|
Erich Hückel
Erich Armand Arthur Joseph Hückel (August 9, 1896, Berlin – February 16, 1980, Marburg) was a German physicist and physical chemist. He is known for two major contributions: *The Debye–Hückel theory of electrolytic solutions *The Hückel method of approximate molecular orbital (MO) calculations on π electron systems. Hückel was born in the Charlottenburg suburb of Berlin. He studied physics and mathematics from 1914 to 1921 at the University of Göttingen. On receiving his doctorate, he became an assistant at Göttingen, but soon became an assistant to Peter Debye at Zürich. It was there that he and Debye developed their theory (the Debye–Hückel theory, in 1923) of electrolytic solutions, elucidating the behavior of strong electrolytes by considering interionic forces, in order to account for their electrical conductivity and their thermodynamic activity coefficients. After spending 1928 and 1929 in England and Denmark, working briefly with Niels Bohr, Hück ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, most populous city, as measured by population within city limits having gained this status after the United Kingdom's, and thus London's, Brexit, departure from the European Union. Simultaneously, the city is one of the states of Germany, and is the List of German states by area, third smallest state in the country in terms of area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of Brandenburg, and Brandenburg's capital Potsdam is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.5 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary ( macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Academy Of Quantum Molecular Science
The International Academy of Quantum Molecular Science (IAQMS) is an international scientific learned society covering all applications of quantum theory to chemistry and chemical physics. It was created in Menton in 1967. The founding members were Raymond Daudel, Per-Olov Löwdin, Robert G. Parr, John Pople and Bernard Pullman. Its foundation was supported by Louis de Broglie. Originally the Academy had 25 regular members under 65 years of age. This was later raised to 30, and then to 35. There is no limit on the number of members over 65 years of age. The members are "chosen among the scientists of all countries who have distinguished themselves by the value of their scientific work, their role of pioneer or leader of a school in the broad field of quantum chemistry, i.e. the application of quantum mechanics to the study of molecules and macromolecules". The Academy presently consists of 90 members (as of 2006). The Academy organizes the International Congress of Quantum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Marburg
The Philipps University of Marburg (german: Philipps-Universität Marburg) was founded in 1527 by Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse, which makes it one of Germany's oldest universities and the oldest still operating Protestant university in the world. It is now a public university of the state of Hesse, without religious affiliation. The University of Marburg has about 23,500 students and 7,500 employees and is located in Marburg, a town of 76,000 inhabitants, with university buildings dotted in or around the town centre. About 14 per cent of the students are international, the highest percentage in Hesse. It offers an International summer university programme and offers student exchanges through the Erasmus programme. History In 1609, the University of Marburg established the world's first professorship in chemistry. In 2012 it opened the first German interactive chemistry museum, called '. Its experimental course programme is aimed at encouraging young people to pursue careers in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the Swabian Jura and the Black Forest. Stuttgart has a population of 635,911, making it the sixth largest city in Germany. 2.8 million people live in the city's administrative region and 5.3 million people in its metropolitan area, making it the fourth largest metropolitan area in Germany. The city and metropolitan area are consistently ranked among the top 20 European metropolitan areas by GDP; Mercer listed Stuttgart as 21st on its 2015 list of cities by quality of living; innovation agency 2thinknow ranked the city 24th globally out of 442 cities in its Innovation Cities Index; and the Globalization and World Cities Research Network ranked the city as a Beta-status global city in their 2020 survey. Stuttgart was one of the host cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Stuttgart
The University of Stuttgart (german: Universität Stuttgart) is a leading research university located in Stuttgart, Germany. It was founded in 1829 and is organized into 10 faculties. It is one of the oldest technical universities in Germany with highly ranked programs in civil, mechanical, industrial and electrical engineering, among others. It is a member of TU9, an incorporated society of the largest and most notable German institutes of technology. The university is especially known for its reputation in the fields of advanced automotive engineering, efficient industrial and automated manufacturing, process engineering, aerospace engineering and activity-based costing. History From 1770 to 1794, the Karlsschule was the first university in Stuttgart. Located in Stuttgart-Hohenheim, it has since 1818 been the University of Hohenheim and is not related to the University of Stuttgart, except for some joint activities. What is now the University of Stuttgart was founde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niels Bohr
Niels Henrik David Bohr (; 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research. Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. He conceived the principle of complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a wave or a stream of particles. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philosophy. Bohr founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
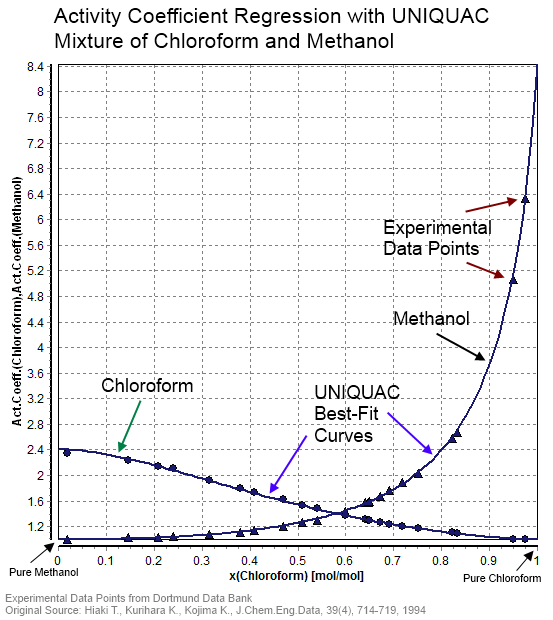
Activity Coefficient
In thermodynamics, an activity coefficient is a factor used to account for deviation of a mixture of chemical substances from ideal behaviour. In an ideal mixture, the microscopic interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same (or macroscopically equivalent, the enthalpy change of solution and volume variation in mixing is zero) and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed directly in terms of simple concentrations or partial pressures of the substances present e.g. Raoult's law. Deviations from ideality are accommodated by modifying the concentration by an ''activity coefficient''. Analogously, expressions involving gases can be adjusted for non-ideality by scaling partial pressures by a fugacity coefficient. The concept of activity coefficient is closely linked to that of activity in chemistry. Thermodynamic definition The chemical potential, \mu_\mathrm, of a substance B in an ideal mixture of liquids or an ideal solution is given by :\mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conductivity (electrolytic)
Conductivity (or specific conductance) of an electrolyte solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. The SI unit of conductivity is Siemens per meter (S/m). Conductivity measurements are used routinely in many industrial and environmental applications as a fast, inexpensive and reliable way of measuring the ionic content in a solution. For example, the measurement of product conductivity is a typical way to monitor and continuously trend the performance of water purification systems. In many cases, conductivity is linked directly to the total dissolved solids (TDS). High quality deionized water has a conductivity of about 0.05 μS/cm at 25 °C, typical drinking water is in the range of 200–800 μS/cm, while sea water is about 50 mS/cm ncorrect according to source(or 50,000 μS/cm). Conductivity is traditionally determined by connecting the electrolyte in a Wheatstone bridge. Dilute solutions follow Kohlrausch's Laws of conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon , twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco Zürich () is the largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zürich. It is located in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zürich. As of January 2020, the municipality has 434,335 inhabitants, the urban area 1.315 million (2009), and the Zürich metropolitan area 1.83 million (2011). Zürich is a hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Both Zurich Airport and Zürich's main railway station are the largest and busiest in the country. Permanently settled for over 2,000 years, Zürich was founded by the Romans, who called it '. However, early settlements have been found dating back more than 6,400 years (although this only indicates human presence in the area and not the presence of a town that early). During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Debye
Peter Joseph William Debye (; ; March 24, 1884 – November 2, 1966) was a Dutch-American physicist and physical chemistry, physical chemist, and List of Nobel laureates in Chemistry, Nobel laureate in Chemistry. Biography Early life Born Petrus Josephus Wilhelmus Debije in Maastricht, Netherlands, Debye enrolled in the Aachen University of Technology in 1901. In 1905, he completed his first degree in electrical engineering. He published his first paper, a mathematically elegant solution of a problem involving eddy currents, in 1907. At Aachen, he studied under the theoretical physicist Arnold Sommerfeld, who later claimed that his most important discovery was Peter Debye. In 1906, Sommerfeld received an appointment at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Munich, Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria, and took Debye with him as his assistant. Debye got his Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D. with a dissertation on radiation pressure in 1908. In 1910, he derived the Planck's law, Planck radiat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |