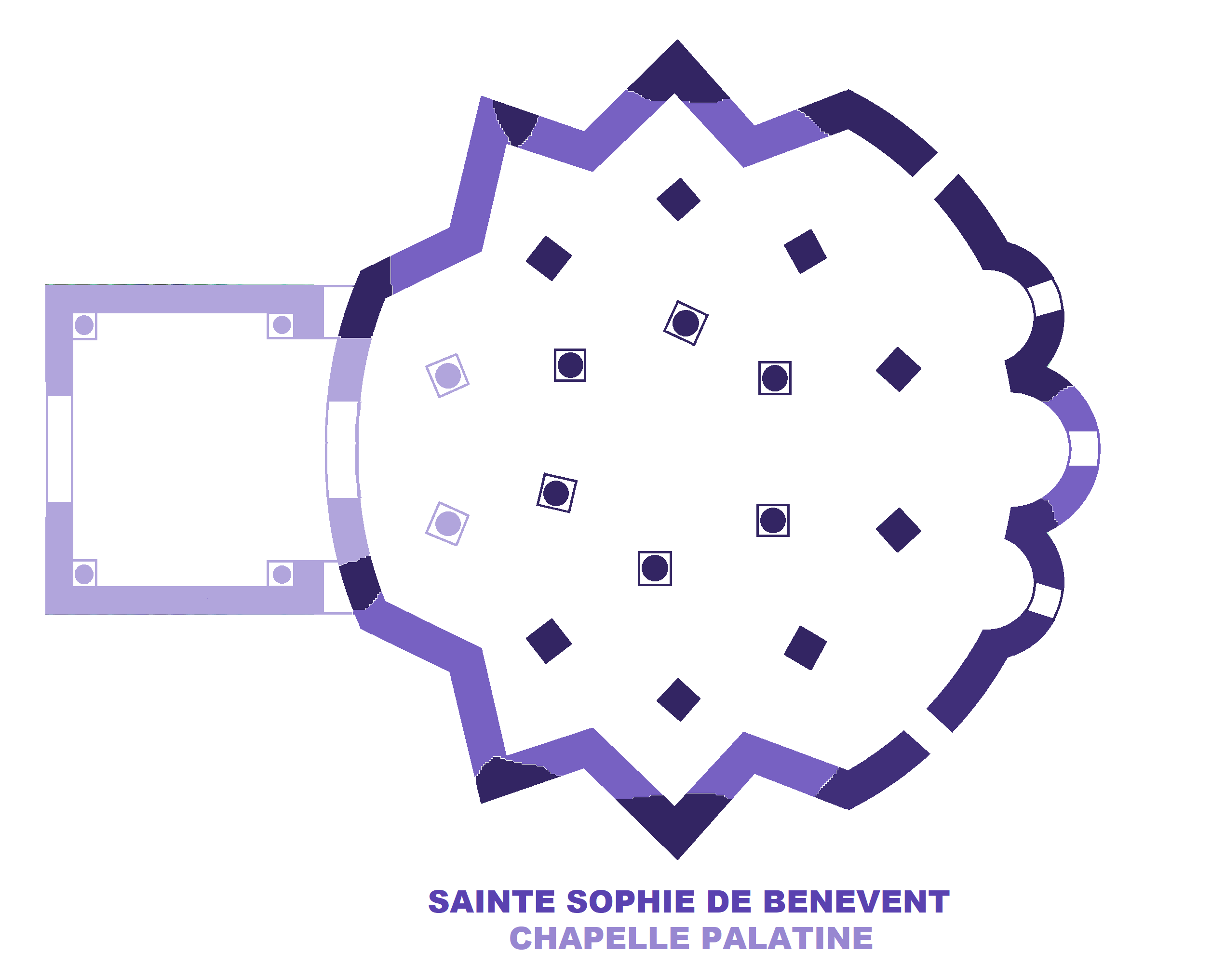
Santa Sofia, Benevento
Santa Sofia is a Roman Catholic church in the town of Benevento, in the region of Campania, in southern Italy; founded in the late-8th century, it retains many elements of its original Lombard architecture. In 2011, it became a UNESCO World Heritage Site as part of a group of seven inscribed as Longobards in Italy. Places of the power (568-774 A.D.), Longobards in Italy. Places of the power (568–774 A.D.). History The church was founded by the Lombards, Lombard Arechis II of Benevento around 760, as testified by numerous privileges signed by him, some of which are in the Museum of Samnium near the church. The edifice was modeled on the Palatine Chapel of the Lombard king Liutprand, King of the Lombards, Liutprand in Pavia and, after the defeat of Desiderius by Charlemagne and the fall of the Lombard kingdom in northern Italy (774), it became the national church of the Lombards who had taken shelter in the Duchy of Benevento. The church was part of a large program of construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Caserta
The Royal Palace of Caserta ( ; ) is a former royal residence in Caserta, Campania, north of Naples in southern Italy, constructed by the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies as their main residence as Kingdom of Naples, kings of Naples. The complex is the largest palace erected in Europe during the 18th century. In 1997, the palace was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site; its nomination described it as "the swan song of the spectacular art of the Baroque, from which it adopted all the features needed to create the illusions of multidirectional space". The Royal Palace of Caserta is the largest former royal residence in the world, over 2 million Cubic metre, m3 in volume covering an area of 47,000 Square metre, m2 and a floorspace of 138,000 square metres distributed across five floors. History The construction of the palace began in 1752 for Charles VII of Naples (later Charles III of Spain), who worked closely with his architect, Luigi Vanvitelli. When Charles saw Vanvitel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th century until the unification of Italy, which took place between 1859 and 1870, culminated in their demise. The state was legally established in the 8th century when Pepin the Short, king of the Franks, gave Pope Stephen II, as a temporal sovereign, lands formerly held by Arian Christian Lombards, adding them to lands and other real estate formerly acquired and held by the bishops of Rome as landlords from the time of Constantine onward. This donation came about as part of a process whereby the popes began to turn away from the Byzantine emperors as their foremost temporal guardians for reasons such as increased imperial taxes, disagreement with respect to iconoclasm, and failure of the emperors, or their exarchs in Italy, to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Henri, Baron Jomini
Antoine-Henri Jomini (; 6 March 177922 March 1869) was a Swiss-French military officer who served as a general in French and later in Russian service, and one of the most celebrated writers on the Napoleonic art of war. Jomini was largely self-taught in military strategy, and his ideas are a staple at military academies, the United States Military Academy at West Point being a prominent example; his theories were thought to have affected many officers who later served in the American Civil War. He may have coined the term ''logistics'' in his '' Summary of the Art of War'' (1838). Early life and business career Jomini was born on 6 March 1779 in Payerne, Vaud, Switzerland, to Benjamin Jomini and Jeanne Marcuard. The Jominis were an old Swiss family, and both his father and paternal grandfather served as mayor of Payerne.Shy, p. 146"Antoine Henri Jomini" In his youth, Jomini "was fascinated by soldiers and the art of war," and hoped to join the military, but his parents pushed hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietro Colletta
Pietro Colletta (January 23, 1775 – November 11, 1831) was a Neapolitan general and historian. Biography Colletta was born in Naples. He entered the Neapolitan artillery in 1796 and took part in the campaign against the French in 1798. On the entry of the French into the Kingdom of Naples and the establishment of the Parthenopaean Republic (1799), Colletta adhered to the new government. When the Bourbon king Ferdinand IV reconquered the city, Colletta was thrown into prison and only escaped the death penalty by means of judiciously administered bribes. Turned out of the army, he became a civil engineer. When the Bourbons were expelled a second time in 1806 and Joseph Bonaparte seized the throne of Naples, he was reinstated in his rank and served in the expedition against the brigands and rebels of Calabria. In 1812, Colletta was promoted to general, and made director of roads and bridges. He served under Joachim Murat and fought the Austrians at the Battle of the Panaro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dean Of The College Of Cardinals
The dean of the College of Cardinals () presides over the College of Cardinals in the Catholic Church, serving as ('first among equals'). The position was established in the 12th century. He always holds the rank of a cardinal bishop and is assisted by a vice-dean. Both are elected by and from the cardinal bishops who are not Eastern Catholic patriarchs, with their election subject to papal confirmation. Except for presiding over the college, the dean and vice-dean have no power over the other cardinals. In the order of precedence in the Catholic Church, the dean and vice-dean, as the two most senior cardinals, are placed second and third, respectively, after the pope. For centuries, the cardinal bishop who had been a bishop of a suburbicarian see the longest was the dean. This custom became a requirement with the canon law of 1917. On 26 February 1965, Pope Paul VI empowered the cardinal bishops to elect the dean from among their number. Both the dean and subdean must reside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tommaso Ruffo
Tommaso Ruffo (1663 – 1753) was an Italian Cardinal, who had been archbishop of Ferrara. Life He was born in Naples, son of Carlo Ruffo, 3rd Duke of Bagnara. He was educated at La Sapienza University, becoming a doctor of canon and civil law. He was a papal diplomat, elected titular archbishop of Nicaea in 1698. On 13 Apr 1698, he was consecrated bishop by Fabrizio Spada, Cardinal-Priest of San Crisogono, with Michelangelo dei Conti, Titular Archbishop of ''Tarsus'', and Francesco Acquaviva d'Aragona, Titular Archbishop of ''Larissa in Thessalia'', serving as co-consecrators. He was created cardinal-priest in 1706, despite having a cousin Giacomo Boncompagni in the College of Cardinals, with the title of S. Lorenzo in Panisperna. Having served as a papal legate, he became archbishop of Ferrara in 1717. He took part in the papal conclave, 1721 and the papal conclave, 1724. He became bishop of Palestrina in 1726 and participated in the papal conclave, 1730. He was bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |