|
Eä
The fictional cosmology of J.R.R. Tolkien's legendarium combines aspects of Christian theology and metaphysics with pre-modern cosmological concepts in the flat Earth paradigm, along with the modern spherical Earth view of the Solar System. The created world, ''Eä'', includes the planet Arda, corresponding to the Earth. It is created flat, with the dwelling of the godlike Valar at its centre. When this is marred by the evil Vala Melkor, the world is reshaped, losing its perfect symmetry, and the Valar move to Valinor, but the Elves can still sail there from Middle-earth. When Men try to go there, hoping for immortality, Valinor and its continent of Aman are removed from Arda, which is reshaped as a round world. Scholars have compared the implied cosmology with that of Tolkien's religion, Catholicism, and of medieval poetry such as ''Pearl'' or Dante's '' Paradiso'', where there are three parts, Earth, Purgatory or the Earthly Paradise, and Heaven or the Celestial Paradise. Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Silmarillion
''The Silmarillion'' () is a book consisting of a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited, partly written, and published posthumously by his son Christopher in 1977, assisted by Guy Gavriel Kay, who became a fantasy author. It tells of Eä, a fictional universe that includes the Blessed Realm of Valinor, the ill-fated region of Beleriand, the island of Númenor, and the continent of Middle-earth, where Tolkien's most popular works—''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''—are set. After the success of ''The Hobbit'', Tolkien's publisher, Stanley Unwin, requested a sequel, and Tolkien offered a draft of the writings that would later become ''The Silmarillion''. Unwin rejected this proposal, calling the draft obscure and "too Celtic", so Tolkien began working on a new story that eventually became ''The Lord of the Rings''. ''The Silmarillion'' has five parts. The first, '' Ainulindalë'', tells in mythic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the Setting (narrative), setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the ''Midgard, Miðgarðr'' of Norse mythology and ''Middangeard'' in Old English works, including ''Beowulf''. Middle-earth is the oecumene (i.e. the human-inhabited world, or the central continent of Earth) in Tolkien's imagined mythopoeia, mythological past. Tolkien's most widely read works, ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings'', are set entirely in Middle-earth. "Middle-earth" has also become Metonym, a short-hand term for Tolkien's legendarium, his large body of fantasy writings, and for the entirety of his fictional world. Middle-earth is the main continent of Cosmology of Tolkien's legendarium#Spherical-earth cosmology, Earth (Arda) in an imaginary period of the past, ending with Tolkien's Third Age, about 6,000 years ago. Tolkien's tales of Middle-earth mostly focus on the north-west of the continent. This region is suggestive of Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
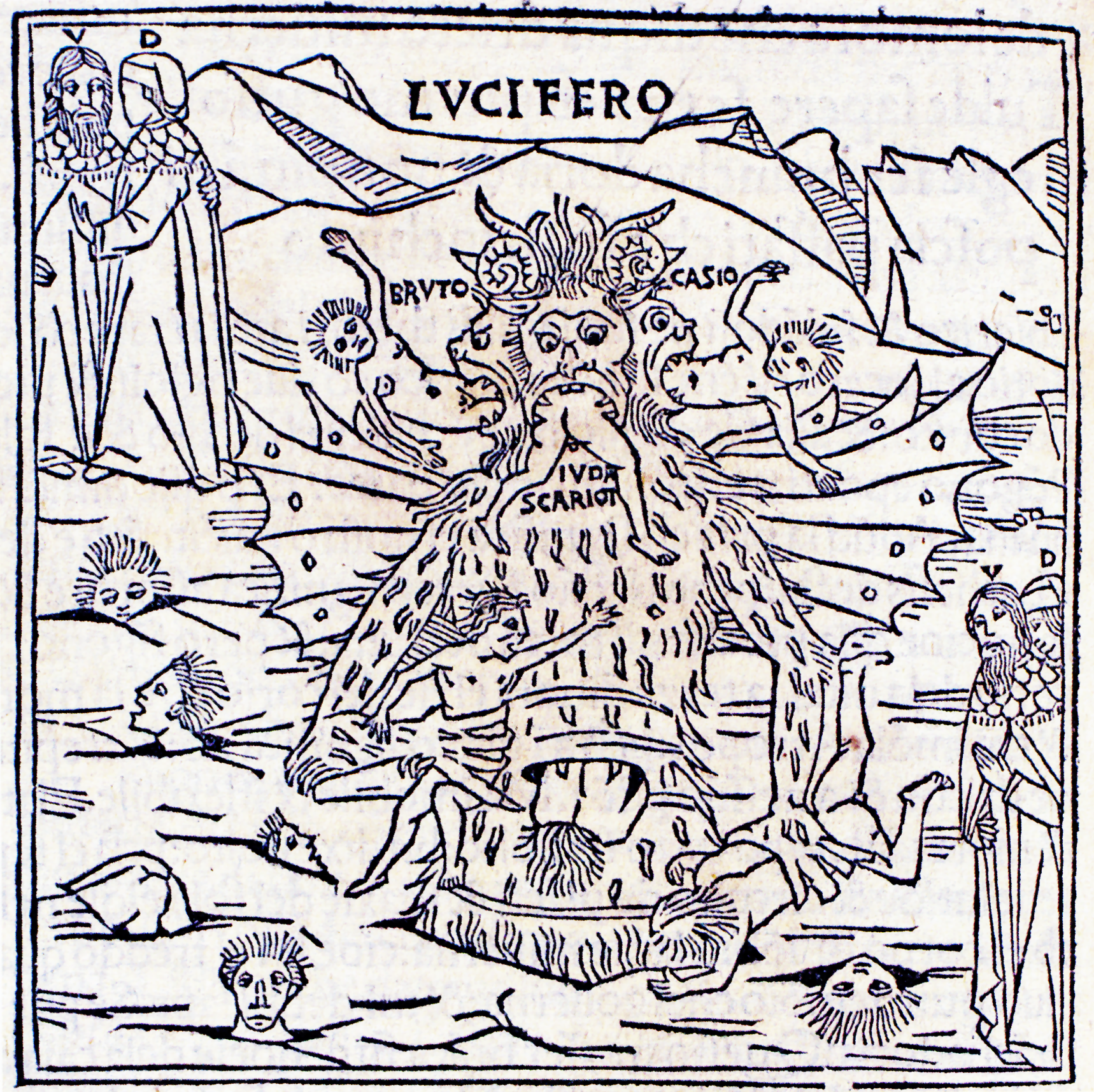
Melkor
Morgoth Bauglir (; originally Melkor ) is a character, one of the godlike Valar and the primary antagonist of Tolkien's legendarium, the mythic epic published in parts as '' The Silmarillion'', ''The Children of Húrin'', '' Beren and Lúthien'', and '' The Fall of Gondolin''. The character is also briefly mentioned in ''The Lord of the Rings''. Melkor is the most powerful of the Valar but he turns to darkness and is renamed Morgoth, the primary antagonist of Arda. All evil in the world of Middle-earth ultimately stems from him. One of the Maiar of Aulë betrays his kind and becomes Morgoth's principal lieutenant and successor, Sauron. Melkor has been interpreted as analogous to Satan, once the greatest of all God's angels, Lucifer, but fallen through pride; he rebels against his creator. Morgoth has likewise been likened to John Milton's fallen angel in ''Paradise Lost'', again a Satan-figure. Tom Shippey has written that ''The Silmarillion'' maps the Book of Genesis w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quenya
Quenya ()Tolkien wrote in his "Outline of Phonology" (in '' Parma Eldalamberon'' 19, p. 74) dedicated to the phonology of Quenya: is "a sound as in English ''new''". In Quenya is a combination of consonants, ibidem., p. 81. is a constructed language, one of those devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for the Elves in his Middle-earth fiction. Tolkien began devising the language around 1910, and restructured its grammar several times until it reached its final state. The vocabulary remained relatively stable throughout the creation process. He successively changed the language's name from ''Elfin'' and ''Qenya'' to the eventual ''Quenya''. Finnish had been a major source of inspiration, but Tolkien was also fluent in Latin and Old English, and was familiar with Greek, Welsh (the primary inspiration for Sindarin, Tolkien's other major Elvish language), and other ancient Germanic languages, particularly Gothic, during his development of Quenya. Tolkien developed a complex internal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valar
The Valar (; singular Vala) are characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth writings. They are "angelic powers" or "gods" subordinate to the one God ( Eru Ilúvatar). The '' Ainulindalë'' describes how some of the Ainur choose to enter the world ( Arda) to complete its material development after its form is determined by the Music of the Ainur. The mightiest of these are called the Valar, or "the Powers of the World", and the others are known as the Maiar. The Valar are mentioned briefly in ''The Lord of the Rings'' but Tolkien had developed them earlier, in material published posthumously in ''The Silmarillion'', especially the "Valaquenta" (Quenya: "Account of the Valar"), ''The History of Middle-earth'', and '' Unfinished Tales''. Scholars have noted that the Valar resemble angels in Christianity but that Tolkien presented them rather more like pagan gods. Their role in providing what the characters in Middle-earth experience as luck or providence is also discussed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valinor
Valinor (Quenya'': Land of the Valar''), the Blessed Realm, or the Undying Lands is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the home of the immortal Valar and Maiar on the continent of Aman, far to the west of Middle-earth; he used the name Aman mainly to mean Valinor. It includes Eldamar, the land of the Elves, who as immortals are permitted to live in Valinor. The name "the Undying Lands" does not mean that the land itself causes mortals to live forever. Generally, only immortal beings are allowed to reside there. Exceptions are made for the surviving bearers of the One Ring: Bilbo and Frodo Baggins and Sam Gamgee, who dwell there for a time, and the dwarf Gimli., "The Grey Havens", and Appendix B, entry for S.R. 1482 and 1541. Tolkien's myth of the attempt of Númenor to capture Aman has been likened to the biblical Tower of Babel and the ancient Greek Atlantis, and the resulting destruction in both cases. They note, too, that a mortal's stay in Valino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evil In Middle-earth
Evil is ever-present in J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional realm of Middle-earth. Tolkien is ambiguous on the philosophical question of whether evil is the absence of good, the Boethian position, or whether it is a force seemingly as powerful as good, and forever opposed to it, the Manichaean view. The major evil characters have varied origins. The first is Melkor, the most powerful of the immortal and angelic Valar; he chooses discord over harmony, and becomes the first dark lord Morgoth. His lieutenant, Sauron, is an immortal Maiar, Maia; he becomes Middle-earth's dark lord after Morgoth is banished from the world. Melkor has been compared to Satan in the Book of Genesis, and to John Milton's fallen angel in ''Paradise Lost''. Others, such as Gollum, Denethor, and Saruman – respectively, a Hobbit, a Men in Middle-earth, Man, and a Wizards in Middle-earth, Wizard – are corrupted or deceived into evil, and die fiery deaths like those of evil beings in Norse sagas. Context: Tol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiar In Middle-earth
The Maiar (singular: Maia) are a fictional class of beings from J. R. R. Tolkien's high fantasy legendarium. Supernatural and angelic, they are "lesser Ainur" who entered the cosmos of '' Eä'' in the beginning of time. The name ''Maiar'' is in the Quenya tongue (one of several languages constructed by Tolkien) from the Elvish root maya- "excellent, admirable". Tolkien, J. R. R., "Words, Phrases and Passages", '' Parma Eldalamberon'' 17, p. 174. Commentators have noted that since the Maiar are immortals but can choose to become fully incarnate in men's bodies on Middle-earth, they can be killed; Tolkien did not explain what happened to them then. Others have observed that their semi-divine nature and the fact that they can be sent on missions to work out the divine purpose makes them much like the angels of Christianity. Description Lesser Ainur Tolkien stated that "Maia is the name of the Kin of the Valar, but especially of those of lesser power than the 9 great rulers". In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainur In Middle-earth
The Ainur () are the immortal spirits existing before the Creation in J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional universe. These were the first beings made of the thought of Eru Ilúvatar. They were able to sing such beautiful music that the world was created from it. History Origins Before the Creation, Eru Ilúvatar made the Ainur or "holy ones". The Universe was created through the " Music of the Ainur" or '' Ainulindalë'', music sung by the Ainur in response to themes introduced by Eru. This universe, the song endowed with existence by Eru, was called Eä in Quenya. The Earth was called Arda. Those of the Ainur who felt concern for the Creation entered it, and became the Valar and the Maiar, the guardians of Creation. Valar The Valar included both good and evil characters. The Vala Melkor claimed the Earth for himself. His brother, Manwë, and several other Valar decided to confront him. Melkor fell into evil and became known as Morgoth, the dark enemy. The conflict b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elvish Languages (Middle-earth)
The Elvish languages of Middle-earth, Constructed languages, constructed by J. R. R. Tolkien, include Quenya and Sindarin. These were the various languages spoken by the Elves in Middle-earth, Elves of Middle-earth as they developed as a society throughout the Ages. In his pursuit for realism and in his love of language, Tolkien was especially fascinated with the development and evolution of language through time. Tolkien created two almost fully developed languages and a dozen more in various beginning stages as he studied and reproduced the way that language adapts and morphs. A philology, philologist by profession, he spent much time on his constructed languages. In the collection of letters he had written, posthumously published by his son, Christopher Tolkien, he stated that he began stories set within this secondary world, the realm of Middle-earth, not with the characters or narrative as one would assume, but with a created set of languages. The stories and characters serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
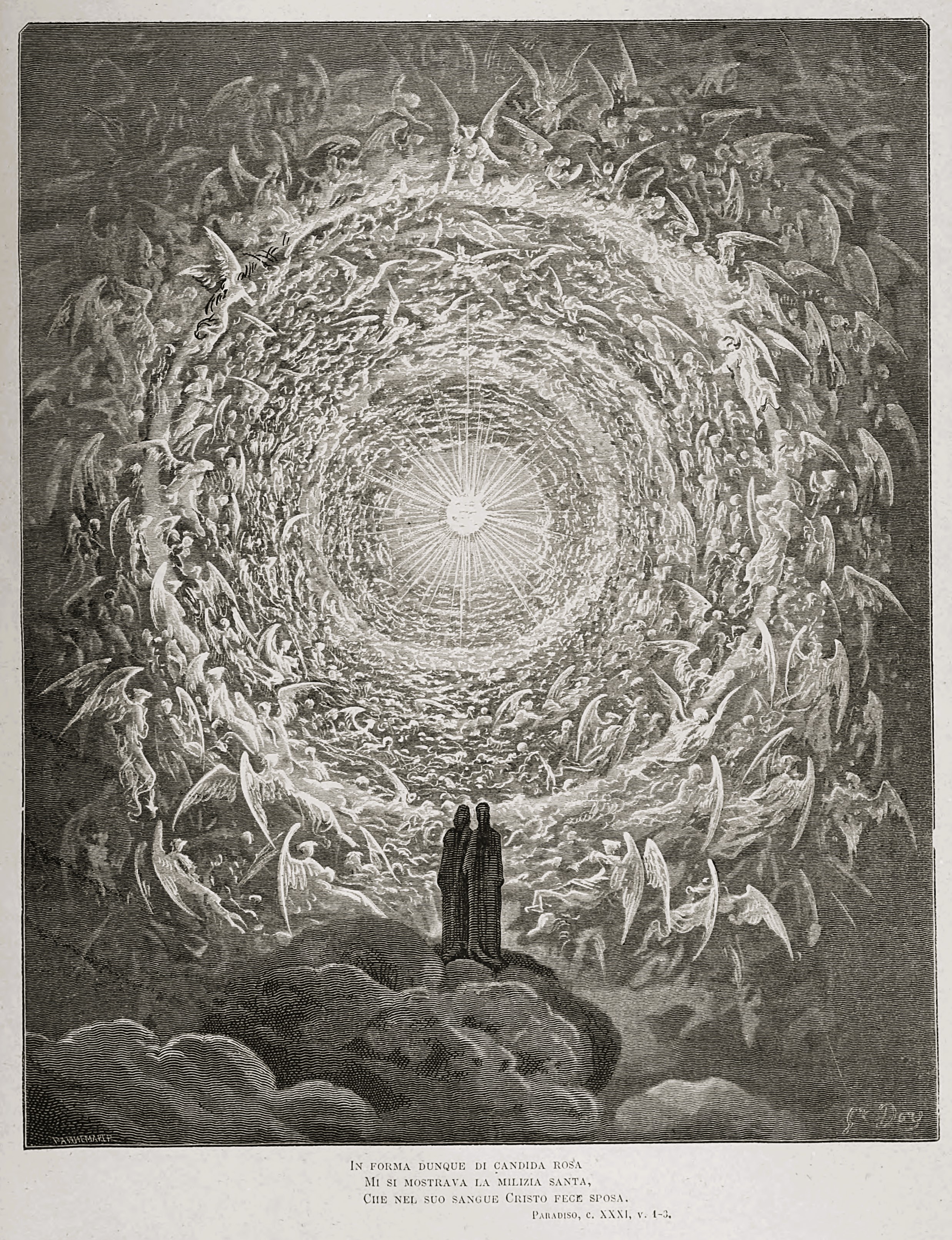
Heaven
Heaven, or the Heavens, is a common Religious cosmology, religious cosmological or supernatural place where beings such as deity, deities, angels, souls, saints, or Veneration of the dead, venerated ancestors are said to originate, be throne, enthroned, or reside. According to the beliefs of some religions, heavenly beings can descend to Earth or Incarnation, incarnate and earthly beings can ascend to Heaven in the afterlife or, in exceptional cases, enter Heaven Entering heaven alive, without dying. Heaven is often described as a "highest place", the Sacred, holiest place, a paradise, in contrast to Hell or the Underworld or the "low places" and History of Christian universalism, universally or conditionally accessible by earthly beings according to various standards of divinity, good and evil, goodness, piety, faith, or other virtues or orthodoxy, right beliefs or simply Will of God, divine will. Some believe in the possibility of a heaven on Earth in a ''world to come''. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |