|
Eyeglasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses (American English), spectacles (Commonwealth English), or colloquially as specs, are Visual perception, vision eyewear with clear or tinted lens (optics), lenses mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's Human eyes, eyes, typically utilizing a bridge over the nose and hinged arms, known as temples or temple pieces, that rest over the ears for support. Glasses are typically used for Corrective lens, vision correction, such as with reading glasses and glasses used for nearsightedness; however, without the specialized lenses, they are sometimes used for cosmetic purposes. Safety glasses are eye protection, a form of personal protective equipment (Personal protective equipment, PPE) that are worn by workers around their eyes for protection. Safety glasses act as a shield to protect the eyes from any type of foreign debris that may cause irritation or injury; these glasses may have protection on the sides of the eyes as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Corrective Lens
A corrective lens is a transmissive optical device that is worn on the eye to improve visual perception. The most common use is to treat refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are worn on the face a short distance in front of the eye. Contact lenses are worn directly on the surface of the eye. Intraocular lenses are surgically implanted most commonly after cataract removal but can be used for purely refractive purposes. Prescription of corrective lenses Corrective lenses are typically prescribed by an ophthalmologist or an optometrist. The prescription consists of all the specifications necessary to make the lens. Prescriptions typically include the power specifications of each lens (for each eye). Strengths are generally prescribed in quarter- diopter steps (0.25 D), because most people cannot generally distinguish between smaller increments (e.g., eighth-diopter steps / 0.125 D). The use of improper corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eyewear
Eyewear is a term used to refer to all devices worn over both of a person's eyes, or occasionally a single eye, for one or more of a variety of purposes. Though historically used for vision improvement and correction, eyewear has also evolved into eye protection, for fashion and aesthetic purposes, and starting in the late 20th century, computers and virtual reality. The primary intention of wearing eyewear can vary based on the need or desire of the wearer. Eyewear comes in different forms such as Glasses, Contact lenses, Sunglasses and many more. . Eyewear (such as glasses and contact lenses) helps most people see clearer or read. Eyewear also can be used for protection, such as sunglasses which protect wearers from the Sun's ultraviolet rays which are damaging to the eyes when unprotected, eyepatches to protect injured eyes from further damage, or goggles which protect the wearer's eyes from debris, water and other chemicals. Variants of eyewear can conversely inhibit or disable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sunglasses
Sunglasses or sun glasses (informally called shades or sunnies; more names Sunglasses#Other names, below) are a form of Eye protection, protective eyewear designed primarily to prevent bright sunlight and high-energy visible light from damaging or discomforting the eyes. They can sometimes also function as a visual aid, as variously termed spectacles or glasses exist, featuring lenses that are colored, polarizer, polarized or darkened. In the early 20th century, they were also known as sun cheaters (cheaters then being an United States, American slang term for glasses). Since the 1930s, sunglasses have been a popular fashion accessory, especially on the beach. The American Optometric Association recommends wearing sunglasses that block ultraviolet radiation (UV) whenever a person is in the sunlight to protect the eyes from UV and blue light, which can cause several #Protection, serious eye problems. Their usage is mandatory immediately after some surgical procedures, such as L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Optometry
Optometry is the healthcare practice concerned with examining the eyes for visual defects, prescribing corrective lenses, and detecting eye abnormalities. In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a post-baccalaureate four-year Doctor of Optometry degree. They are trained and licensed to practice medicine for eye related conditions, in addition to providing refractive (optical) eye care. Within their scope of practice, optometrists are considered physicians and bill medical insurance(s) (example: Medicare) accordingly. In the United Kingdom, optometrists may also provide medical care (e.g. prescribe medications and perform various surgeries) for eye-related conditions in addition to providing refractive care. The Doctor of Optometry degree is rarer in the UK. Many optometrists participate in academic research for eye-related conditions and diseases. In addition to prescribing glasses and contact lenses for vision related deficiencies, optometrists are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
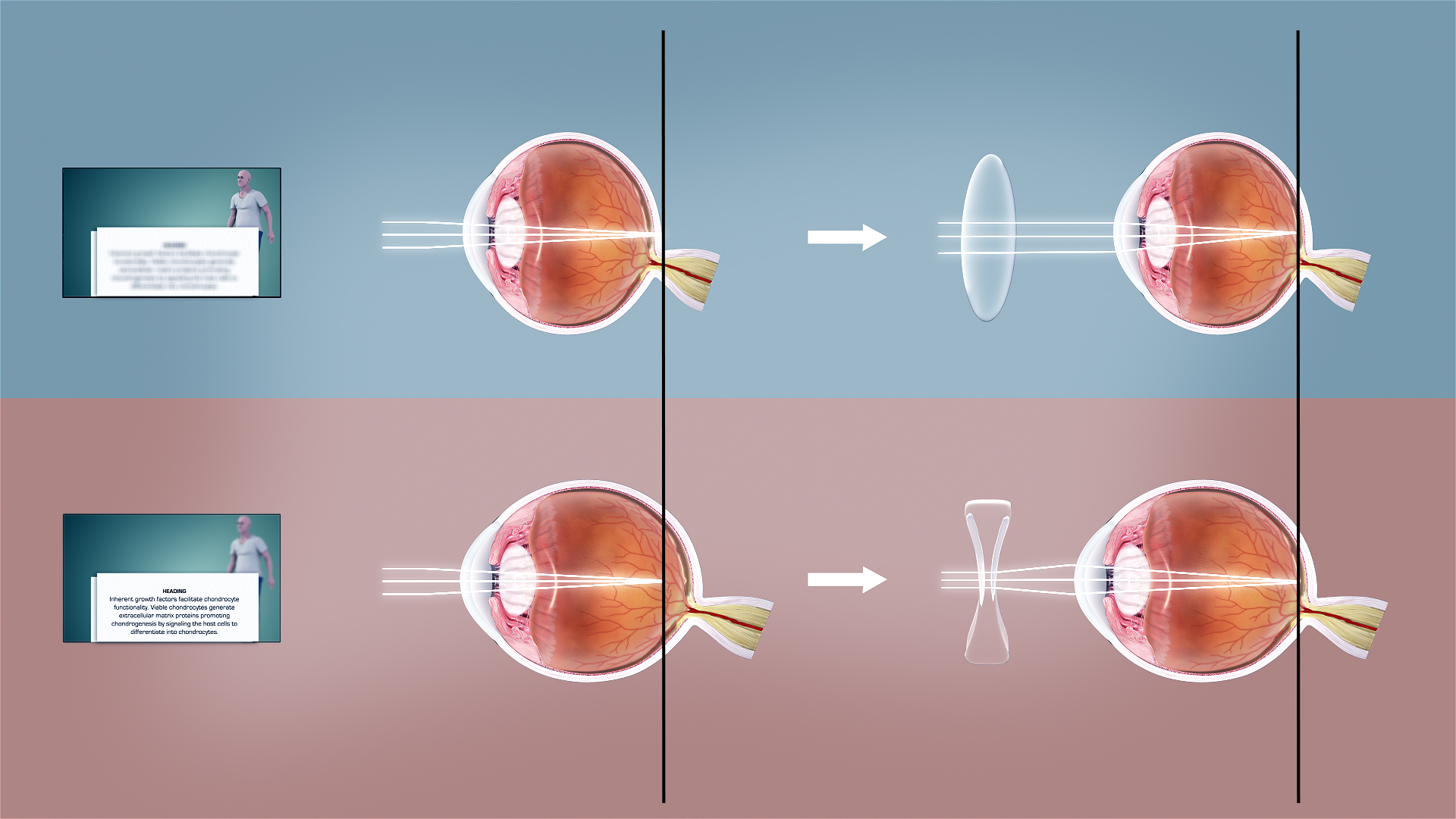
Refractive Error
Refractive error is a problem with focus (optics), focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and/or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are myopia, near-sightedness, hyperopia, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurred vision, blurry, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision, headaches, and eye strain. Near-sightedness is due to the length of the eyeball being too long; far-sightedness the eyeball too short; astigmatism the cornea being the wrong shape, while presbyopia results from aging of the lens of the eye such that it cannot change shape sufficiently. Some refractive errors occur more often among those whose parents are affected. Diagnosis is by eye examination. Refractive errors are corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
3D Glasses
Stereoscopy, also called stereoscopics or stereo imaging, is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope. Most stereoscopic methods present a pair of two-dimensional images to the viewer. The left image is presented to the left eye and the right image is presented to the right eye. When viewed, the human brain perceives the images as a single 3D view, giving the viewer the perception of 3D depth. However, the 3D effect lacks proper focal depth, which gives rise to the Vergence-accommodation conflict. Stereoscopy is distinguished from other types of 3D displays that display an image in three full dimensions, allowing the observer to increase information about the 3-dimensional objects being displayed by head and eye m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stereoscopy
Stereoscopy, also called stereoscopics or stereo imaging, is a technique for creating or enhancing the depth perception, illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope. Most stereoscopic methods present a pair of two-dimensional images to the viewer. The left image is presented to the left eye and the right image is presented to the right eye. When viewed, the human brain perceives the images as a single 3D view, giving the viewer the perception of Three-dimensional space, 3D depth. However, the 3D effect lacks proper focal depth, which gives rise to the Vergence-accommodation conflict. Stereoscopy is distinguished from other types of 3d display#3D displays, 3D displays that display an image in Three-dimensional space, three full dimensions, allowing the observer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Myopia
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. Other symptoms may include headaches and eye strain. Severe myopia is associated with an increased risk of macular degeneration, retinal detachment, cataracts, and glaucoma. Myopia results from the length of the eyeball growing too long or less commonly the lens being too strong. It is a type of refractive error. Diagnosis is by the use of cycloplegics during eye examination. Tentative evidence indicates that the risk of myopia can be decreased by having young children spend more time outside. This decrease in risk may be related to natural light exposure. Myopia can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or by refractive surgery. Eyeglasses are the simplest and safest method of correction. Contact lenses can provide a rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. The lens and cornea of an eye without astigmatism are nearly spherical, with only a single radius of curvature, and any refractive errors present can be corrected with simple glasses. In an eye with astigmatism, either the lens or the cornea is slightly egg-shaped, with higher curvature in one direction than the other. This gives distorted or blurred vision at any distance and requires corrective lenses that apply different optical powers at different rotational angles. Astigmatism can lead to symptoms that include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night. Astigmatism often is present at birth, but can change or develop later in life. If it occurs in early life and is left untreated, it may result in amblyopia. The cause of astigmatism is unclear, although it is believed to be partly related to genetic factors. The underlying mechanism involves an irregular c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hypermetropia
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead of on, the retina due to insufficient accommodation by the lens. Minor hypermetropia in young patients is usually corrected by their accommodation, without any defects in vision. But, due to this accommodative effort for distant vision, people may complain of eye strain during prolonged reading. If the hypermetropia is high, there will be defective vision for both distance and near. People may also experience accommodative dysfunction, binocular dysfunction, amblyopia, and strabismus. Newborns are almost invariably hypermetropic, but it gradually decreases as the newborn gets older. There are many causes for this condition. It may occur when the axial length of eyeball is too short or if the lens or cornea is flatter than normal. Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Microfiber Cloth
Microfiber (microfibre in British English) is synthetic fibre finer than one denier or decitex/thread, having a diameter of less than ten micrometers. The most common types of microfiber are made variously of polyesters; polyamides (e.g., nylon, Kevlar, Nomex); and combinations of polyester, polyamide, and polypropylene. Microfiber is used to make mats, knits, and weaves, for apparel, upholstery, industrial filters, and cleaning products. The shape, size, and combinations of synthetic fibers are chosen for specific characteristics, including softness, toughness, absorption, water repellence, electrostatics, and filtering ability. They are commonly used for cleaning scratch prone surfaces such as displays, glass, and lenses. Microfiber cloth makes use of van der Waals force to remove dirt without scratches. History Production of ultra-fine fibers (finer than 0.7 denier) dates to the late 1950s, using melt-blown spinning and flash spinning techniques. Initially, only fine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |