|
Edgar Sengier
Edgar Edouard Bernard Sengier (9 October 1879 – 26 July 1963) was a Belgian mining engineer and director of the Union Minière du Haut Katanga mining company that operated in Belgian Congo during World War II. Sengier is credited with giving the American government access to much of the uranium necessary for the Manhattan Project, much of which was already stored in a Staten Island warehouse due to his foresight to stockpile the ore to prevent it from falling into a possible enemy's hands. For his actions he became the first non-American civilian to be awarded the Medal for Merit by the United States government. Early life Born in Kortrijk, Sengier graduated in 1903 as a mining engineer from the University of Leuven and joined the Union Minière du Haut Katanga (UMHK) in 1911 as it was beginning to exploit copper mines in Katanga Province in the Belgian Congo. The UMHK was owned jointly by the Société Générale de Belgique, a Belgian investment company, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kortrijk
Kortrijk ( , ; vls, Kortryk or ''Kortrik''; french: Courtrai ; la, Cortoriacum), sometimes known in English as Courtrai or Courtray ( ), is a Belgian city and municipality in the Flemish province of West Flanders. It is the capital and largest city of the judicial and administrative arrondissement of Kortrijk. The wider municipality comprises the city of Courtrai proper and the villages of Aalbeke, Bellegem, Bissegem, Heule, Kooigem, Marke, and Rollegem. Courtrai is also part of the cross-border Lille-Kortrijk-Tournai metropolitan area. The city is on the river Leie, southwest of Ghent and northeast of Lille. Mouscron in Wallonia is just south of Courtrai. Courtrai originated from a Gallo-Roman town, ''Cortoriacum'', at a crossroads near the Leie river and two Roman roads. In the Middle Ages, Courtrai grew significantly thanks to the flax and wool industry with France and England and became one of the biggest and richest cities in Flanders. The city is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Hope, Ontario
Port Hope is a municipality in Southern Ontario, Canada, approximately east of Toronto and about west of Kingston. It is located at the mouth of the Ganaraska River on the north shore of Lake Ontario, in the west end of Northumberland County. The private Trinity College School opened here in 1868. History Cayuga people, one of the Six Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy, migrated to the Port Hope area from New York state in 1779. They had been forced from their homeland south of the Great Lakes after having been allies of the British during the American Revolution. Great Britain had ceded these lands, along with territory it occupied in the Thirteen Colonies east of the Mississippi River, after the United States won independence. In 1793, United Empire Loyalists from the northern colonies became the first permanent settlers of European heritage in Port Hope, as the Crown granted them land as compensation for being forced to leave the colonies (much of their property was conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eldorado Mining And Refining
Eldorado Resources was a Canadian mining company active between 1926 and 1988. The company was originally established by brothers Charles and Gilbert LaBine as a gold mining enterprise in 1926, but transitioned to focus on radium in the 1930s and uranium beginning in the 1940s. The company was nationalized into a Crown corporation in 1943 when the Canadian federal government purchased share control. Eldorado Resources was merged with the Saskatchewan Mining Development Corporation in 1988 and the resulting entity was privatized as Cameco Corporation. The remediation of some mining sites and low-level nuclear waste continue to be overseen by the Government of Canada through Canada Eldor Inc., a subsidiary of the Canada Development Investment Corporation. History Eldorado was originally established as Eldorado Gold Mines but, after finding radioactive deposits at Great Bear Lake, Northwest Territories in 1930, the company transitioned to primarily mining radioactive materials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Rosen
Louis Rosen (June 10, 1918 – August 15, 2009) was a nuclear physicist, the "father" of the Los Alamos Neutron Science Center accelerator (LAMPF, now known as LANSCE). Dr. Rosen held a bachelor's degree and a master's degree from the University of Alabama and a Doctorate in Physics from Pennsylvania State University.Douglas Martin, "Louis Rosen, 91, Dies; Worked on First Nuclear Bombs" ''New York Times'', September 5, 2009. He had never taken a course in before arriving in Los Alamos. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other nations, its primary duties are advising the U.S. president on international relations, administering diplomatic missions, negotiating international treaties and agreements, and representing the United States at the United Nations conference. Established in 1789 as the first administrative arm of the U.S. executive branch, the State Department is considered among the most powerful and prestigious executive agencies. It is headed by the secretary of state, who reports directly to the U.S. president and is a member of the Cabinet. Analogous to a foreign minister, the secretary of state serves as the federal government's chief diplomat and representative abroad, and is the first Cabinet official in the order of precedence and in the pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie Groves
Lieutenant General Leslie Richard Groves Jr. (17 August 1896 – 13 July 1970) was a United States Army Corps of Engineers officer who oversaw the construction of the Pentagon and directed the Manhattan Project, a top secret research project that developed the atomic bomb during World War II. The son of a U.S. Army chaplain, Groves lived at various Army posts during his childhood. In 1918, he graduated fourth in his class at the U.S. Military Academy at West Point and was commissioned into the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. In 1929, he went to Nicaragua as part of an expedition to conduct a survey for the Inter-Oceanic Nicaragua Canal. Following the 1931 earthquake, Groves took over Managua's water supply system, for which he was awarded the Nicaraguan Presidential Medal of Merit. He attended the Command and General Staff School at Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, in 1935 and 1936; and the Army War College in 1938 and 1939, after which he was posted to the War Department General S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Nichols
Major General Kenneth David Nichols CBE (13 November 1907 – 21 February 2000), also known by Nick, was an officer in the United States Army, and a civil engineer who worked on the secret Manhattan Project, which developed the atomic bomb during World War II. He served as Deputy District Engineer to James C. Marshall, and from 13 August 1943 as the District Engineer of the Manhattan Engineer District. Nichols led both the uranium production facility at the Clinton Engineer Works at Oak Ridge, Tennessee, and the plutonium production facility at Hanford Engineer Works in Washington state. Nichols remained with the Manhattan Project after the war until it was taken over by the Atomic Energy Commission in 1947. He was the military liaison officer with the Atomic Energy Commission from 1946 to 1947. After briefly teaching at the United States Military Academy at West Point, he was promoted to major general and became chief of the Armed Forces Special Weapons Project, responsib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth D
Kenneth is an English given name and surname. The name is an Anglicised form of two entirely different Gaelic personal names: ''Cainnech'' and '' Cináed''. The modern Gaelic form of ''Cainnech'' is ''Coinneach''; the name was derived from a byname meaning "handsome", "comely". A short form of ''Kenneth'' is '' Ken''. Etymology The second part of the name ''Cinaed'' is derived either from the Celtic ''*aidhu'', meaning "fire", or else Brittonic ''jʉ:ð'' meaning "lord". People :''(see also Ken (name) and Kenny)'' Places In the United States: * Kenneth, Indiana * Kenneth, Minnesota * Kenneth City, Florida In Scotland: * Inch Kenneth, an island off the west coast of the Isle of Mull Other * " What's the Frequency, Kenneth?", a song by R.E.M. * Hurricane Kenneth * Cyclone Kenneth Intense Tropical Cyclone Kenneth was the strongest tropical cyclone to make landfall in Mozambique since modern records began. The cyclone also caused significant damage in the Comoro Islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
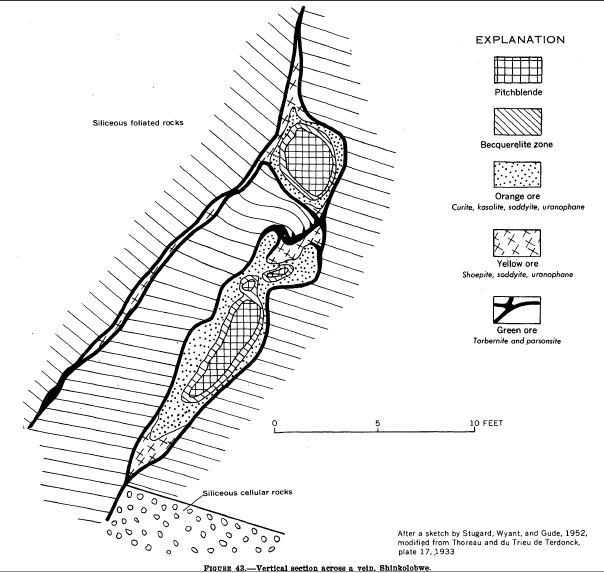
Shinkolobwe
Shinkolobwe, or Kasolo, or Chinkolobew, or Shainkolobwe, was a radium and uranium mine in the Haut-Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), located 20 km west of Likasi (formerly Jadotville), 20 km south of Kambove, and about 145 km northwest of Lubumbashi. The mine produced the most economical uranium ore in the world and was used for the Manhattan Project and subsequent nuclear weapons produced by the United States in the 1940s and 50s. Before World War II, uranium extracted here was originally taken to Belgium to be processed; this supply was captured by the Wehrmacht in 1940 and subsequently used for the unsuccessful German nuclear program. The Shinkolobwe mine was officially closed in 2004. Toponym The mine's name was taken from the long-gone nearby village of Shinkolobwe, which is the indigenous thorny fruit in the Lingala language. It is also slang for "a man who is easygoing on the surface but who becomes angry when provoked". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France during the Second World War. On 3 September 1939, France declared war on Germany following the German invasion of Poland. In early September 1939, France began the limited Saar Offensive and by mid-October had withdrawn to their start lines. German armies invaded Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands on 10 May 1940. Italy entered the war on 10 June 1940 and attempted an invasion of France. France and the Low Countries were conquered, ending land operations on the Western Front until the Normandy landings on 6 June 1944. In ''Fall Gelb'' ("Case Yellow"), German armoured units made a surprise push through the Ardennes and then along the Somme valley, cutting off and surrounding the Allied units that had advanced into Belgium to meet the German armies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frédéric Joliot-Curie
Jean Frédéric Joliot-Curie (; ; 19 March 1900 – 14 August 1958) was a French physicist and husband of Irène Joliot-Curie, with whom he was jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1935 for their discovery of Induced radioactivity. They were the second ever married couple, after his wife's parents, to win the Nobel Prize, adding to the Curie family legacy of five Nobel Prizes. Joliot-Curie and his wife also founded the Orsay Faculty of Sciences, part of the Paris-Saclay University. Biography Early years Born in Paris, France, Frédéric Joliot was a graduate of ESPCI Paris. In 1925 he became an assistant to Marie Curie, at the Radium Institute. He fell in love with her daughter Irène Curie, and soon after their marriage in 1926 they both changed their surnames to Joliot-Curie. At the insistence of Marie, Joliot-Curie obtained a second baccalauréat, a bachelor's degree, and a doctorate in science, doing his thesis on the electrochemistry of radio-elements. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_at_West_Point_in_1918.png)