|
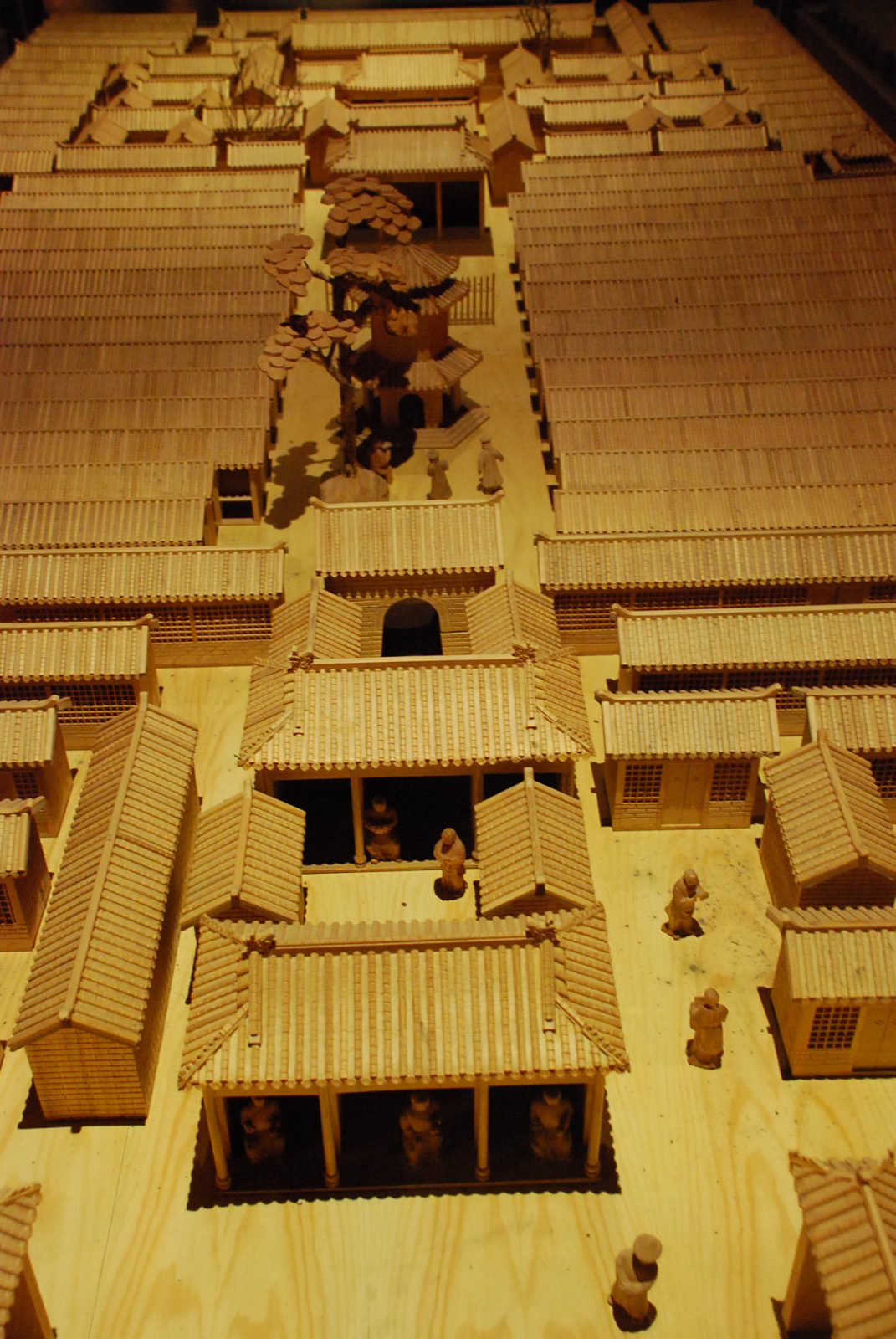
Examination Hall, Peking
Examination may refer to: * Physical examination, a medical procedure * Questioning and more specific forms thereof, for example in law: ** Cross-examination ** Direct examination * Exam as assessment, also "test", "exams", "evaluation" ** Civil service entrance examination *** Imperial examination See also * Analysis * Appraisal (other) * Assessment (other) * Evaluation In common usage, evaluation is a systematic determination and assessment of a subject's merit, worth and significance, using criteria governed by a set of Standardization, standards. It can assist an organization, program, design, project or any o ... * Evaluation (other) * Exam (other) * Investigation (other) * Study (other) * * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
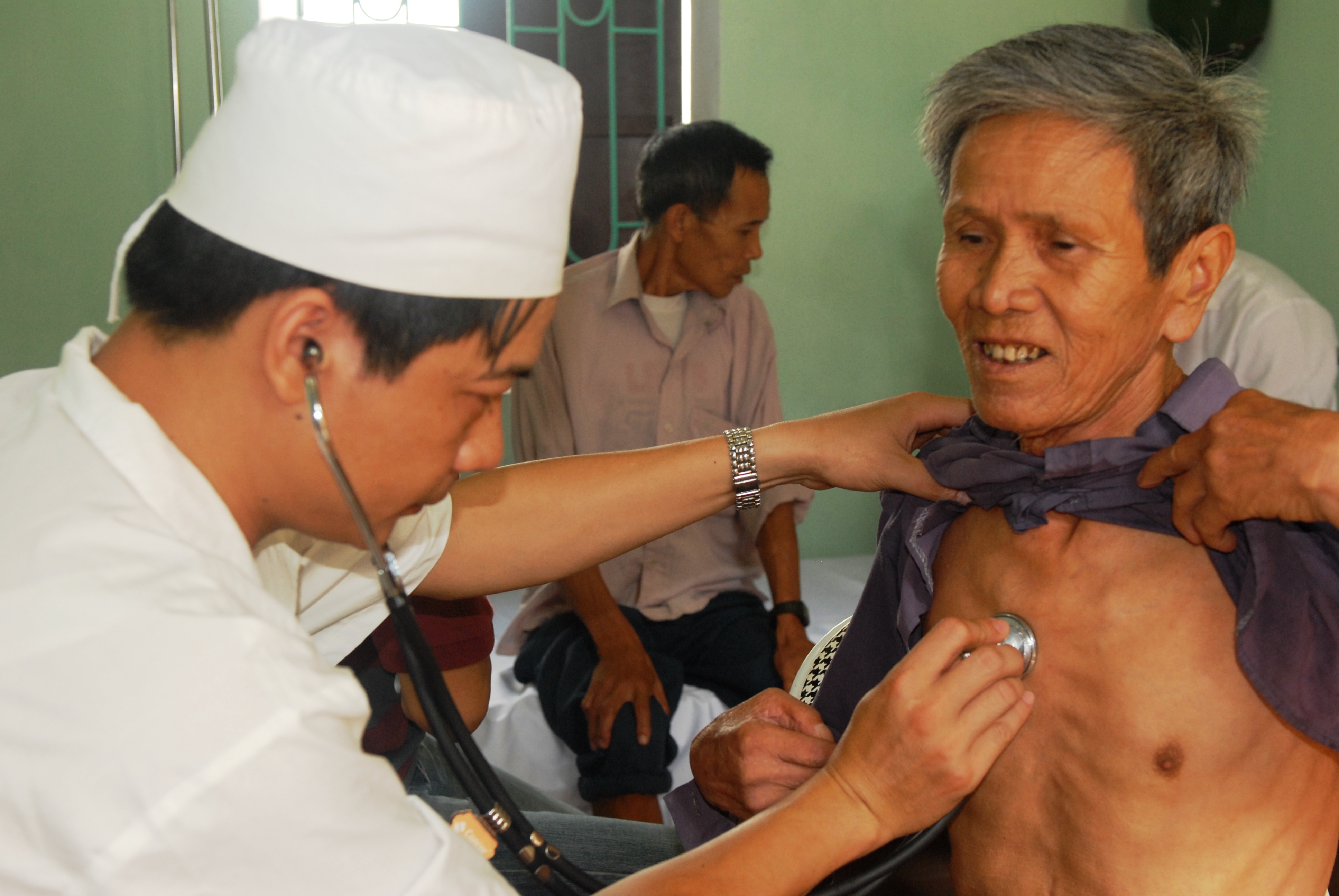
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a medical diagnosis, diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Question
A question is an utterance which serves as a request for information. Questions are sometimes distinguished from interrogatives, which are the grammar, grammatical forms, typically used to express them. Rhetorical questions, for instance, are interrogative in form but may not be considered wiktionary:bona fide, bona fide questions, as they are not expected to be answered. Questions come in a number of varieties. For instance; ''Polar questions'' are those such as the English language, English example "Is this a polar question?", which can be answered with yes and no, "yes" or "no". ''Alternative questions'' such as "Is this a polar question, or an alternative question?" present a list of possibilities to choose from. ''Open-ended question, Open questions'' such as "What kind of question is this?" allow many possible resolutions. Questions are widely studied in linguistics and philosophy of language. In the subfield of pragmatics, questions are regarded as illocutionary acts whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-examination
In law, cross-examination is the interrogation of a witness by one's opponent. It is preceded by direct examination (known as examination-in-chief in Law of the Republic of Ireland, Ireland, the Law of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, Australian legal system, Australia, Law of Canada, Canada, Law of South Africa, South Africa, Law of India, India and Law of Pakistan, Pakistan) and may be followed by a Redirect examination, redirect (known as re-examination in the aforementioned countries). A redirect examination, performed by the attorney or pro se individual who performed the direct examination, clarifies the witness' testimony provided during cross-examination including any subject matter raised during cross-examination but not discussed during direct examination. Recross examination addresses the witness' testimony discussed in redirect by the opponent. Depending on the judge's discretion, opponents are allowed multiple opportunities to redirect and recross examine witnesse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Examination
The direct examination or examination-in-chief is one stage in the process of adducing evidence from witnesses in a court of law. Direct examination is the questioning of a witness by the lawyer/side/party that called such witness in a trial. Direct examination is usually performed to elicit evidence Evidence for a proposition is what supports the proposition. It is usually understood as an indication that the proposition is truth, true. The exact definition and role of evidence vary across different fields. In epistemology, evidence is what J ... in support of facts which will satisfy a required element of a party's claim or defense. In direct examination, one is generally prohibited from asking leading questions. This prevents a lawyer from feeding answers to a favorable witness. An exception to this rule occurs if one side has called a witness, but it is either understood or becomes clear, that the witness is hostile to the calling lawyer's side of the controversy, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exam
An examination (exam or evaluation) or test is an educational assessment intended to measure a test-taker's knowledge, skill, aptitude, physical fitness, or classification in many other topics (e.g., beliefs). A test may be administered verbally, on paper, on a computer-adaptive testing, computer, or in a predetermined area that requires a test taker to demonstrate or perform a set of skills. Tests vary in style, rigor and requirements. There is no general consensus or invariable standard for test formats and difficulty. Often, the format and difficulty of the test is dependent upon the educational philosophy of the instructor, subject matter, class size, policy of the educational institution, and requirements of accreditation or governing bodies. A test may be administered formally or informally. An example of an informal test is a reading test administered by a parent to a child. A formal test might be a final examination administered by a teacher in a classroom or an IQ te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Service Entrance Examination
Civil service examinations are examinations implemented in various countries for recruitment and admission to the civil service. They are intended as a method to achieve an effective, rational public administration on a merit system for recruiting prospective politicians and public sector employees. The most ancient example of such exams were the imperial examinations of ancient China. Competitive exam Competitive examinations are tests where candidates are ranked according to their grades and/or percentile and then top rankers are selected. If the examination is open for ''n'' positions, then the first ''n'' candidates in ranks pass, the others are rejected. They are used as entrance examinations for university and college admissions such as the Joint Entrance Examination or to secondary schools. Types are civil service examinations, required for positions in the public sector; the U.S. Foreign Service Exam, and the United Nations Competitive Examination. Competitive ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Examination
The imperial examination was a civil service examination system in History of China#Imperial China, Imperial China administered for the purpose of selecting candidates for the Civil service#China, state bureaucracy. The concept of choosing bureaucrats by merit rather than by birth started Imperial examination in Chinese mythology, early in Chinese history, but using written examinations as a tool of selection started in earnest during the Sui dynasty (581–618), then into the Tang dynasty (618–907). The system became dominant during the Song dynasty (960–1279) and lasted for almost a millennium until its abolition during the late Qing reforms, late Qing dynasty reforms in 1905. The key sponsors for abolition were Yuan Shikai, Yin Chang and Zhang Zhidong. Aspects of the imperial examination still exist for entry into the civil service of both China and Taiwan. The exams served to ensure a common knowledge of writing, Chinese classics, and literary style among state officials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analysis
Analysis (: analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (384–322 BC), though ''analysis'' as a formal concept is a relatively recent development. The word comes from the Ancient Greek (''analysis'', "a breaking-up" or "an untying" from ''ana-'' "up, throughout" and ''lysis'' "a loosening"). From it also comes the word's plural, ''analyses''. As a formal concept, the method has variously been ascribed to René Descartes ('' Discourse on the Method''), and Galileo Galilei. It has also been ascribed to Isaac Newton, in the form of a practical method of physical discovery (which he did not name). The converse of analysis is synthesis: putting the pieces back together again in a new or different whole. Science and technology Chemistry The field of chemistry uses analysis in three ways: to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appraisal (other)
Appraisal may refer to: Decision-making * Appraisal (decision analysis), a decision method * Archival appraisal, process for determining which records need to be kept, and for how long * Project appraisal, comparing options to deliver an objective * Economic appraisal, an appraisal based on comparison of monetary equivalents Property valuation * Real estate appraisal, the practice of determining the value of real property * Business valuation, the process of determining the value of businesses * Art valuation, the process of determining the value of works of art * Domain appraisal, the act of evaluating the worth of a specific domain name * Archival appraisal, the appraisal of archival collections in libraries * Appraisal value, the value of a company based on a projection of future cash flow Other uses * Appraisal (discourse analysis), the ways that writers or speakers express approval or disapproval for things or ideas * Appraisal theory, a psychological theory of emotion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assessment (other)
Assessment may refer to: Healthcare * Health assessment, identifies needs of the patient and how those needs will be addressed *Nursing assessment, gathering information about a patient's physiological, psychological, sociological, and spiritual status *Psychiatric assessment, gathering information about a person in a psychiatric or mental health service * Psychological assessment, examination of a person's mental health by a professional such as a psychologist Other uses * ''Assessment'' (journal) (ASMNT), a psychology journal *Educational assessment, documenting knowledge, skills, aptitudes, and beliefs *Environmental impact assessment, assessment of environmental consequences of a plan * Library assessment, to learn about the needs of patrons *Risk assessment, determining value of risk related to a concrete situation and a recognized threat * Survey data collection, marketing assessments * Tax assessment, determining amounts to be paid or assessed for tax or insurance purposes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaluation
In common usage, evaluation is a systematic determination and assessment of a subject's merit, worth and significance, using criteria governed by a set of Standardization, standards. It can assist an organization, program, design, project or any other intervention or initiative to assess any aim, realizable concept/proposal, or any alternative, to help in decision-making; or to generate the degree of achievement or value in regard to the aim and Goal, objectives and results of any such action that has been completed. The primary purpose of evaluation, in addition to gaining insight into prior or existing initiatives, is to enable Human self-reflection, reflection and assist in the identification of future change. Evaluation is often used to characterize and appraise subjects of interest in a wide range of human enterprises, including the arts, criminal justice, foundation (charity), foundations, non-profit organizations, government, health care, and other human services. It is long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaluation (other)
Evaluation is the process of judging something or someone based on a set of standards. Evaluation may also refer to: Measurement or appraisal * Education: ** Educational assessment ** Competency evaluation (language), a means for teachers to determine the ability of their students ** Narrative evaluation, a form of performance measurement and feedback which can be used instead of grading * Competency evaluation (law), an assessment of the ability of a defendant to understand and rationally participate in a court process * Formation evaluation in petroleum exploration, used to determine the commercial-viability of a potential oil or gas field * Human resources: ** Evaluation (workplace), a tool employers use to review the performance of an employee ** Performance evaluation, a method by which the job performance of an employee is evaluate ** Evaluation (basketball), a statistical formula used to rank basketball players in some European leagues ** Evaluation camp, a program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |