|
Errantia
Errantia is a diverse group of marine life, marine polychaete worms in the phylum Annelida. Traditionally a subclass (biology), subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, it is currently regarded as a monophyletic group within the larger Pleistoannelida, composed of Errantia and Sedentaria. These worms are found worldwide in marine environments and brackish water. Phylogeny The phylogeny of polychaetes is slowly being resolved. Errantia and Sedentaria are the two biggest clades of polychaetes, and together they compose clade Pleistoannelida. Two groups are nested within Errantia: Aciculata (Eunicida + Phyllodocida) and Protodriliformia (progenesis, small meiofaunal worms such as the Protodrilida). Historically, the order Amphinomida was part of this subclass. However, phylogenetic analyses place Amphinomida inside a basal clade with Sipunculida and ''Lobatocerebrum'', and this clade is the sister group to Pleistoannelida. Some taxon, taxa, such as Spintheridae and Myzostomida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistoannelida
Pleistoannelida is a group of annelid worms that comprises the vast majority of the diversity in phylum Annelida. Discovered through phylogenetic analyses, it is the largest clade of annelids, comprised by the last common ancestor of the highly diverse sister groups Errantia and Sedentaria (Clitellata and related polychaetes) and all the descendants of that ancestor. Most groups in the clade find their ancestors within the Cambrian explosion when Annelid diversity expanded dramatically. The Pleistoannelida clade covers a variety of traits. However, the evolution of simple to complex eyes, developed papillae for burrowing, and for some specialized radioles for feeding can be seen universally across every species. New findings have discovered the range of Annelid diversity have led to uncertainty if groups with developed ancestral traits should remain within the clade. Furthermore, there's been a lack of recently discovered Annelid traits being used in the categorization of groups wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelida
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The annelids are Symmetry in biology, bilaterally symmetrical, Triploblasty, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have Parapodium, parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistics, Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Siboglinidae, Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedentaria
Sedentaria is a diverse clade of annelid worms. It is traditionally treated as a subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, but it is also a monophyletic group uniting several polychaetes and the monophyletic class Clitellata. It is the sister group of Errantia. Sedentaria are mainly found within marine environments that have low oxygen levels and are specially adapted to these low oxygen environments by increasing gill surface area and having high-affinity respiratory proteins. Furthermore, they go through a process of metabolic depression which lowers their energy use so that they can inhibit these low oxygen zones . Phylogeny The phylogeny of polychaetes is slowly being resolved. Sedentaria and Errantia are the two biggest clades of polychaetes, and together they compose clade Pleistoannelida. Sedentaria's most basal clade is Orbiniida. Other groups that are nested within Sedentaria are: Clitellata, the Sabellida/ Spionida clade, Opheliida, Echiura, Cirratulifor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protodriliformia
Protodriliformia is a clade of small marine polychaetes, comprised by the groups of meiofaunal interstitial worms Protodrilida and Polygordiidae, formerly considered " archiannelids". It is the most basal clade of Errantia. Evolutionary history Phylogenetic analysis of annelids has found Protodriliformia to be the earliest diverging clade of Errantia. At the same time, the other half of " archiannelid" worms, Orbiniida, was found to be the earliest diverging clade of Sedentaria. The convergence Convergence may refer to: Arts and media Literature *''Convergence'' (book series), edited by Ruth Nanda Anshen *Convergence (comics), "Convergence" (comics), two separate story lines published by DC Comics: **A four-part crossover storyline that ... between these two groups occurred through progenesis and miniaturization, as a way to adapt to the marine interstitial ecosystem between sand grains (i.e. interstitium). This means that the larval or juvenile stages of a larger pleist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eunicidae
Eunicidae is a family of marine polychaetes (bristle worms). The family comprises marine annelids distributed in diverse benthic habitats across Oceania, Europe, South America, North America, Asia and Africa. The Eunicid anatomy typically consists of a pair of appendages near the mouth (mandibles) and complex sets of muscular structures on the head (maxillae) in an eversible pharynx. One of the most conspicuous of the eunicids is the giant, dark-purple, iridescent " Bobbit worm" (''Eunice aphroditois''), a bristle worm found at low tide under boulders on southern Australian shores. Its robust, muscular body can be as long as 2 m. Eunicidae jaws are known from as far back as Ordovician sediments. Cultural tradition surrounds Palola worm (''Palola viridis'') reproductive cycles in the South Pacific Islands. Eunicidae are economically valuable as bait in both recreational and commercial fishing. Commercial bait-farming of Eunicidae can have adverse ecological impacts. Bait-fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm (''Arenicola marina'') and the Alitta virens, sandworm or Alitta succinea, clam worm ''Alitta''. Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vents. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe Nereus (underwater vehicle), ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep, the deepest known spot in the Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphinomida
Amphinomida is an order of marine polychaetes. The order contains two families: * ''Amphinomidae Amphinomidae, also known as the fireworms, bristle worms or sea mice, are a family (biology), family of marine polychaetes, many species of which bear chaetae mineralized with carbonate. The best-known amphinomids are the fireworms, which can ca ...'' Lamarck, 1818 * '' Euphrosinidae'' Williams, 1852 The fossil record of this taxon (not abundant in annelids overall because this taxon lacks a mineralized skeleton) includes ''Palaeocampa anthrax'' Meek & Worthen, 1865 from the Late Carboniferous site of Montceau-les-Mines. References Errantia Annelid orders {{annelid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eunicida
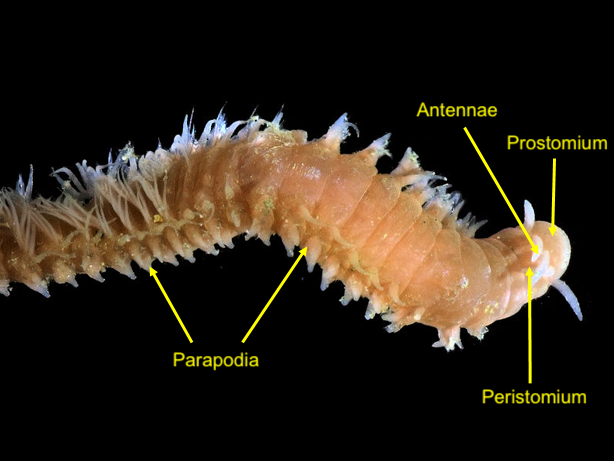
Eunicida is an order of polychaete worms. Characteristics Members of this order have an elongated, segmented body and a distinct head, normally with a separate peristomium and prostomium. Many, but not all, live in tubes which vary from a mucous sheath to a tough, horny casing. The palps vary from globular to cylindrical and there are from 0 to 7 antennae, usually smooth but occasionally jointed. There is a muscular pharynx with a dorsal pair of mandibles and a set of ventral, toothed, maxillary plates. Some species have tentacular cirri and all have unbranched parapodia. In some species, dorsal cirri, branchiae, ventral cirri and chaetae occur, but not in others. Natural History Museum. Retrieved 2012-01-17. Fossil record The |
Phyllodocida
Phyllodocida is an order of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata. These worms are mostly marine, though some are found in brackish water. Most are active benthic creatures, moving over the surface or burrowing in sediments, or living in cracks and crevices in bedrock. A few construct tubes in which they live and some are pelagic, swimming through the water column. There are estimated to be more than 4,600 accepted species in the order. Characteristics Phyllodocida are segmented worms and range in size from a few millimetres long to over a metre. Each segment bears a pair of paddle-like parapodia. The prostomium generally has one or two pairs of eyes, a dorsal pair of antennae, a ventral pair of sensory palps and a pair of organs on the neck. The peristomium is a ring, often hidden dorsally by the prostomium and the first segment. There is a muscular proboscis with one or more pairs of jaws. The next few segments tend to differ from those further back in having enlarged d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrosinidae
The Euphrosinidae are a family of polychaete worms. The name is from Greek ''Euphrosyne'', meaning merriment; she was one of the three Graces. Clade In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ... Species ''Euphrosinidae'' contains the following genera *'' Euphrosine'' Lamarck, 1818 (many species) *'' Euphrosinella'' Detinova, 1985 (3 species) *'' Euphrosinopsis'' Kudenov, 1993 (5 species). *'' Palmyreuphrosyne'' Fauvel, 1913 (2 species) Notes References Errantia Annelid families {{annelid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spintheridae
Spintheridae is a family of marine polychaete worms with a single genus, ''Spinther'', containing these species: * '' Spinther alaskensis'' Hartman, 1948 * '' Spinther arcticus'' (M. Sars, 1851) (includes '' Spinther miniaceus'' Grube, 1860) *'' Spinther australiensis'' Augener, 1913 * '' Spinther citrinus'' (Stimpson, 1854) *'' Spinther ericinus'' Yamamoto & Imajima, 1985 *'' Spinther hystrix'' Uschakov, 1950 * '' Spinther japonicus'' Imajima and Hartman, 1964 * '' Spinther oniscoides'' Johnston, 1845 *'' Spinther sagamiensis'' Imajima, 2003 *'' Spinther usarpia'' Hartman, 1967 * '' Spinther vegae'' Augener, 1928 (includes '' Spinther wireni'' Hartman, 1948) The animal lives as a symbiont on sponges. Johnston's paper does not explain the choice of the name, but ancient Greek σπινθήρ means "spark." In images of the living animal, it appears to be surrounded by a cloud of pinpoints of light. References Polychaetes Taxa named by George Johnston (naturalist) {{an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |