|
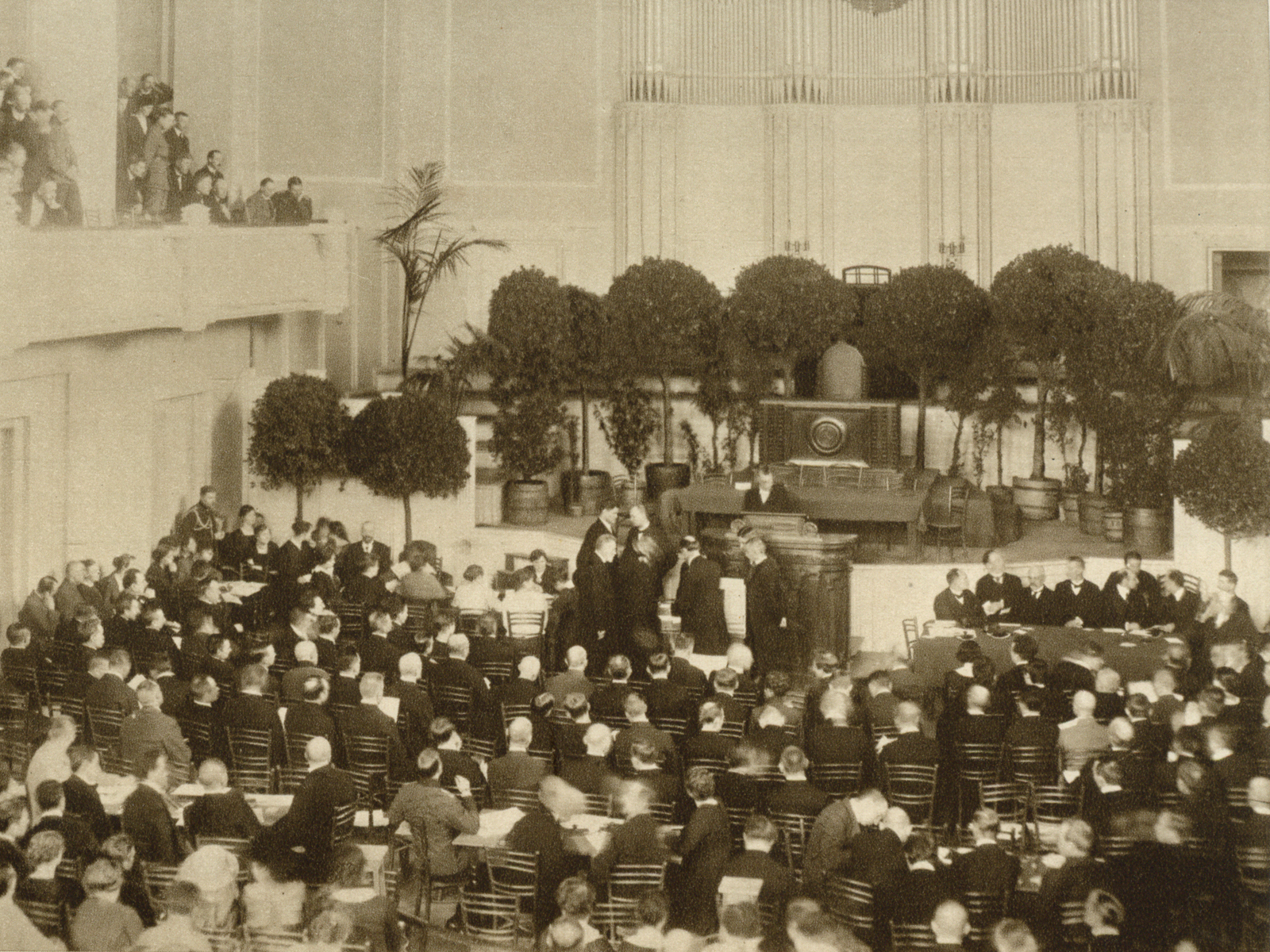
Estonian Constituent Assembly
The Estonian Constituent Assembly ( et, Asutav Kogu) was elected on 5–7 April 1919, called by the Estonian Provisional Government during the Estonian War of Independence. Estonian Constituent Assembly elections Activity The 120 members of the Constituent Assembly met at the opening session on 23 April 1919, the birthday of the Estonian Parliament and elected the chairman, Social Democrat August Rei. On 7 May the Assembly passed the Public Elementary Schools Act: The principle of compulsory and free primary 6-year elementary school education was established. On 8 May 1919 the Estonian provisional government resigned, and the first fully democratically elected Government of Estonia headed by Prime Minister Otto Strandman (Estonian Labor Party) took office. On 15 May the assembly reaffirmed the Estonian Declaration of Independence, aimed at the international community for recognizing Estonia as an independent state. On 4 June 1919 the Assembly adopted a temporary Constitutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian Provisional Government
The Estonian Provisional Government ( et, Eesti Ajutine Valitsus) was formed on 24 February 1918, by the Salvation Committee appointed by ''Maapäev'', the Estonian Province Assembly. History Konstantin Päts' first provisional cabinet The Provisional Government was led by Konstantin Päts. Jüri Vilms was appointed minister of justice, Jaan Poska minister of foreign affairs, Juhan Kukk minister of finance, Jaan Raamot minister of food and agriculture, Andres Larka minister of war. Villem Maasik was minister of labour and welfare, Ferdinand Peterson minister of roads and Peeter Põld minister of education. The main functions of the Provisional Government were lobbying for diplomatic recognition for Estonian independence abroad, oppose the German occupation of Estonia and organise elections to the Estonian Constituent Assembly. After the formation of the Provisional Government, the country was occupied by German troops and became administered by Ober Ost. As the result of Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian War Of Independence
The Estonian War of Independence ( et, Vabadussõda, literally "Freedom War"), also known as the Estonian Liberation War, was a defensive campaign of the Estonian Army and its allies, most notably the United Kingdom, against the Bolshevik westward offensive of 1918–1919 and the 1919 aggression of the ''Baltische Landeswehr''. The campaign was the struggle of the newly established democratic nation of Estonia for independence in the aftermath of World War I. It resulted in a victory for Estonia and was concluded in the 1920 Treaty of Tartu. Preface In November 1917, upon the disintegration of the Russian Empire, a diet of the Autonomous Governorate of Estonia, the Estonian Provincial Assembly, which had been elected in the spring of that year, proclaimed itself the highest authority in Estonia. Soon thereafter, the Bolsheviks dissolved the Estonian Provincial Assembly and temporarily forced the pro-independence Estonians underground in the capital Tallinn. A few months later, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Rei
August Rei VR III/1 ( – 29 March 1963) was an Estonian politician, the Head of State (''Riigivanem'') of Estonia in 1928–1929, and the Prime Minister in duties of the President of Estonia in the government in exile in 1945–1963. Early life and education August Rei was born in Kurla, Pilistvere parish, Kreis Fellin, Governorate of Livonia, Russian Empire (now Türi Parish, Järva County). Rei studied in the Tartu Emperor Alexander High School (the former State High School of the Livonian Governorate), but graduated from the Novgorod State High School. In 1904–1905 and 1907–1911, studied law in the St. Petersburg University. Beginnings of political influence In 1905–1907, Rei participated in the Russian revolution of 1905. In 1906, he edited the underground paper ''Sotsiaaldemokraat'' (''Social Democrat'') in Tallinn. Between 1912 and 1913, he was in compulsory army service. In 1913–1914 he worked as a lawyer in Viljandi. In 1914–1917 Rei was an artillery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Estonia
The Government of the Republic of Estonia (''Estonian language, Estonian: Vabariigi Valitsus'') is the cabinet (government), cabinet of Estonia. Under the Constitution of Estonia, Constitution, it exercises executive power pursuant to the Constitution and laws of Estonia. The cabinet carries out the country's domestic and foreign policy, shaped by parliament (Riigikogu); it directs and co-ordinates the work of government institutions and bears full responsibility for everything occurring within the authority of executive power. The government, headed by the Prime Minister of Estonia, Prime Minister, thus represents the political leadership of the country and makes decisions in the name of the whole executive power. The following duties are attributed to the cabinet by the Constitution of Estonia: # executes the domestic and foreign policies of the state; # directs and co-ordinates the activities of government agencies; # administers the implementation of laws, resolutions of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not the head of state, but rather the head of government, serving under either a monarch in a democratic constitutional monarchy or under a president in a republican form of government. In parliamentary systems fashioned after the Westminster system, the prime minister is the presiding and actual head of government and head/owner of the executive power. In such systems, the head of state or their official representative (e.g., monarch, president, governor-general) usually holds a largely ceremonial position, although often with reserve powers. Under some presidential systems, such as South Korea and Peru, the prime minister is the leader or most senior member of the cabinet, not the head of government. In many systems, the prime minister ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Strandman
Otto August Strandman ( – 5 February 1941) was an Estonian politician, who served as prime minister (1919) and State Elder of Estonia (1929–1931). He was one of the leaders of the centre-left Estonian Labour Party, that saw its biggest support after the 1919 and 1920 elections. Strandman was a key figure in composing the radical land reform law and the 1920 Constitution. He also served as Minister of Agriculture (1918–1919), Minister of Justice (acting 1918; 1920–1921), Minister of Finance (1924), Minister of Foreign Affairs (1918, 1920–1921 and 1924) and Minister of War (1919). While he was holding the office of the Minister of Finance, he stabilized the economy and managed to avoid hyperinflation. Strandman served as the speaker of the Estonian Provincial Assembly in 1917–1918, and as speaker of the newly independent country's parliament (''Riigikogu'') in 1921. He was also a diplomat, serving as the Estonian envoy in Warsaw, Poland (1927–1929), and in Paris, F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian Declaration Of Independence
__NOTOC__ The Estonian Declaration of Independence, also known as the Manifesto to the Peoples of Estonia ( et, Manifest Eestimaa rahvastele), is the founding act of the Republic of Estonia from 1918. It is celebrated on 24 February, the National Day or Estonian Independence Day. The declaration was drafted by the Salvation Committee elected by the elders of the Estonian Provincial Assembly. Originally intended to be proclaimed on 21 February 1918, the proclamation was delayed until the evening of 23 February, when the manifesto was printed and read out aloud publicly in Pärnu. On the next day, 24 February, the manifesto was printed and distributed in the capital, Tallinn. Historical context During World War I, between retreating Russian and advancing German troops, and the nearing occupation by the German Empire, then Maapäev — the Salvation Committee of the Estonian National Council — declared on 24 February 1918 the independence of Estonia. The German Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Estonia
Constitution of Estonia is the fundamental law of the Republic of Estonia and establishes the state order as that of a democratic republic where the supreme power is vested in its citizens. The first Constitution was adopted by the freely elected Estonian Constituent Assembly on 15 June 1920 and came into force on 21 December 1920. Heavily amended on 24 January 1934, following a referendum in 1933, it was in force until the second Constitution was enacted on 1 January 1938. It remained in force, ''de facto'', until 16 June 1940, when the Soviet Union occupied Estonia and, ''de jure'', until 28 June 1992, when the third and current Constitution of the Republic of Estonia was adopted by referendum. History First Constitution (1920–1933/38) The first Constitution was a reflection of Jean-Jacques Rousseau's idea of national sovereignty. Power was split between the judiciary, the executive and the legislature according to the principles of Montesquieu. The Constitution provided f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Reform
Land reform is a form of agrarian reform involving the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution, generally of agricultural land. Land reform can, therefore, refer to transfer of ownership from the more powerful to the less powerful, such as from a relatively small number of wealthy or noble owners with extensive land holdings (e.g., plantations, large ranches, or agribusiness plots) to individual ownership by those who work the land. Such transfers of ownership may be with or without compensation; compensation may vary from token amounts to the full value of the land. Land reform may also entail the transfer of land from individual ownership—even peasant ownership in smallholdings—to government-owned collective farms; it has also, in other times and places, referred to the exact opposite: division of government-owned collective farms into smallholdings. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic German
Baltic Germans (german: Deutsch-Balten or , later ) were ethnic German inhabitants of the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, in what today are Estonia and Latvia. Since their coerced resettlement in 1939, Baltic Germans have markedly declined as a geographically determined ethnic group. However, it is estimated that several thousand people with some form of (Baltic) German identity still reside in Latvia and Estonia. Since the Middle Ages, native German-speakers formed the majority of merchants and clergy, and the large majority of the local landowning nobility who effectively constituted a ruling class over indigenous Latvian and Estonian non-nobles. By the time a distinct Baltic German ethnic identity began emerging in the 19th century, the majority of self-identifying Baltic Germans were non-nobles belonging mostly to the urban and professional middle class. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Catholic German traders and crusaders (''see '') began settling in the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livonian Crusade
The Livonian crusade refers to the various military Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – in what is now Latvia and Estonia – during the Papal -sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12–13th century. The Livonian crusade was conducted mostly by the Holy Roman Empire and the Kingdom of Denmark. It ended with the creation of Terra Mariana and the Danish duchy of Estonia. The lands on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea were one of the last parts of Europe to be Christianised. On 2 February 1207, in the territories conquered, an ecclesiastical state called ''Terra Mariana'' was established as a principality of the Holy Roman Empire, and proclaimed by Pope Innocent III in 1215 as a subject of the Holy See. After the success of the crusade, the Teutonic- and Danish- occupied territory was divided into six feudal principalities by William of Modena. Wars against Livs and Latgalians (1198–1209) By the time German traders began to arrive in the second half of the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |