|
Extended Rotation Forest
An extended rotation forest is a forest stand for which the harvest age is increased beyond the optimum economic harvest age to provide larger trees, wildlife habitat, and other non-timber values. Advantages of extended rotation forestry included enhanced carbon storage, better wood quality and the ability to create habitat for old growth dependent species. The main disadvantages of extended rotations is the lower present value of the stand and timber supply issues. These impacts can be mitigated by the application of commercial thinning. In the Pacific Northwest of the United States, commercially thinned stands have yet to reach cumulation age in spite of reaching ages of over 100 years on good to moderate sites. In managed for values other than timber, extended rotations are being considered. In Oregon, some environmental groups are calling for rotations as long as 250 years. The argument centres on the assertion that short-rotation management on either biological or financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' (FRA 2020) found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the predominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are found around the globe. More than half of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, Canada, China, Russia, and the United States). The largest share of forests (45 percent) are in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
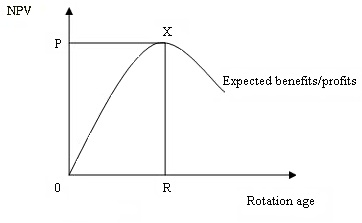
Optimal Rotation Age
In forestry, the optimal rotation age is the growth period required to derive maximum value from a stand of timber. The calculation of this period is specific to each stand and to the economic and sustainability goals of the harvester. Economically optimum rotation age In forestry rotation analysis, economically optimum rotation can be defined as “that age of rotation when the harvest of stumpage will generate the maximum revenue or economic yield”. In an economically optimum forest rotation analysis, the decision regarding optimum rotation age is undertake by calculating the maximum net present value. It can be shown as follows: *Revenue (R) = Volume × Price *Cost (C) = Cost of harvesting + handling. *Hence, Profit = Revenue − Cost. Since the benefit is generated over multiple years, it is necessary to calculate that particular age of harvesting which will generate the maximum revenue. The age of maximum revenue is calculated by discounting for future expected benefi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildlife Habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors will include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, with habitat generalist species able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species requiring a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-timber Forest Product
Non-timber forest products (NTFPs) are useful foods, substances, materials and/or commodities obtained from forests other than timber. Harvest ranges from wild collection to farming. They typically include game animals, fur-bearers, nuts, seeds, berries, mushrooms, oils, sap, foliage, pollarding, medicinal plants, peat, mast, fuelwood, fish, insects, spices, and forage. Overlapping concepts include non-wood forest products (NWFPs), wild forest products, minor forest produce, special, minor, alternative and secondary forest products – for further distinctions see the definition section below Research on NTFPs has focused on their ability to be produced as commodities for rural incomes and markets, as an expression of traditional knowledge or as a livelihood option for rural household needs, as a key component of sustainable forest management and conservation strategies, and for their important role in improving dietary diversity and providing nutritious food, particularly for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |