|
FK Csíkszereda Miercurea Ciuc
Asociația Futball Klub Csíkszereda Miercurea Ciuc (, ), commonly known as Csíkszereda Miercurea Ciuc or simply Csíkszereda, is a Romanian professional football club based in Miercurea Ciuc, Harghita County, which competes in the Liga I. The current name of the team is an amalgamation of both the Hungarian and Romanian names of the city, respectively, with Miercurea Ciuc having a majority of Szekler population. Csíkszereda was originally established in 1904 in Austria-Hungary, and was an amateur team without notable results at national level. Refounded in 1919, it participated in the Romanian leagues until 1940, and eventually reached the second tier of Hungary after Northern Transylvania was assigned to the latter country. After World War II, the region was returned to Romania and Csíkszereda took a downward slope until 1971, when it participated in the Romanian third division for the first time. After the fall of communism in 1989, the team encountered financial issu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
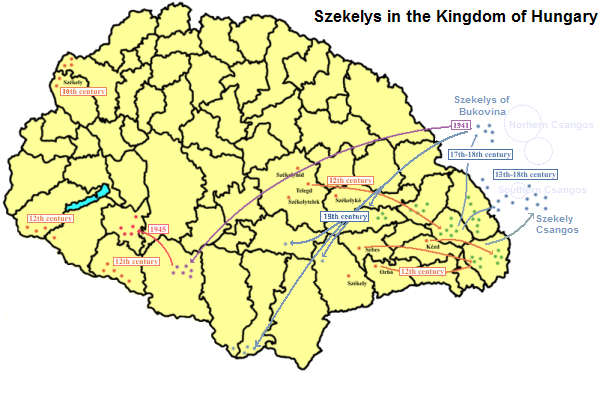
Székelys
The Székelys (, Old Hungarian script, Székely runes: ), also referred to as Szeklers, are a Hungarians, Hungarian subgroup living mostly in the Székely Land in Romania. In addition to their native villages in Suceava County in Bukovina, a significant population descending from the Székelys of Bukovina currently lives in Tolna County, Tolna and Baranya County, Baranya counties in Hungary and certain districts of Vojvodina, Serbia. In the Middle Ages, the Székelys played a role in the defense of the Kingdom of Hungary#Middle Ages, Kingdom of Hungary against the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in their posture as guards of the eastern border. With the Treaty of Trianon of 1920, Transylvania (including the Székely Land) became part of Romania, and the Székely population was a target of Romanianization efforts. In 1952, during the Socialist Republic of Romania, communist rule of Romania, the former counties with the highest concentration of Székely population – Mureș County#His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2018–19 Liga III
The 2018–19 Liga III was the 63rd season of Liga III, the third tier of the Romanian football league system. The season began on 24 August 2018 and ended on 25 May 2019. Team changes To Liga III Promoted from Liga IV * 1. FC Gloria (debut) * Bragadiru (debut) * Ceahlăul Piatra Neamț (after 38 years of absence) * Crișul Chișineu-Criș (after 26 years of absence) * Dumbrăvița (debut) * Făurei (after 12 years of absence) * FC U Craiova (debut) * Flacăra Horezu (after 17 years of absence) * SCM Gloria Buzău (debut) * Hunedoara (after 2 years of absence) * Medgidia (after 8 years of absence) * Minaur Baia Mare (after 3 years of absence) * MSE Târgu Mureș (debut) * Ocna Mureș (after 11 years of absence) * Rapid București (debut) * SR Brașov (debut) * Sticla Arieșul Turda (after 4 years of absence) * Șomuz Fălticeni (debut) * Unirea Bascov (debut) Relegated from Liga II * Afumați (after 2 years of absence) * Știința Miros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lajos Sătmăreanu
Lajos Sătmăreanu (also known as Ludovic Sătmăreanu, , born 21 February 1944) is a Romanian former football player of Hungarian ethnicity. Club career Lajos Sătmăreanu, nicknamed '' Facchetti of the Carpathians'' was born on 21 February 1944 in Salonta, Romania and started to play football in 1958 at local club, Recolta. He made his Divizia A debut on 17 March 1963, playing for Crișana Oradea in a 4–2 away loss against Steaua București, shortly afterwards moving to play at neighboring team, Flamura Roșie in Divizia B for one season. After another Divizia B season, this time spent at ASA Târgu Mureș, Sătmăreanu went to play at Steaua for 10 seasons, winning one league title in the 1967–68 season, being used by coach Ștefan Kovács in 26 matches and also winning five Cupa României, scoring the last goal of the 4–0 victory against UTA Arad from the 1966 final. For the way he played in 1968, Sătmăreanu was placed third in the ranking for the Romanian F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
József Pecsovszky
József Pecsovszky or Iosif Petschovschi (also known as József Perényi; 2 July 1921 – 6 October 1968) was a Romanian footballer. His nickname was ''Peci''. He could play in any position on the pitch, he was even goalkeeper once. Career Pecsovszky played 273 games in Divizia A, scoring a massive 86 goals. For Romania he won 32 caps, scoring 11 goals. Pecsovszky made his debut in Divizia A at the age of 16, as player of Chinezul Timișoara. Pecsovszky played in the Hungarian Football Championship between 1941 and 1944 under the name of ''József Perényi'', winning the Hungarian title with Nagyváradi AC, and played three times for the Hungary national team. His fame was such that in 1946 a Hungarian footballer tried, and even did so for a short while, to steal Pecsovszky's identity, when he recommended himself as the real Pecsovszky in order to sign a contract with RC Strasbourg of France. Petschovski was suspended in October 1947 for a period of three months because be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magyar Autonomous Region
The Magyar Autonomous Region (1952–1960) (; ) and Mureș-Magyar Autonomous Region (1960–1968) were autonomous Regions of the People's Republic of Romania, regions in the Romanian People's Republic (later the Socialist Republic of Romania). History One of the key factors behind the autonomous region was the desire of the communist Romanian government to win over the Hungarian population in Transylvania. Support for the Romanian Communist Party was very strong in ethnically Hungarian areas, and Hungarian communists made up 26% of all communists in Romania before World War II. Following the Hungarian Northern Transylvania, rule of Northern Transylvania during World War II, ethnic Hungarians now made up 10% of Romanian population, and the communist government adopted a policy of appeasement towards the Hungarian minority; this was a pragmatic stance as in contrast to largely pro-socialist Hungarians in Romania, ethnic Romanians were unsupportive of the Communist Party and the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raion
A raion (also spelt rayon) is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet states. The term is used for both a type of subnational entity and a division of a city. The word is from the French (meaning 'honeycomb, department'), and is commonly translated as ' district' in English. A raion is a standardized administrative entity across most of the former Soviet Union and is usually a subdivision two steps below the national level, such as a subdivision of an oblast. However, in smaller USSR republics, it could be the primary level of administrative division. After the fall of the Soviet Union, some of the republics kept the ''raion'' (e.g. Azerbaijan, Belarus, Ukraine, Russia, Moldova, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan) while others dropped it (e.g. Georgia, Uzbekistan, Estonia, Latvia, Armenia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan). In Bulgaria, it refers to an internal administrative subdivision of a city not related to the administrative division of the country as a whole, or, in the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Communism In Romania
National communism in Romania is a term referring to a form of nationalism promoted in the Socialist Republic of Romania between the early 1960s and 1989; the term itself was not used by the Communist regime. Having its origins in Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej's political emancipation from the Soviet Union, it was greatly developed by Nicolae Ceaușescu, who began in 1971, through his July Theses manifesto, a national cultural revolution. Part of the national mythology was Nicolae Ceaușescu's cult of personality and the idealization of Romanian history, known in Romanian historiography as protochronism. This nationalistic ideology was built upon a mixture of both Marxist–Leninist principles and doctrines of Romanian nationalism. The driving force behind the ideology of national communism was the belief that Romanians are an isolated "Latin island" in Eastern Europe who have endlessly and unanimously fought off external forces throughout two thousand years to achieve unity and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Székely Land
The Székely Land or Szeklerland (, , Old Hungarian script, Székely runes: 𐲥𐳋𐳓𐳉𐳗𐳌𐳞𐳖𐳇; and sometimes ; ; ) is a historic and ethnographic area in present-day Romania, inhabited mainly by Székelys, a subgroup of Hungarians. Its cultural centre is the city of Târgu Mureș (Marosvásárhely), the largest settlement in the region. Székelys (or Szeklers) live in the valleys and hills of the Eastern Carpathian Mountains, corresponding mostly to the present-day Harghita County, Harghita, Covasna County, Covasna, and parts of Mureș County, Mureș counties in Romania. Originally, the name ''Székely Land'' denoted the territories of a number of History of the Székely people, autonomous Székely seats within Transylvania. The self-governing Székely seats had their own administrative system, and existed as legal entities from medieval times until the 1870s. The privileges of the Székely and Transylvanian Saxons, Saxon Seat (territorial-administrative uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemzeti Bajnokság III
Nemzeti Bajnokság III (''NB III'', ''National Championship III'') is the third tier of Football in Hungary, Hungarian football (from the autumn of 1997 till the spring of 2005, NB III was the fourth tier, the third was NB II). The tier contains 4 groups (northeast, northwest, southeast and southwest) of 16 teams. From NB III, the champions of each group will battle promotion play-off, two teams winning play-off are promoted to the Nemzeti Bajnokság II, NB II. The three lowest teams of each group and two worst 13th place teams are relegated to the first tier of local divisions (''Megyei Bajnokság I, MB I''). From NB II, the four lowest teams are relegated to NB III from 2024–25 season. Groups From 2023 onwards, the league divided into 4 groups of 16 teams: *Northeast group *Northwest group *Southeast group *Southwest group List of champions Regional classification Tripartite classification Quadratite classification ;Notes * Note 1: In the 2015-16 Nemzeti Bajnokság II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Football League System ...
The Hungarian football league system is a series of connected leagues for club football in Hungary. This system has hierarchical format with promotion and relegation between leagues at different levels. History The governing body of football in Hungary, the Hungarian Football Federation, was founded in 1901. The five founding clubs were Budapesti TC, Magyar Úszó Egylet, Ferencvárosi TC, Műegyetemi AFC, and Budapesti SC. Structure References {{Reflist Hungary Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and the Kingdom of Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all of Maramureș and part of Crișana, from the Kingdom of Romania to the Kingdom of Hungary (1920–46), Kingdom of Hungary. Background After World War I, the multiethnic Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen, Kingdom of Hungary was divided by the 1920 Treaty of Trianon to form several new nation states, but Hungary noted that the new state borders did not follow ethnic boundaries. The new nation state of Hungary was about a third the size of prewar Hungary, and millions of ethnic Hungarians were left outside the new Hungarian borders. Many historically-important areas of Hungary were assigned to other countries, and the distribution of natural resources was uneven. The various non-Hungarian populations generally saw the treaty as justice for their historically-margina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hungary (1920–1946)
The Kingdom of Hungary referred to retrospectively as the Regency and the Horthy era, existed as a country from 1920 to 1946 under the rule of Miklós Horthy, Regent of Hungary, who officially represented the Holy Crown of Hungary, Hungarian monarchy. In reality there was no king, and attempts by Charles I of Austria, King Charles IV to return to the throne shortly before his death were Charles IV of Hungary's attempts to retake the throne, prevented by Horthy. Hungary under Horthy was characterized by its Conservatism, conservative, Nationalism, nationalist, and fiercely Anti-communism, anti-communist character; some historians have described this system as Para-fascism, para-fascist. The government was based on an unstable alliance of conservatives and right-wingers. Foreign policy was characterized by revisionism—the total or partial revision of the Treaty of Trianon, which had seen Hungary lose over 70% of its Kingdom of Hungary, historic territory along with over three mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |