|
Euphemia Of Münsterberg
Euphemia of Münsterberg (c. 1385 – 17 November 1447), also known as Euphemia, Countess of Oettingen, was a princess from the Münsterberg (Ziębice) branch of the Piast dynasty, by marriage Countess of Öttingen and sovereign Duchess of Münsterberg during 1435–1443. She was the third child and eldest daughter of Duke Bolko III of Münsterberg and Euphemia, daughter of Duke Bolesław of Bytom. Life In 1397 Euphemia married the widower Count Frederick III of Oettingen. They had nine children, five sons and four daughters. Perhaps under her influence, a German translation of the ''"Life of St. Hedwig of Andechs"'' with rich colors and illustrations was made, which remained in the Comital Library of Oettingen. After the death of her husband (23 January 1423), Euphemia returned to Münsterberg. After the death of her brother John in 1428, the Duchy of Ziębice was incorporated into the Bohemian Kingdom The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziębice
Ziębice () is a town in Ząbkowice Śląskie County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies on the Oława River, approximately east of Ząbkowice Śląskie and south of the regional capital Wrocław. It is the seat of the administrative district (gmina) called Gmina Ziębice. As of 2019, the town has a population of 8,708. History The area became part of the emerging Polish state under its first historic ruler Mieszko I in the 10th century. The town was first mentioned in 1234 under the Old Polish spelling ''Sambice''. This Slavic town was probably destroyed in 1241 during the Mongol invasion of Europe. According to records, a new town under German town law, called ''Munsterberck'' (1253) or ''Sambiz videlicet Munsterberg'' (1268). The town became home of a German-speaking population as the result of Ostsiedlung. As a result of the fragmentation of Poland, it formed part of the duchies of Silesia until 1290, Świdnica until 1322, and afterwards it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
Sigismund of Luxembourg (15 February 1368 – 9 December 1437) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1433 until his death in 1437. He was elected King of Germany (King of the Romans) in 1410, and was also King of Bohemia from 1419, as well as prince-elector of Margraviate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg (1378–1388 and 1411–1415). As the husband of Mary, Queen of Hungary, he was also King of Hungary and Croatia in union with Hungary, Croatia (''jure uxoris'') from 1387. He was the last male member of the House of Luxembourg. Sigismund was the son of Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor and his fourth wife Elizabeth of Pomerania. He married Mary, Queen of Hungary in 1385 and was crowned King of Hungary soon after. He fought to restore and maintain authority to the throne. Mary died in 1395, leaving Sigismund the sole ruler of Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary. In 1396, Sigismund led the Battle of Nicopolis, Crusade of Nicopolis but was decisively defeated by the Ottoman Empire. Afterwards, he founded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1380s Births
138 may refer to: *138 (number) *138 BC *AD 138 *138 (New Jersey bus) *138 Tolosa 138 Tolosa is a brightly coloured, stony background asteroid from the inner region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered by French astronomer Henri Joseph Perrotin on 19 May 1874, and named by the Latin and Occitan name ( and ) of the Frenc ..., a main-belt asteroid * Tatra 138, a heavy truck {{numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Silesia
The Duchy of Silesia (, ) with its capital at Wrocław was a medieval provincial duchy of Poland located in the region of Silesia. Soon after it was formed under the Piast dynasty in 1138, it fragmented into various Silesian duchies. In 1327, the remaining Duchy of Wrocław as well as most other duchies ruled by the Silesian Piasts passed under the suzerainty of the Kingdom of Bohemia as the Duchies of Silesia. The acquisition was completed when King Casimir III the Great of Poland renounced his rights to Silesia in the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin. Geography During the time of its establishment, the Silesian lands covered the basin of the upper and middle Oder river. In the south the Sudetes mountain range up to the Moravian Gate formed the border with the lands of Bohemia – including Kłodzko Land – and Moravia. After a more than century-long struggle, the boundary had just been determined by an 1137 agreement with the Bohemian duke Soběslav I. In the west Lower S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of King Casimir III the Great. Branches of the Piast dynasty continued to rule in the Duchy of Masovia (until 1526) and in the Duchies of Silesia until the last male Silesian Piast died in 1675. The Piasts intermarried with several noble lines of Europe, and possessed numerous titles, some within the Holy Roman Empire. The Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellonian kings ruling after the death of Casimir IV of Poland were also descended in the female line from Casimir III's daughter. Origin of the name The early dukes and kings of Poland are said to have regarded themselves as descendants of the semi-legendary Piast the Wheelwright (''Piast Kołodziej''), first mentioned in the ''Cronicae et gesta ducum sive pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William, Duke Of Opava
Duke William of Opava (; – 15 August 1452) was a member of Opava branch of the Bohemian Přemyslid dynasty. He was Duke of Opava from 1433 to 1452 and Duke of Münsterberg from 1443 to 1452. Life His parents were Przemko I, Duke of Opava (d. 1433) and his second wife, Catherine of Münsterberg (d. 1422). His father died in 1433, leaving five sons. The oldest brother, Wenceslaus II took up the guardianship for his younger half-brothers William, Ernest and Przemko II, while Wenceslaus's younger brother Nicholas IV styled himself Lord of Zlaté Hory. Although their father had stipulated in his will that they should rule the duchy jointly, the brothers divided their inheritance around 1435. William and Ernest received shares of Opava; the Duchy of Głubczyce was split off for Wenceslas. The youngest brother, Przemko II, was destined for an ecclesiastical career and did not receive a share of the duchy. The duchy was now so fragmented that the revenue did not cover the D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hynek Krušina Of Lichtenburg
Hynek Krušina of Lichtenburg (also: ''Henry Kruschina of Lichtenburg'', in ; 1392 – 4 March 1454, Kłodzko (, )) was a knight, Hussite commander and governor and lien holders of the County of Kladsko, the Duchy of Münsterberg and the city of Ząbkowice Śląskie (). Origin, family and possessions Hynek Krušina was a member of the Lichtenburg family, which in turn was a branch of the powerful Ronov dynasty. His father was John Krušina of Lichtenburg, who was a Royal Colonel and Chamberlain and Burgrave of the Duchy of Jawor. After his father died, Hynek was influenced by Čeněk of Wartenberg. Čeněk probably persuaded Hynek to participate in the Bohemian Diet of 1415, where he protested against the condemnation of Jan Hus at the Council of Constance. Hynek and his brothers Alexander (who died ) and Jan inherited his possessions of Opočno, Kumburk Castle and Albrechtice. As Alexander and Jan were still minors, Hynek acted as their guardian and regent. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chałupki, Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Chałupki is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kamieniec Ząbkowicki, within Ząbkowice Śląskie County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately south-east of Kamieniec Ząbkowicki, south-east of Ząbkowice Śląskie, and south of the regional capital Wrocław. References Villages in Ząbkowice Śląskie County {{ZąbkowiceŚląskie-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castellan
A castellan, or constable, was the governor of a castle in medieval Europe. Its surrounding territory was referred to as the castellany. The word stems from . A castellan was almost always male, but could occasionally be female, as when, in 1194, Beatrice of Bourbourg inherited her father's castellany of Bourbourg upon the death of her brother, Roger. Initial functions During the Migration Period after the fall of the Western Roman Empire (third to sixth century), foreign tribes entered Western Europe, causing strife. The answer to recurrent invasion was to create fortified areas which evolved into castles. Some military leaders gained control of several areas, each with a castle. The problem lay in exerting control and authority in each area when a leader could only be in one place at a time. To overcome this, they appointed castellans as their trusted vassals to manage a castle in exchange for obligations to the landlord, often a noble. In the 9th century, as fortification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
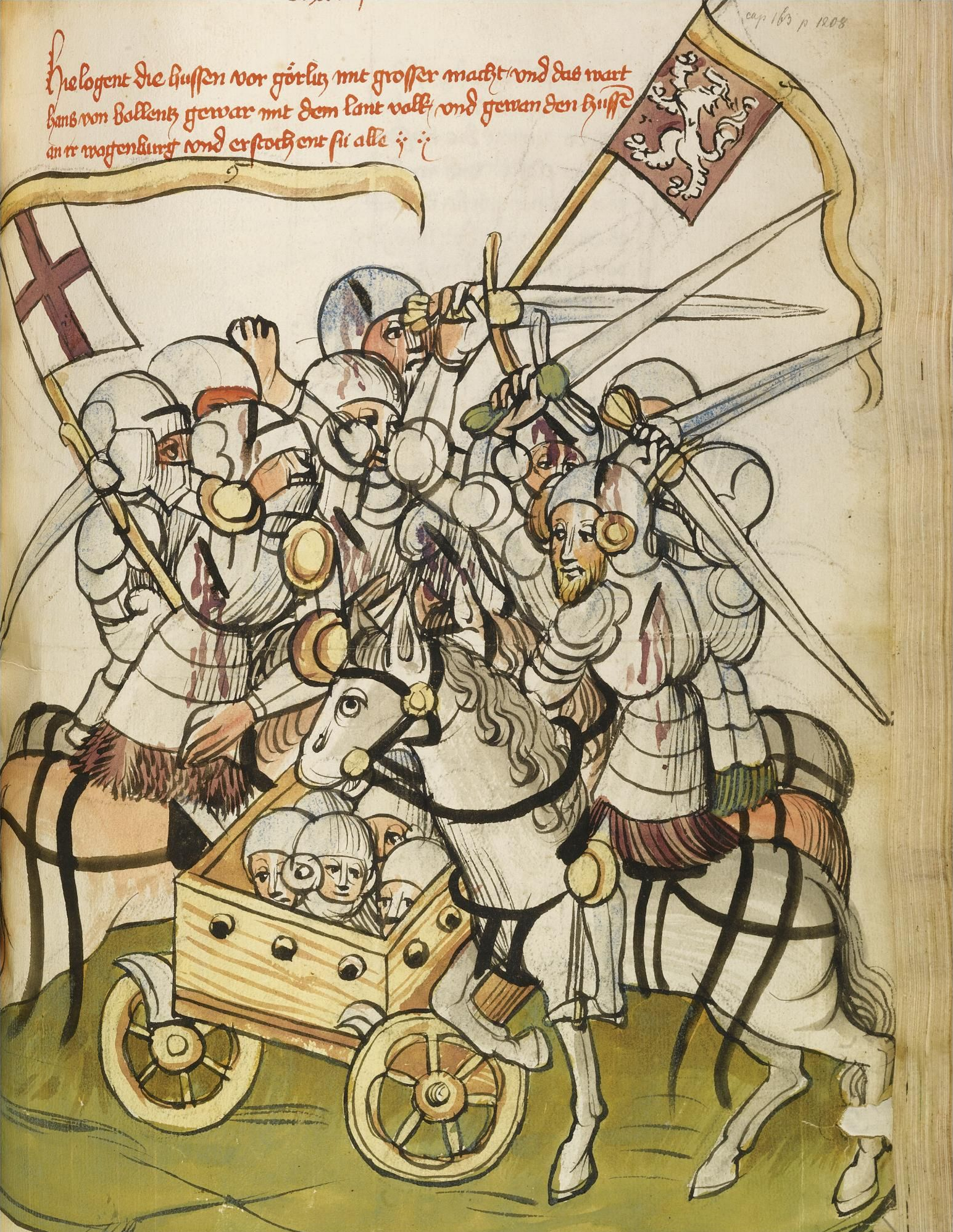
Hussite
file:Hussitenkriege.tif, upright=1.2, Battle between Hussites (left) and Crusades#Campaigns against heretics and schismatics, Catholic crusaders in the 15th century file:The Bohemian Realm during the Hussite Wars.png, upright=1.2, The Lands of the Bohemian Crown during the Hussite Wars. The movement began during the Renaissance in Prague and quickly spread south and then through the rest of the Kingdom of Bohemia. Eventually, it expanded into the remaining domains of the Bohemian Crown as well. The Hussites (Czech language, Czech: ''Husité'' or ''Kališníci'', "Chalice People"; Latin: ''Hussitae'') were a Czech Proto-Protestantism, proto-Protestant Christian movement influenced by both the Byzantine Rite and John Wycliffe that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus (floruit, fl. 1401–1415), a part of the Bohemian Reformation. The Czech lands had originally been Christianized by Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Greek missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius, who introduced the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henryków, Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Henryków is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Ziębice, within Ząbkowice Śląskie County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately north of Ziębice, north-east of Ząbkowice Śląskie, and south of the regional capital Wrocław. The village contains the landmark Cistercian Monastery Complex. A Latin chronicle, the Book of Henryków, compiled at Henryków abbey in the 13th century contains the first known sentence written in the Polish language Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spo .... There is a train station in Henryków. Gallery Henrykow former Cistercian abbey 2019 P03 aerial view.jpg, Aerial view of the Cistercian Monastery Henrykow june 2014 040.JPG, Monument to the Book of Henryków Henrykow - budynek b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guilder
Guilder is the English translation of the Dutch and German ''gulden'', originally shortened from Middle High German ''guldin pfenninc'' (" gold penny"). This was the term that became current in the southern and western parts of the Holy Roman Empire for the Fiorino d'oro (introduced in 1252 in the Republic of Florence). Hence, the name has often been interchangeable with ''florin'' (currency sign ''ƒ'' or ''fl.''). The guilder is also the name of several currencies used in Europe and the former colonies of the Dutch Empire. Gold guilder The guilder or gulden was the name of several gold coins used during the Holy Roman Empire. It first referred to the Italian gold florin, introduced in the 13th century. It then referred to the Rhenish gulden (''florenus Rheni'') issued by several states of the Holy Roman Empire from the 14th century. The Rhenish gulden was issued by Trier, Cologne and Mainz in the 14th and 15th centuries. Basel minted its own ''Apfelgulden'' between 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |