|
Etest
Etest (previously known as the Epsilometer test) is a way of determining antimicrobial sensitivity by placing a strip impregnated with antimicrobials onto an agar plate. A strain of bacterium or fungus will not grow near a concentration of antibiotic or antifungal if it is sensitive. For some microbial and antimicrobial combinations, the results can be used to determine a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Etest is a proprietary system manufactured by bioMérieux. It is a laboratory test used in healthcare settings to help guide physicians by indicating what concentration of antimicrobial could successfully be used to treat patients' infections. Use Etest is a quantitative technique for determining the antibiotic sensitivity and minimum inhibitory concentration (in µg/mL) of some bacteria including Gram-negative and Gram-positive aerobic bacteria such as Enterobacteriaceae, ''Pseudomonas'', ''Burkholderia'', ''Staphylococcus'', and ''Enterococcus'' species and fastidious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-test Ngono
Etest (previously known as the Epsilometer test) is a way of determining antimicrobial sensitivity by placing a strip impregnated with antimicrobials onto an agar plate. A strain of bacterium or fungus will not grow near a concentration of antibiotic or antifungal if it is sensitive. For some microbial and antimicrobial combinations, the results can be used to determine a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Etest is a proprietary system manufactured by bioMérieux. It is a laboratory test used in healthcare settings to help guide physicians by indicating what concentration of antimicrobial could successfully be used to treat patients' infections. Use Etest is a quantitative technique for determining the antibiotic sensitivity and minimum inhibitory concentration (in µg/mL) of some bacteria including Gram-negative and Gram-positive aerobic bacteria such as Enterobacteriaceae, ''Pseudomonas'', '' Burkholderia'', ''Staphylococcus'', and '' Enterococcus'' species and fastidio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-test Caspofungin
Etest (previously known as the Epsilometer test) is a way of determining antimicrobial sensitivity by placing a strip impregnated with antimicrobials onto an agar plate. A strain of bacterium or fungus will not grow near a concentration of antibiotic or antifungal if it is sensitive. For some microbial and antimicrobial combinations, the results can be used to determine a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Etest is a proprietary system manufactured by bioMérieux. It is a laboratory test used in healthcare settings to help guide physicians by indicating what concentration of antimicrobial could successfully be used to treat patients' infections. Use Etest is a quantitative technique for determining the antibiotic sensitivity and minimum inhibitory concentration (in µg/mL) of some bacteria including Gram-negative and Gram-positive aerobic bacteria such as Enterobacteriaceae, ''Pseudomonas'', '' Burkholderia'', ''Staphylococcus'', and '' Enterococcus'' species and fastidio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
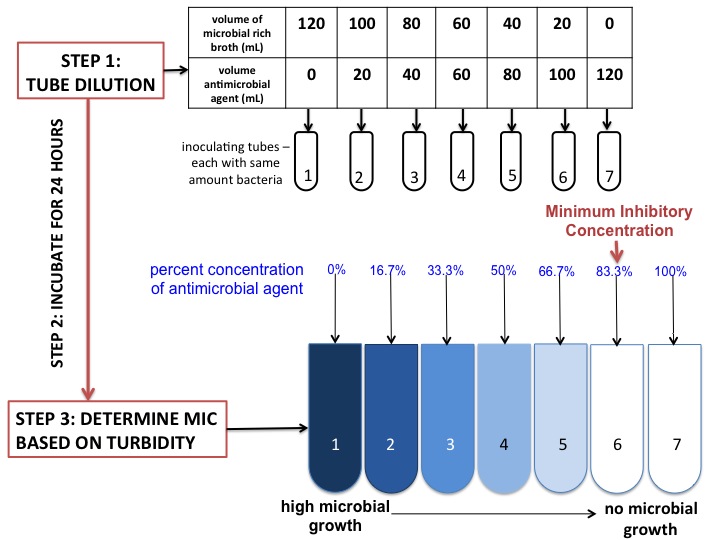
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
In microbiology, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical, usually a drug, which prevents visible growth of a bacterium or bacteria. MIC depends on the microorganism, the affected human being (in vivo only), and the antibiotic itself. It is often expressed in micrograms per milliliter (μg/mL) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). The MIC is determined by preparing solutions of the chemical in vitro at increasing concentrations, incubating the solutions with separate batches of cultured bacteria, and measuring the results using agar dilution or broth microdilution. Results have been graded into susceptible (often called sensitive), increased exposure, or resistant to a particular antimicrobial by using a breakpoint. Breakpoints are agreed upon values, published in guidelines of a reference body, such as the U.S. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC) or the European Committe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing
Antibiotic sensitivity testing or antibiotic susceptibility testing is the measurement of the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. It is used because bacteria may have resistance to some antibiotics. Sensitivity testing results can allow a clinician to change the choice of antibiotics from empiric therapy, which is when an antibiotic is selected based on clinical suspicion about the site of an infection and common causative bacteria, to directed therapy, in which the choice of antibiotic is based on knowledge of the organism and its sensitivities. Sensitivity testing usually occurs in a medical laboratory, and uses culture methods that expose bacteria to antibiotics, or genetic methods that test to see if bacteria have genes that confer resistance. Culture methods often involve measuring the diameter of areas without bacterial growth, called zones of inhibition, around paper discs containing antibiotics on agar culture dishes that have been evenly inoculated with bacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing
Antibiotic sensitivity testing or antibiotic susceptibility testing is the measurement of the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. It is used because bacteria may have resistance to some antibiotics. Sensitivity testing results can allow a clinician to change the choice of antibiotics from empiric therapy, which is when an antibiotic is selected based on clinical suspicion about the site of an infection and common causative bacteria, to directed therapy, in which the choice of antibiotic is based on knowledge of the organism and its sensitivities. Sensitivity testing usually occurs in a medical laboratory, and uses culture methods that expose bacteria to antibiotics, or genetic methods that test to see if bacteria have genes that confer resistance. Culture methods often involve measuring the diameter of areas without bacterial growth, called zones of inhibition, around paper discs containing antibiotics on agar culture dishes that have been evenly inoculated with bacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Diffusion Test
The disk diffusion test (also known as the agar diffusion test, Kirby–Bauer test, disc-diffusion antibiotic susceptibility test, disc-diffusion antibiotic sensitivity test and KB test) is a culture-based microbiology assay used in diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories. In diagnostic labs, the assay is used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria isolated from a patient's infection to clinically approved antibiotics. This allows physicians to prescribe the most appropriate antibiotic treatment. In drug discovery labs, especially bioprospecting labs, the assay is used to screen biological material (e.g. plant extracts, bacterial fermentation broths) and drug candidates for antibacterial activity. When bioprospecting, the assay can be performed with paired strains of bacteria to achieve dereplication and provisionally identify antibacterial mechanism of action. In diagnostic laboratories, the test is performed by inoculating the surface of an agar plate with bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually yes obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). Types of antifungal There are two types of antifungals: local and systemic. Local antifungals are usually administered topically or vaginally, depending on the condition being treated. Systemic antifungals are administered orally or intravenously. Of the clinically employed azole antifungals, only a handful are used systemically. These include ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, fosfluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, and isavuconazole. Examples of non-azole systemic antifungals include griseofulvin and terbinafine. Classes Polyenes A polyene is a molecule with multiple c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BioMérieux
bioMérieux SA is a French multinational biotechnology company founded and headquartered in Marcy-l'Étoile, France, close to Lyon. bioMérieux is present in 44 countries and serves more than 160 countries through a large network of distributors. bioMérieux provides diagnostic solutions (reagents, instruments, software, services) which determine the source of disease and contamination to improve patient health and ensure consumer safety. Its products are used for diagnosing infectious diseases, cancer screening, and monitoring and cardiovascular emergencies. They are also used for detecting microorganisms in agri-food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic products. bioMérieux is listed on the NYSE Euronext Paris stock exchange (BIM – ISIN: FR0013280286). Revenue bioMérieux had revenues of €3.1 billion as of 2020 with 93% of sales occurring outside France. History In 1897, Marcel Mérieux, former assistant to Louis Pasteur, founded the Mérieux Biological Institute, which later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |