|
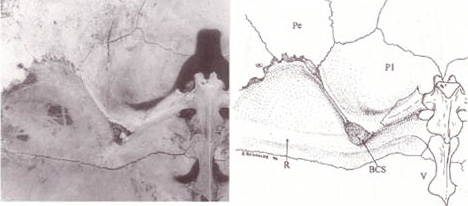
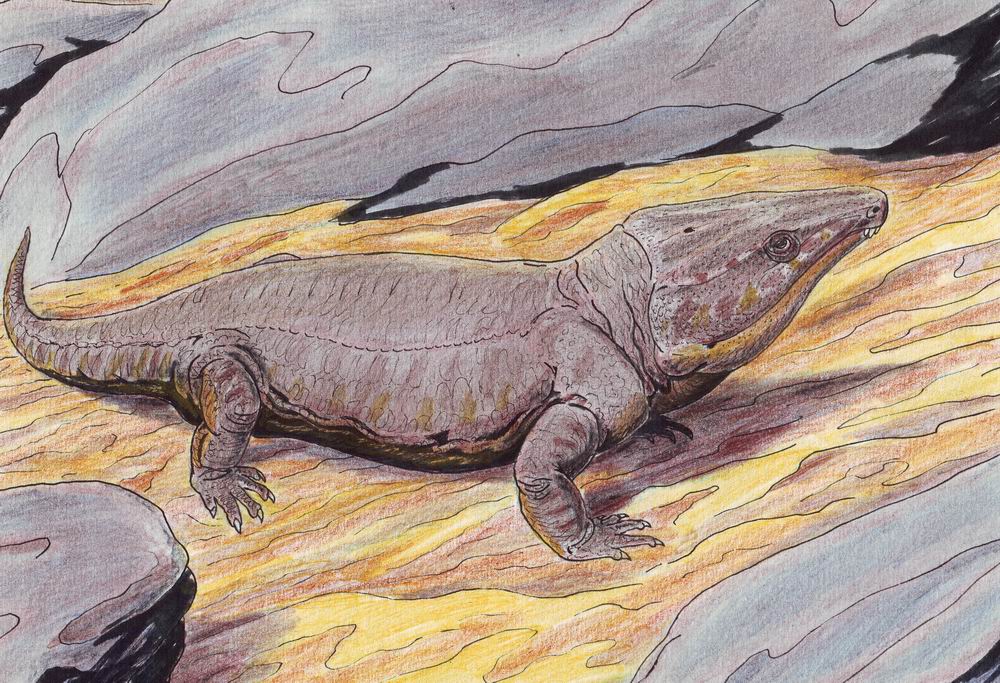
Eunotosaurus
''Eunotosaurus'' (''Latin (language), Latin'': Stout-backed lizard) is an extinct genus of amniote, possibly a close relative of turtles. ''Eunotosaurus'' lived in the late Middle Permian (Capitanian stage) and fossils can be found in the Karoo Supergroup of South Africa and Malawi. ''Eunotosaurus'' resided in the swamps of what is now southern Africa. Its ribs were wide and flat, forming broad plates similar to a primitive turtle shell, and the vertebrae were nearly identical to those of some turtles. Accordingly, it is often considered as a possible transitional fossil between turtles and their prehistoric ancestors. However, it is possible that these turtle-like features evolved independently of the same features in turtles, since other anatomical studies and phylogenetic analyses suggest that ''Eunotosaurus'' may instead have been a parareptile, an early-diverging neodiapsid unrelated to turtles, or a synapsid. Description ''Eunotosaurus'' reached up to in total body length. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Turtle Shell
The turtle shell is a shield for the ventral and dorsal parts of turtles (the Order (biology), order Testudines), completely enclosing all the turtle's vital organs and in some cases even the head. It is constructed of modified bony elements such as the ribs, parts of the pelvis and other bones found in most reptiles. The bone of the shell consists of both skeletal and dermal bone, showing that the complete enclosure of the shell likely evolved by including dermal armor into the rib cage. The turtle's shell is an important study, not just because of the apparent protection it provides for the animal but also as an identification tool, in particular with fossils, as the shell is one of the likely parts of a turtle to survive fossilization. Hence understanding the shell structure in living species provides comparable material with fossils. The shell of the hawksbill turtle, among other species, has been used as a material for a wide range of small decorative and practical items sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Captorhinidae
Captorhinidae is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive Reptile, reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea. Description Captorhinids are a clade of small to very large lizard-like animals that date from the Late Carboniferous through the Permian. Their skulls were much stronger than those of their relatives, the protorothyridids, and had teeth that were better able to deal with tough plant material. The postcranial skeleton is similar to those of seymouriamorphs and diadectomorphs; these animals were grouped together with the captorhinids in the order Cotylosauria as the first reptiles in the early 20th century, but are now usually regarded as Stem group, stem-amniotes no closer to reptiles than to mammals. Captorhinids have broad, robust skulls that are generally triangular in shape when seen in dorsal view. The premaxillae are characteristically downturned. The largest captorh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cotylosaur
Captorhinidae is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea. Description Captorhinids are a clade of small to very large lizard-like animals that date from the Late Carboniferous through the Permian. Their skulls were much stronger than those of their relatives, the protorothyridids, and had teeth that were better able to deal with tough plant material. The postcranial skeleton is similar to those of seymouriamorphs and diadectomorphs; these animals were grouped together with the captorhinids in the order Cotylosauria as the first reptiles in the early 20th century, but are now usually regarded as stem-amniotes no closer to reptiles than to mammals. Captorhinids have broad, robust skulls that are generally triangular in shape when seen in dorsal view. The premaxillae are characteristically downturned. The largest captorhinid, the herbivor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neodiapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The earliest traditionally identified diapsids, the Araeoscelidia, araeoscelidians, appeared about three hundred million years ago during the late Carboniferous period. All diapsids other than the most primitive ones in the clade Araeoscelidia are often placed into the clade Neodiapsida. The diapsids are extremely diverse, and include birds and all modern reptile groups, including turtles, which were historically thought to lie outside the group. All modern reptiles and birds are placed within the neodiapsid subclade Sauria. Although some diapsids have lost either one hole (lizards), or both holes (snakes and turtles), or have a heavily restructured skull (modern birds), they are still scientific classification, classified as diapsids based on their ancestry. At least 17,084 species of diapsid animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tetrapoda, stem tetrapod ancestors during the Carboniferous geologic period, period. Amniota is defined as the smallest crown clade containing humans, the Greek tortoise, and the Nile crocodile. Amniotes are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the anamniote, non-amniote lissamphibians (frogs/toads, salamanders/newts and caecilians) — by: the development of three fetal membranes, extraembryonic membranes (amnion for embryonic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage); thicker and keratinized skin; rib, costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage); the presence of adrenal cortex, adrenocortical and chromaffin cell, chromaffin tissues as adrenal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parareptile
Parareptilia ("near-reptiles") is an extinct group of Basal (phylogenetics), basal Sauropsida, sauropsids ("Reptile, reptiles"), traditionally considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous, Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian, Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first Bipedalism, bipedal reptiles (Bolosauridae, bolosaurids such as ''Eudibamus''), the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems (Nycteroleteridae, nycteroleterids and others), and the first large herbivorous reptiles (the pareiasaurs). The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic, Triassic period were the Procolophonoidea, procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Turtle
Turtles are reptiles of the order (biology), order Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other Amniote, amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed Turtle shell#Carapace, carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scale (anatomy), scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bones deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Supratemporal Bone
The supratemporal bone is a paired cranial bone present in many tetrapods and tetrapodomorph fish. It is part of the temporal region (the portion of the skull roof behind the eyes), usually lying medial (inwards) relative to the squamosal and lateral (outwards) relative to the parietal and/or postparietal. It may also contact the postorbital or intertemporal (which lie forwards), or tabular (which lies backwards), when those bones are present. The supratemporal is a common component of the skull in many extinct amphibians, though it is apparently absent in the lightweight skulls of living lissamphibians (frogs and salamanders). Embryological studies of salamanders suggests that the supratemporal fuses with the squamosal in early development. A separate supratemporal was retained by early synapsids and reptiles, but was strongly reduced in many groups. Squamates (lizards and snakes) still possess a small supratemporal, though archosaurs (crocodilians and birds) and mammals lack i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian is also known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sharpey's Fibers
Sharpey's fibres (bone fibres, or perforating fibres) are a matrix of connective tissue consisting of bundles of strong predominantly type I collagen fibres connecting periosteum to bone. They are part of the outer fibrous layer of periosteum, entering into the outer circumferential and interstitial lamellae of bone tissue. Sharpey's fibres also attach muscle to the periosteum of bone by merging with the fibrous periosteum and underlying bone as well. A good example is the attachment of the rotator cuff muscles to the blade of the scapula. In the teeth, Sharpey's fibres are the terminal ends of principal fibres (of the periodontal ligament) that insert into the cementum and into the periosteum of the alveolar bone. A study on rats suggests that the three-dimensional structure of Sharpey's fibres intensifies the continuity between the periodontal ligament fibre and the alveolar bone (tooth socket), and acts as a buffer medium against stress. Sharpey's fibres in the primary acell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intercostal Muscle
The intercostal muscles comprise many different groups of muscle Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...s that run between the ribs, and help form and move the chest wall. The intercostal muscles are mainly involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing by helping expand and shrink the size of the chest cavity. Structure There are three principal layers: # External intercostal muscles also known as intercostalis externus aid in quiet and forced inhalation. They originate on ribs 1–11 and have their insertion on ribs 2–12. The external intercostals are responsible for the elevation of the ribs and bending them more open, thus expanding the transverse dimensions of the thoracic cavity. The muscle fibers are directed downwards, forwards and medially in the anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |