|
Erik Stensiö
Prof Erik Helge Osvald Stensiö HFRSE (2 October 1891 – 11 January 1984), né Andersson, was an influential Swedish paleozoologist and founder of the so-called "Stockholm School" of vertebrate paleontology. He later took his new surname, Stensiö, from his place of origin and is occasionally referred to with both names (as Erik Andersson Stensiö, Erik A. Stensiö or Erik A:son Stensiö) Life Erik Helge Oswald Andersson, as his original name was, was born in the village of Stensjö by in Döderhult parish in Kalmar County, the son of Johan Fredrik Andersson (d.1907), a farmer, and his wife, Otilia Maria Erlandson (d.1940). He was educated at Linköping Gymnasium. He then studied science at the University of Uppsala, graduating BSc in 1912. He received his Ph.D. and a docentship in paleontology from Uppsala University in 1921 and became professor and keeper at the Zoopaleontological (later called the Paleozoological) department of the Swedish Museum of Natural History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CREDENTIAL
A credential is a piece of any document that details a qualification, competence, or authority issued to an individual by a third party with a relevant or ''de facto'' authority or assumed competence to do so. Examples of credentials include academic diplomas, academic degrees, Professional certification, certifications, security clearances, Identity document, identification documents, badges, passwords, user names, key (lock), keys, power of attorney, powers of attorney, and so on. Sometimes publications, such as scientific papers or books, may be viewed as similar to credentials by some people, especially if the publication was peer reviewed or made in a well-known Academic journal, journal or reputable publisher. Types and documentation of credentials A person holding a credential is usually given documentation or secret knowledge (''e.g.,'' a password or key) as proof of the credential. Sometimes this proof (or a copy of it) is held by a third, trusted party. While in some c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and Literature, letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This society received a royal charter in 1783, allowing for its expansion. Elections Around 50 new fellows are elected each year in March. there are around 1,650 Fellows, including 71 Honorary Fellows and 76 Corresponding Fellows. Fellows are entitled to use the post-nominal letters FRSE, Honorary Fellows HonFRSE, and Corresponding Fellows CorrFRSE. Disciplines The Fellowship is split into four broad sectors, covering the full range of physical and life sciences, arts, humanities, social sciences, education, professions, industry, business and public life. A: Life sciences * A1: Biomedical and cognitive sciences * A2: Clinical sciences * A3: Organismal and environmental biology * A4: Cell and molecular biology B: Physical, enginee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitzbergen
Svalbard ( , ), previously known as Spitsbergen or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago that lies at the convergence of the Arctic Ocean with the Atlantic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it lies about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen (37,673 km2), followed in size by Nordaustlandet (14,443 km2), (5,073 km2), and Barentsøya (1,288 km2). Bjørnøya or Bear Island (178 km2) is the most southerly island in the territory, situated some 147 km south of Spitsbergen. Other small islands in the group include Hopen to the southeast of Edgeøya, Kongsøya and Svenskøya in the east, and Kvitøya to the northeast. The largest settlement is Longyearbyen, situated in Isfjorden on the west coast of Spitsbergen. Whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries used the islands as a base; subsequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the Division (taxonomy), division Selachii and are the sister group to the Batoidea, Batomorphi (Batoidea, rays and skate (fish), skates). Some sources extend the term "shark" as an informal category including Extinction, extinct members of Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) with a shark-like morphology, such as hybodonts. Shark-like chondrichthyans such as ''Cladoselache'' and ''Doliodus'' first appeared in the Devonian Period (419–359 million years), though some fossilized chondrichthyan-like scales are as old as the Ordovician, Late Ordovician (458–444 million years ago). The earliest confirmed modern sharks (Selachii) are known from the Early Jurassic around , with the oldest known member being ''Agaleus'', though records of true shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderm
Placoderms (from Ancient Greek πλάξ [''plax'', ''plakos''] 'Plate (animal anatomy), plate' and δέρμα [''derma''] 'skin') are vertebrate animals of the class (biology), class Placodermi, an extinct group of prehistoric fish known from Paleozoic fossils during the Silurian and the Devonian geological period, periods. While their endoskeletons are mainly cartilaginous, their head and thorax were covered by articulated armour (zoology), armoured plates (hence the name), and the rest of the body was scale (zoology), scaled or naked depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish (their fish jaw, jaws likely Evolution, evolved from the first pair of gill arches), as well as the first vertebrates to have true tooth, teeth. They were also the first fish clade to develop pelvic fins, the second set of paired fins and the homology (biology), homologous precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods. 380-million-year-old fossils of three other genera, ''Incisoscutum'', ''M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Museum Of Natural History
The Swedish Museum of Natural History (), in Stockholm, is one of two major museums of natural history in Sweden, the other one being located in Gothenburg. The museum was founded in 1819 by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, but goes back to the collections acquired mostly through donations by the academy since its foundation in 1739. These collections had first been made available to the public in 1786. The museum was separated from the Academy in 1965. One of the keepers of the collections of the academy during its earlier history was Anders Sparrman, a student of Carl Linnaeus and participant in the voyages of Captain James Cook. Another important name in the history of the museum is the zoologist, paleontologist and archaeologist Sven Nilsson, who brought the previously disorganised zoological collections of the museum into order during his time as keeper (1828–1831) before returning to Lund as professor. The present buildings for the museum in Frescati, Stockho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala University
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation. Initially founded in the 15th century, the university rose to significance during the rise of Swedish Empire, Sweden as a great power at the end of the 16th century and was then given relative financial stability with a large donation from Monarchy of Sweden, King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus in the early 17th century. Uppsala also has an important historical place in Swedish national culture, and national identity, identity for the Swedish establishment: in historiography, religion, literature, politics, and music. Many aspects of Swedish academic culture in general, such as the white student cap, originated in Uppsala. It shares some peculiarities, such as the student nation system, with Lund University and the University of Helsink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Docent
The term "docent" is derived from the Latin word , which is the third-person plural present active indicative of ('to teach, to lecture'). Becoming a docent is often referred to as habilitation or doctor of science and is an academic qualification that shows that the holder is qualified to be employed at the level of associate or full professor. The title of "docent" is conferred by some European universities to denote a specific academic appointment within a set structure of academic ranks at or below the full professor rank, similar to a British readership, a French (MCF), and equal to or above the title of ''assistant professor''. Docent is the highest academic title in several countries, and the qualifying criteria are research output that corresponds to 3–5 doctoral dissertations, supervision of PhD students, and experience in teaching at the undergraduate and graduate level. Docent is also used at some (mainly German) universities generically for a person who h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Uppsala
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation. Initially founded in the 15th century, the university rose to significance during the rise of Sweden as a great power at the end of the 16th century and was then given relative financial stability with a large donation from King Gustavus Adolphus in the early 17th century. Uppsala also has an important historical place in Swedish national culture, and identity for the Swedish establishment: in historiography, religion, literature, politics, and music. Many aspects of Swedish academic culture in general, such as the white student cap, originated in Uppsala. It shares some peculiarities, such as the student nation system, with Lund University and the University of Helsinki. Uppsala belongs to the Coimbra Group of European universities and to the Guild of European Research-Intensive Universities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linköping
Linköping ( , ) is a city in southern Sweden, with around 167,000 inhabitants as of 2024. It is the seat of Linköping Municipality and the capital of Östergötland County. Linköping is also the episcopal see of the Diocese of Linköping (Church of Sweden) and is well known for its cathedral. Linköping is the center of an old cultural region and celebrated its 700th anniversary in 1987. Dominating the city's skyline from afar is the steeple of Linköping Cathedral, the cathedral (). Nowadays, Linköping is known for its Linköping University, university and its High tech, high-technology industry. Linköping wants to create a sustainable development of the city and therefore plans to become a Carbon neutrality, carbon-neutral community by 2025. Located on the Östergötland Plain, Linköping is closely linked to Norrköping, roughly to the east, near the sea. History The city is possibly named after the ''Lionga thing, Lionga ting'' assembly which according to Medieval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
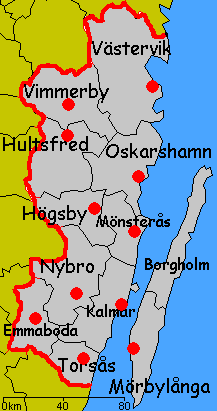
Kalmar County
Kalmar County () is a Counties of Sweden, county or ''län'' in southern Sweden. It borders the counties of Kronoberg County, Kronoberg, Jönköping County, Jönköping, Blekinge County, Blekinge and Östergötland County, Östergötland. To the east in the Baltic Sea is the island Gotland County, Gotland. The counties are mainly administrative units. Geographically Kalmar County covers the eastern part in the Småland province, and the entire island of Öland. Culture Much of Öland's present day landscape known as the Stora Alvaret has been designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. This southern part of Öland is known for a large number of rare species; early Paleolithic settlement at Alby, Öland, Alby; other prehistoric remains such as the Gettlinge Gravefield and Eketorp Fortress; and the Ottenby Nature Preserve. Administration Kalmar County was integrated with Kronoberg County until 1672. Blekinge County, Blekinge was a part of Kalmar County between 1680 and 168 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |