|
FAMAS
The FAMAS ( French: ''Fusil d'Assaut de la Manufacture d'Armes de Saint-Étienne'', lit. 'Assault rifle from the Saint-Étienne Weapon Factory') is a bullpup assault rifle designed and manufactured in France by MAS in 1978. It is known by French troops as ''Le Clairon'' (The Bugle) due to its distinctive shape. The FAMAS is known for its high rate of fire of around 900–1,100 rounds per minute. Beginning in 2017, the FAMAS was replaced in most frontline units in the French Army by the HK416F, and the FAMAS is expected to remain in limited service until 2028. History The first French bullpup rifles were developed between 1946 and 1950 at the AME (''Atelier Mécanique de Mulhouse'') and MAS, testing rounds such as .30 US Carbine, 7.92×33mm Kurz, 7.65×38mm (Made by ''Cartoucherie de Valence'') and some other intermediate calibres. Since France was engaged in the First Indochina War at the time, and was also the second-largest contributor to NATO, the research budgets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacture D'armes De Saint-Étienne
The , often abbreviated to MAS ("Saint-Étienne Weapons Factory" in English), was a French state-owned weapons manufacturer in the town of Saint-Étienne, Loire. Founded in 1764, it was merged into the French state-owned defense conglomerate GIAT Industries in 2001. History Saint-Étienne was well known as a center of sword and knife manufacturing beginning in the Middle Ages. In 1665, a Royal Arms Depot was created in Paris to store military weapons made in Saint-Étienne. The was created by royal decree in 1764 under the supervision of the General Inspector of the Royal Arms Manufacture of Charleville. 12,000 weapons were being produced each year when the French Revolution began in 1789. The city was renamed Armsville during the Revolutionary period and production increased to arm the French Revolutionary Army. Subsequently, the French Empire required a threefold increase in production to meet the needs of the Grande Armée in its conquest of Europe. By 1838, durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
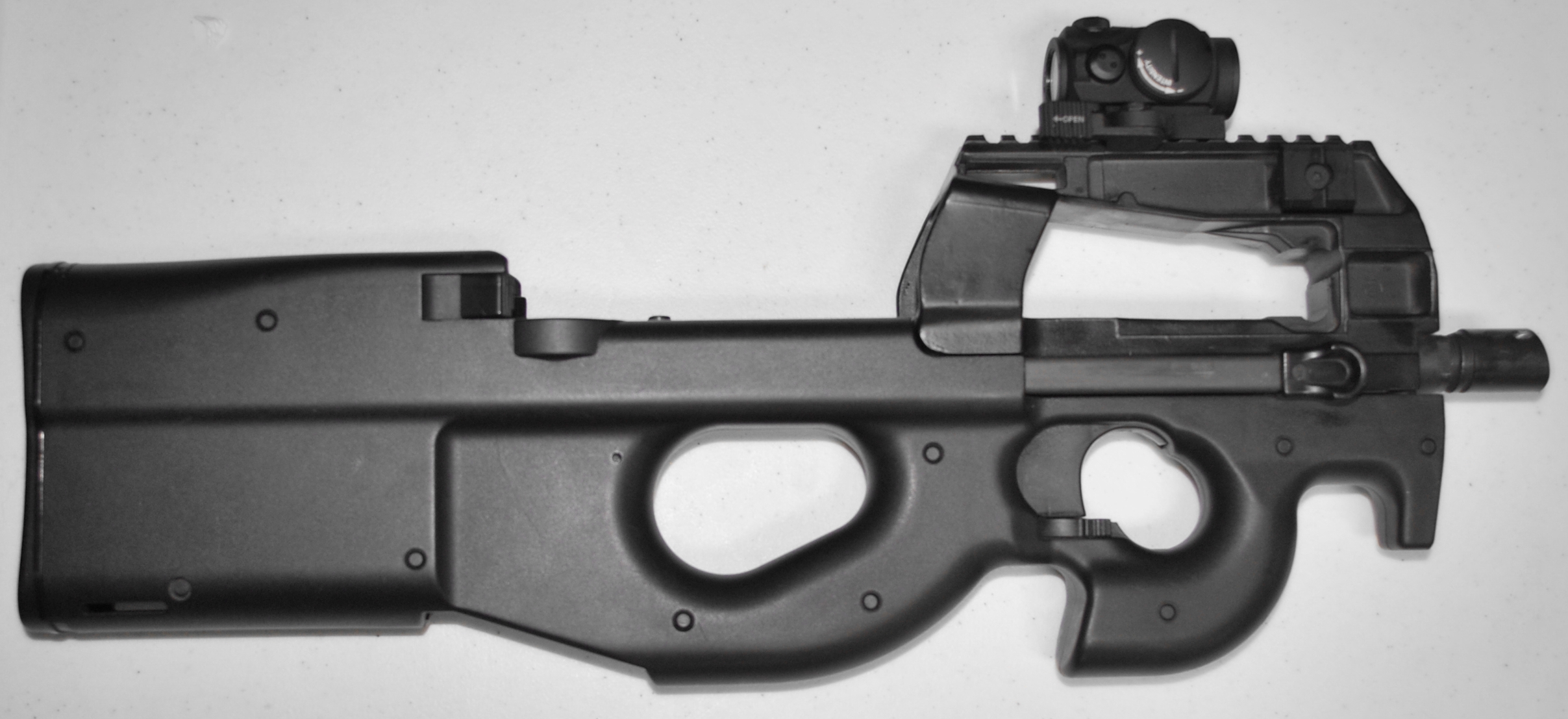
Bullpup
A bullpup firearm is one with its firing grip located in front of the Chamber (firearms), breech of the weapon, instead of behind it. This creates a weapon with a shorter overall length for a given barrel length, and one that is often lighter, more compact, concealable, and more maneuverable than a conventionally configured firearm. Where it is desirable for troops to be issued a more compact weapon, the use of a bullpup configuration allows for barrel length to be retained, thus preserving muzzle velocity, range, and ballistic effectiveness. The bullpup concept was first tested militarily in 1901 with the British Thorneycroft carbine, but it was not until the Cold War that more successful designs and improvements led to wider adoption. In 1977, the Austrian Federal Army, Austrian Army became the first military force in the world to adopt a bullpup rifle, the Steyr AUG, as a service rifle, principal combat weapon. Since then the militaries in many countries have followed suit w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blowback (arms)
Blowback is a system of operation for self-loading firearms that obtains energy from the motion of the cartridge case as it is pushed to the rear by expanding gas created by the ignition of the propellant charge. Several blowback systems exist within this broad principle of operation, each distinguished by the methods used to control bolt movement. In most actions that use blowback operation, the breech is not locked mechanically at the time of firing: the inertia of the bolt and recoil , relative to the weight of the bullet, delay opening of the breech until the bullet has left the barrel. A few locked breech designs use a form of blowback (example: primer actuation) to perform the unlocking function. The blowback principle may be considered a simplified form of gas operation, since the cartridge case behaves like a piston driven by the powder gases. Other operating principles for self-loading firearms include delayed blowback, blow forward, gas operation, and recoil ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullpup
A bullpup firearm is one with its firing grip located in front of the Chamber (firearms), breech of the weapon, instead of behind it. This creates a weapon with a shorter overall length for a given barrel length, and one that is often lighter, more compact, concealable, and more maneuverable than a conventionally configured firearm. Where it is desirable for troops to be issued a more compact weapon, the use of a bullpup configuration allows for barrel length to be retained, thus preserving muzzle velocity, range, and ballistic effectiveness. The bullpup concept was first tested militarily in 1901 with the British Thorneycroft carbine, but it was not until the Cold War that more successful designs and improvements led to wider adoption. In 1977, the Austrian Federal Army, Austrian Army became the first military force in the world to adopt a bullpup rifle, the Steyr AUG, as a service rifle, principal combat weapon. Since then the militaries in many countries have followed suit w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
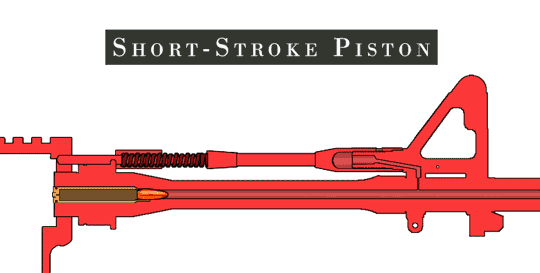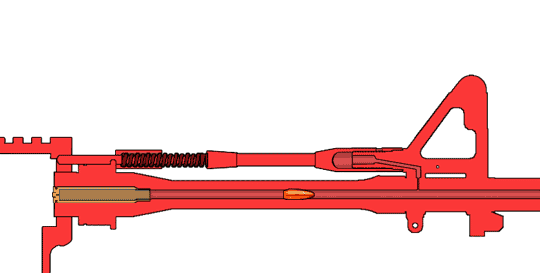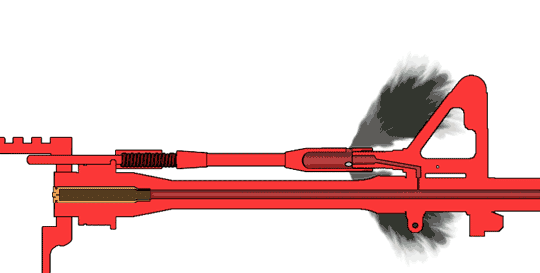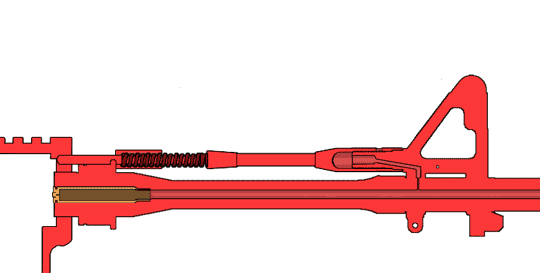
Heckler & Koch HK416
The Heckler & Koch HK416 is an assault rifle chambered for the 5.56×45mm NATO Cartridge (firearms), cartridge. It is designed and manufactured by the German company Heckler & Koch. Although the design is based on the AR-15 class of firearm (specifically the Colt M4 carbine family issued to the U.S. military), it uses a proprietary Gas-operated reloading, short-stroke gas piston system from Heckler & Koch's earlier Heckler & Koch G36, G36 family of rifles. The HK416 is the standard assault rifle of the Norwegian Armed Forces and the United States Marine Corps (designated M27 IAR, M27), and it has been selected by the French Armed Forces to replace the FAMAS and by the German Army to replace the Heckler & Koch G36, G36 as the standard issue service rifle. Other users include the Irish Army Ranger Wing, as well as the United States Navy, US Navy's SEAL Team Six, who used it to Killing of Osama bin Laden, kill Osama bin Laden in 2011. History The United States Army's Delta Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nexter
KNDS France (formerly known as Nexter, GIAT Industries or ''Groupement des Industries de l'Armée de Terre'', Army Industries Group) is a French government-owned weapons manufacturer, based in Versailles. The company was wholly government-owned as GIAT from 1991 to 2006 and as Nexter from 2006 to 2015, when it merged with Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW) to form KNDS: a single company jointly owned, via holding companies, by the French state and the private owners of KMW. In 2024, Nexter was renamed KNDS France. Group organization KNDS France and its subsidiaries are divided into several smaller entities, with the main one being KNDS France. The sub-companies are: * KNDS Ammo France * KNDS Ammo Italy S.P.A * KNDS Belgium * KNDS France Mechanics * KNDS France Robotics * KNDS France Training * KNDS OptSys * KNDS CBRN History The GIAT group was founded in 1973 by combining the industrial assets of the technical direction of Army weapons of the French Ministry of Defense. The com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Rifle
A battle rifle is a service rifle chambered to fire a fully powered cartridge. The term "battle rifle" is a retronym created largely out of a need to differentiate automatic rifles chambered for fully powered cartridges from automatic rifles chambered for intermediate cartridges, which were later categorized as assault rifles. Battle rifles were most prominent from the 1940s to the 1970s, when they were used as service rifles. While modern battle rifles largely resemble modern assault rifle designs, which replaced battle rifles in most roles, the term may also describe older military full-power semi-automatic rifles such as the M1 Garand, SVT-40, Gewehr 41, Gewehr 43, Type 4 rifle, Type 4, FN Model 1949, and MAS-49 rifle, MAS-49. History World War I Semi-automatic First examples of semi-automatic fully powered-cartridge rifles used in World War I are the Meunier rifle, Meunier A6, Fusil Automatique Modèle 1917 in 8×50mmR Lebel and the Winchester Model 1910 in .401 Wincheste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIG SG 540
The SG 540 is a 5.56×45mm NATO assault rifle developed in the early 1970s by Schweizerische Industrie Gesellschaft (SIG, currently SAN Swiss Arms AG) of Neuhausen am Rheinfall, Neuhausen, Switzerland as a private venture primarily destined for export markets and as a potential replacement for the 7.5×55mm Swiss SIG SG 510, SG 510 automatic rifle known as the Stgw 57 in Swiss service. History Work on a new generation of lightweight rifle using the intermediate 5.56mm round began at SIG in the 1960s and resulted in the somewhat unsuccessful SIG SG 530, SG 530-1 design that employed a Gas-operated reloading, gas-assisted Blowback (arms)#Delayed blowback systems#Roller delayed, roller-delayed blowback operating mechanism which proved too complicated and expensive to manufacture. As a result, in 1969 SIG chose to dispense with the complex roller-delayed action opting instead for a design using the more robust and simple piston-operated rotating bolt locking mechanism (derived from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assault Rifle
An assault rifle is a select fire rifle that uses an intermediate cartridge, intermediate-rifle cartridge and a Magazine (firearms), detachable magazine.C. Taylor, ''The Fighting Rifle: A Complete Study of the Rifle in Combat'', F.A. Moyer ''Special Forces Foreign Weapons Handbook'', R.J. Scroggie, F.A. Moyer ''Special Forces Combat Firing Techniques'', Musgave, Daniel D., and Thomas B. Nelson, ''The World's Assault Rifles'', vol. II, The Goetz Company, Washington, D.C. (1967): 1 Assault rifles were first put into mass production and accepted into widespread service during World War II. The first assault rifle to see major usage was the German StG 44, a development of the earlier Maschinenkarabiner 42(H), Mkb 42.''Firearms: The Life Story of a Technology'', by Roger Pauly. Greenwood Publishing Group. 2004. pp. 145–146 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FA-MAS Type 62
The FA-MAS Type 62 is a 7.62×51mm NATO rifle developed by the French Army as a replacement for the MAS-49/56. It was the last in series of 40 different prototype rifles designed between 1952 and 1962. However, the introduction of the 5.56×45mm cartridge caused the French to rethink their approach and the project was eventually cancelled. The Type 62's bayonet was later adopted for use on the FAMAS rifle. Predecessors Type-55 The MAS-55 has its gas piston underneath its barrel and operated in a similar way to the FM1924/29 light machine gun but resulted in a heavy rifle for its type. Type-56 The Type-56 was a simpler alternative to the Type-55 and was closer to the FN FAL. Type-59 The Type-59 came with an improved stock and foregrip. It also came with a folding stock, bipod and infra-red sight as the AP61. See also *List of battle rifles Battle rifles are full-length, semi-automatic or select fire rifles that are chambered for a full-power rifle cartridge, and have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
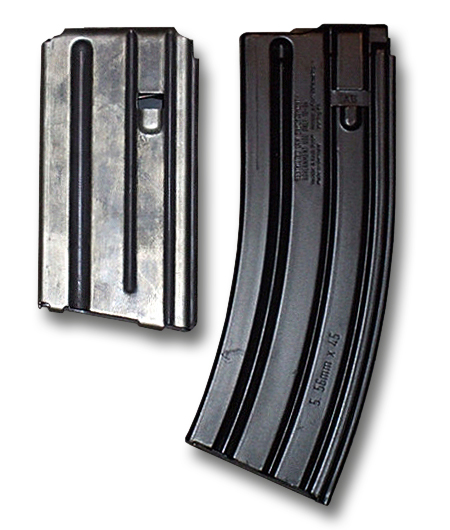
STANAG Magazine
A STANAG magazine or NATO magazine is a type of detachable firearm magazine proposed by NATO in October 1980. Shortly after NATO's acceptance of the 5.56×45mm NATO rifle cartridge, Draft Standardization Agreement ( STANAG) 4179 was proposed in order to allow NATO members to easily share rifle ammunition and magazines down to the individual soldier level. The U.S. M16 rifle's magazine proportions were proposed for standardization. Many NATO members, but not all, subsequently developed or purchased rifles with the ability to accept this type of magazine. However, the standard was never ratified and remains a "Draft STANAG". Magazines The STANAG magazine concept is only an interface, dimensional and controls (magazine latch, bolt stop, etc.) requirement. Therefore, it not only allows one type of magazine to interface with various weapon systems, but also allows STANAG magazines to be made in various configurations and capacities. The standard capacities of STANAG-compatible mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |