|
FASTRAND
FASTRAND was a magnetic drum mass storage system built by Sperry Rand Corporation (later Sperry Univac) for their UNIVAC 1100 series and 418/490/494 series computers. A FASTRAND subsystem consisted of one or two Control Units and up to eight FASTRAND units. A dual-access FASTRAND subsystem included two complete control units, and provided parallel data paths that allowed simultaneous operations on any two FASTRAND units in the subsystem. Each control unit interfaced to one (optionally two) 1100 Series (36-bit), or 490 Series (30-bit), parallel I/O channels. A voice coil actuator moved a bar containing multiple single track recording heads, so these drums operated much like moving head disk drives with multiple disks. The heads "flew" on self-acting hydrodynamic air bearings. The drums had a plated magnetic recording surface. An optional feature called Fastband included 24 additional tracks with fixed read/write heads. This feature provided rapid access (35 ms. average access time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Drum
Drum memory was a magnetic data storage device invented by Gustav Tauschek in 1932 in Austria. Drums were widely used in the 1950s and into the 1960s as computer memory. For many early computers, drum memory formed the main working memory of the computer. It was so common that these computers were often referred to as ''drum machines''. Some drums were also used as secondary storage as for example various IBM drum storage drives. Drums were displaced as primary computer memory by magnetic core memory, which offered a better balance of size, speed, cost, reliability and potential for further improvements. Drums in turn were replaced by hard disk drives for secondary storage, which were both less expensive and offered denser storage. The manufacturing of drums ceased in the 1970s. Technical design A drum memory or drum storage unit contained a large metal cylinder, coated on the outside surface with a ferromagnetic recording material. It could be considered the precu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIVAC Hardware
UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) was a line of electronic digital stored-program computers starting with the products of the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation. Later the name was applied to a division of the Remington Rand company and successor organizations. The BINAC, built by the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation, was the first general-purpose computer for commercial use, but it was not a success. The last UNIVAC-badged computer was produced in 1986. History and structure J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly built the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) at the University of Pennsylvania's Moore School of Electrical Engineering between 1943 and 1946. A 1946 patent rights dispute with the university led Eckert and Mauchly to depart the Moore School to form the Electronic Control Company, later renamed Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation (EMCC), based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. That company first built a computer called BINAC (BINary Automat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIVAC 1100/2200 Series
The UNIVAC 1100/2200 series is a series of compatible 36-bit computer systems, beginning with the UNIVAC 1107 in 1962, initially made by Sperry Rand. The series continues to be supported today by Unisys Corporation as the ClearPath Dorado Series. The solid-state 1107 model number was in the same sequence as the earlier vacuum-tube computers, but the early computers were not compatible with the solid-state successors. Architecture Data formats * Fixed-point, either integer or fraction **Whole word – 36-bit (ones' complement) **Half word – two 18-bit fields per word (unsigned or ones' complement) **Third word – three 12-bit fields per word (ones' complement) **Quarter word – four 9-bit fields per word (unsigned) **Sixth word – six 6-bit fields per word (unsigned) *Floating point **Single precision – 36 bits: sign bit, 8-bit characteristic, 27-bit mantissa **Double precision – 72 bits: sign bit, 11-bit characteristic, 60-bit mantissa *Alphanumeric ** FIELDATA – UNIV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
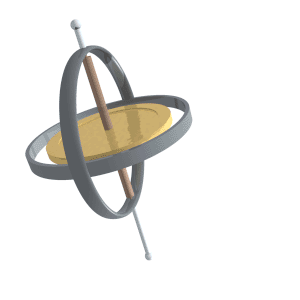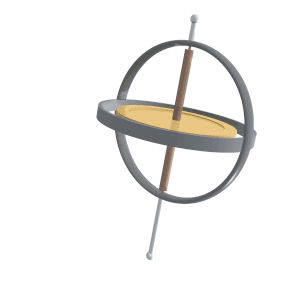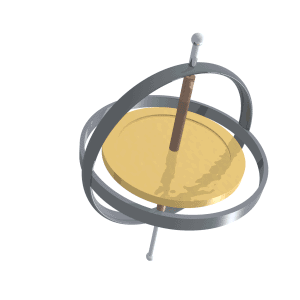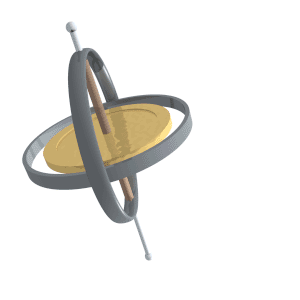
Gyroscopic Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called ''nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, but the angular velocit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Read-and-write Head
A disk read-and-write head is the small part of a disk drive which moves above the disk platter and transforms the platter's magnetic field into electrical current (reads the disk) or, vice versa, transforms electrical current into magnetic field (writes the disk). The heads have gone through a number of changes over the years. In a hard drive, the heads ''fly'' above the disk surface with clearance of as little as 3 nanometres. The flying height has been decreasing with each new generation of technology to enable higher areal density. The flying height of the head is controlled by the design of an air bearing etched onto the disk-facing surface of the ''slider''. The role of the air bearing is to maintain the flying height constant as the head moves over the surface of the disk. The air bearings are carefully designed to maintain the same height across the entire platter, despite differing speeds depending on the head distance from the center of the platter. If the head hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperry Rand
Sperry Corporation was a major American equipment and electronics company whose existence spanned more than seven decades of the 20th century. Sperry ceased to exist in 1986 following a prolonged hostile takeover bid engineered by Burroughs Corporation, which merged the combined operation under the new name Unisys. Some of Sperry's former divisions became part of Honeywell, Lockheed Martin, Raytheon Technologies, and Northrop Grumman. The company is best known as the developer of the artificial horizon and a wide variety of other gyroscope-based aviation instruments like autopilots, bombsights, analog ballistics computers and gyro gunsights. In the post-WWII era the company branched out into electronics, both aviation related, and later, computers. History Early history The company was founded in 1910 by Elmer Ambrose Sperry, as the Sperry Gyroscope Company, to manufacture navigation equipment—chiefly his own inventions the marine gyrostabilizer and the gyrocomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotational Latency
Higher performance in hard disk drives comes from devices which have better performance characteristics. These performance characteristics can be grouped into two categories: access time and data transfer time (or rate). Access time The ''access time'' or ''response time'' of a rotating drive is a measure of the time it takes before the drive can actually transfer data. The factors that control this time on a rotating drive are mostly related to the mechanical nature of the rotating disks and moving heads. It is composed of a few independently measurable elements that are added together to get a single value when evaluating the performance of a storage device. The access time can vary significantly, so it is typically provided by manufacturers or measured in benchmarks as an average. The key components that are typically added together to obtain the access time are: * Seek time * Rotational latency * Command processing time * Settle time Seek time With rotating drives, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Storage Density
Density is a measure of the quantity of information bits that can be stored on a given length (''linear density'') of track, area of surface (''areal density''), or in a given volume (''volumetric density'') of a computer storage medium. Generally, higher density is more desirable, for it allows more data to be stored in the same physical space. Density therefore has a direct relationship to storage capacity of a given medium. Density also generally affects the performance within a particular medium, as well as price. Storage device classes Solid state media Solid state drives use flash memory to store non-volatile media. They are the latest form of mass produced storage and rival magnetic disk media. Solid state media data is saved to a pool of NAND flash. NAND itself is made up of what are called floating gate transistors. Unlike the transistor designs used in DRAM, which must be refreshed multiple times per second, NAND flash is designed to retain its charge state e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Device
A peripheral or peripheral device is an auxiliary device used to put information into and get information out of a computer. The term ''peripheral device'' refers to all hardware components that are attached to a computer and are controlled by the computer system, but they are not the core components of the computer, such as the CPU or power supply unit. In other words, peripherals can also be defined as devices that can be easily removed and plugged into a computer system. Several categories of peripheral devices may be identified, based on their relationship with the computer: *An ''input device'' sends data or instructions to the computer, such as a mouse, keyboard, graphics tablet, image scanner, barcode reader, game controller, light pen, light gun, microphone and webcam; *An '' output device'' provides output data from the computer, such as a computer monitor, projector, printer, headphones and computer speaker; *An ''input/output device'' performs both input and outpu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |