|
Explorer 41
Explorer 41, also called as IMP-G and IMP-5, was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 41 as launched on 21 June 1969 on Vandenberg AFB, California, with a Thor-Delta E1 launch vehicle. Explorer 41 was the seventh satellite launched as part of the overall Interplanetary Monitoring Platform series, though it received the post-launch designation "IMP-5" because two previous flights had used the "AIMP" ("Anchored IMP") designation instead. It was preceded by the second of those flights, Explorer 35 ( MP-E / AIMP-2), launched in July 1967. Its predecessor in the strict IMP series of launches was Explorer 34, launched in May 1967, which shared a similar design to Explorer 41. The next launch was of an IMP satellite was Explorer 43 (IMP-I / IMP-6) in 1971. Spacecraft and mission Explorer 41 (IMP-G) was a spin-stabilized satellite placed into a high-inclination, highly elliptical orbit to measure energetic particles, magnetic fields, and plasma in cislu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Physics
Space physics, also known as solar-terrestrial physics or space-plasma physics, is the study of plasmas as they occur naturally in the Earth's upper atmosphere ( aeronomy) and within the Solar System. As such, it encompasses a far-ranging number of topics, such as heliophysics which includes the solar physics of the Sun, the solar wind, planetary magnetospheres and ionospheres, auroras, cosmic rays, and synchrotron radiation. Space physics is a fundamental part of the study of space weather and has important implications in not only to understanding the universe, but also for practical everyday life, including the operations of communications and weather satellites. Space physics is distinct from astrophysical plasma and the field of astrophysics, which studies similar plasma phenomena beyond the Solar System. Space physics utilizes in situ measurements from high altitude rockets and spacecraft, in contrast to astrophysical plasma that relies deduction of theory and astronomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer 34
Explorer 34 (IMP-F, IMP-4), was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 34 as launched on 24 May 1967 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, with Thor-Delta E1 launch vehicle. Explorer 34 was the fifth satellite launched as part of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform program, but was known as "IMP-4" because the preceding launch was more specifically part of the "Anchored IMP" sub-program. The spacecraft was put into space between the launches of Explorer 33 (IMP-D / AIMP-1) in 1966 and Explorer 35 (IMP-E / AIMP-2) in July 1967, but the next satellite to use Explorer 34's general design was Explorer 41 (IMP-G / IMP-5), which flew in 1969. Launch Explorer 34 was placed into a high-inclination, highly elliptical orbit. The apogee point was located near the ecliptic plane and had an initial local time of about 19:00 hours. The spacecraft was spin-stabilized and had an initial spin period of 2.6-seconds. The spin vector was approximately perpendicu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
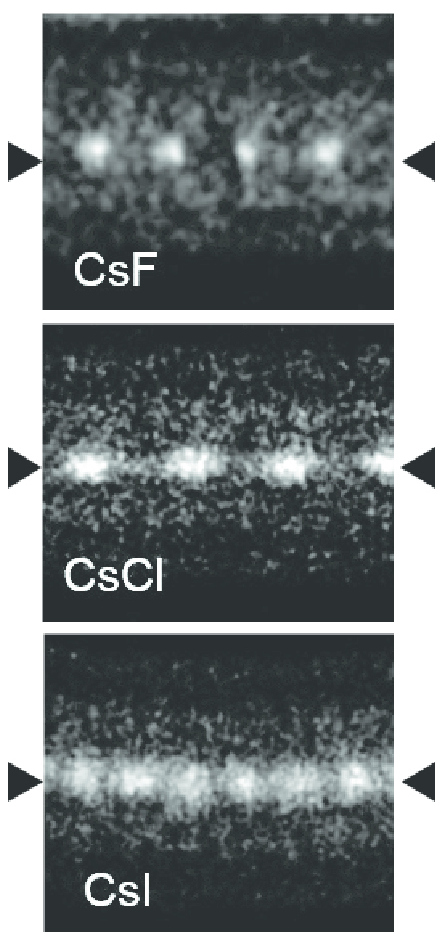
Caesium Iodide
Caesium iodide or cesium iodide (chemical formula CsI) is the ionic compound of caesium and iodine. It is often used as the input phosphor of an X-ray image intensifier tube found in fluoroscopy equipment. Caesium iodide photocathodes are highly efficient at extreme ultraviolet wavelengths. Synthesis and structure Bulk caesium iodide crystals have the cubic CsCl crystal structure, but the structure type of nanometer-thin CsI films depends on the substrate material – it is CsCl for mica and NaCl for LiF, NaBr and NaCl substrates. Caesium iodide atomic chains can be grown inside double-wall carbon nanotubes. In such chains I atoms appear brighter than Cs atoms in electron micrographs despite having a smaller mass. This difference was explained by the charge difference between Cs atoms (positive), inner nanotube walls (negative) and I atoms (negative). As a result, Cs atoms are attracted to the walls and vibrate more strongly than I atoms, which are pushed toward the nanotube a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronvolt
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV, also written electron-volt and electron volt) is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating from rest through an electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When used as a unit of energy, the numerical value of 1 eV in joules (symbol J) is equivalent to the numerical value of the charge of an electron in coulombs (symbol C). Under the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, this sets 1 eV equal to the exact value Historically, the electronvolt was devised as a standard unit of measure through its usefulness in electrostatic particle accelerator sciences, because a particle with electric charge ''q'' gains an energy after passing through a voltage of ''V.'' Since ''q'' must be an integer multiple of the elementary charge ''e'' for any isolated particle, the gained energy in units of electronvolts conveniently equals that integer times the voltage. It is a common unit of ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, per the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetotail
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body, the magnetic field resembles a magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation, that also protects all living organisms from potentially detrimental and dangerous consequences. This is studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert discovered that the magnetic field on the surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", and ''metron'', "measure". Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry, telecommand. Although the term commonly refers to wireless data transfer mechanisms (e.g., using radio, ultrasonic, or infrared systems), it also encompasses data transferred over other media such as a telephone or computer network, optical link or other wired communications like power line carriers. Many modern telemetry systems take advantage of the low cost and ubiquity of GSM networks by using SMS to receive and transmit telemetry data. A ''telemeter'' is a physical device used in telemetry. It consists of a sensor, a transmission path, and a display, recording, or control device. Electronic devices are widely used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotations Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apsis
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion. General description There are two apsides in any elliptic orbit. The name for each apsis is created from the prefixes ''ap-'', ''apo-'' (), or ''peri-'' (), each referring to the farthest and closest point to the primary body the affixing necessary suffix that describes the primary body in the orbit. In this case, the suffix for Earth is ''-gee'', so the apsides' names are ''apogee'' and ''perigee''. For the Sun, its suffix is ''-helion'', so the names are ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion''. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic orbits are ellipses. The barycenter of the two bodies may lie well within the bigger body—e.g., the Earth–Moon barycenter is about 75% of the way from Earth's center to its surface. If, compared to the larger mass, the smaller mass is negligible (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Sun's apparent motion The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of a year. Because Earth takes one year to orbit the Sun, the apparent position of the Sun takes one year to make a complete circuit of the ecliptic. With slightly more than 365 days in one year, the Sun moves a little less than 1° eastward every day. This small difference in the Sun's position against the stars causes any particular spot on Earth's surface to catch up with (and stand directly north or south of) the Sun about four minutes later each day than it would if Earth did not orbit; a day on Earth is therefore 24 ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cislunar Space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, cosmic neutrino background, neutrinos, cosmic dust, dust, and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature of outer space, as set by the cosmic background radiation, background radiation from the Big Bang, is . The Warm–hot intergalactic medium, plasma between galaxies is thought to account for about half of the baryonic matter, baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe, having a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a kinetic temperature of millions of kelvins. Local concentrations of matter have condensed into stars and galaxy, galaxies. Studies indicate that 90% of the mass in most galaxies is in an unknown form, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma ()πλάσμα , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek English Lexicon'', on Perseus is one of the four fundamental states of matter. It contains a significant portion of charged particles – ions and/or s. The presence of these charged particles is what primarily sets plasma apart from the other fundamental states of matter. It is the most abundant form of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

