|
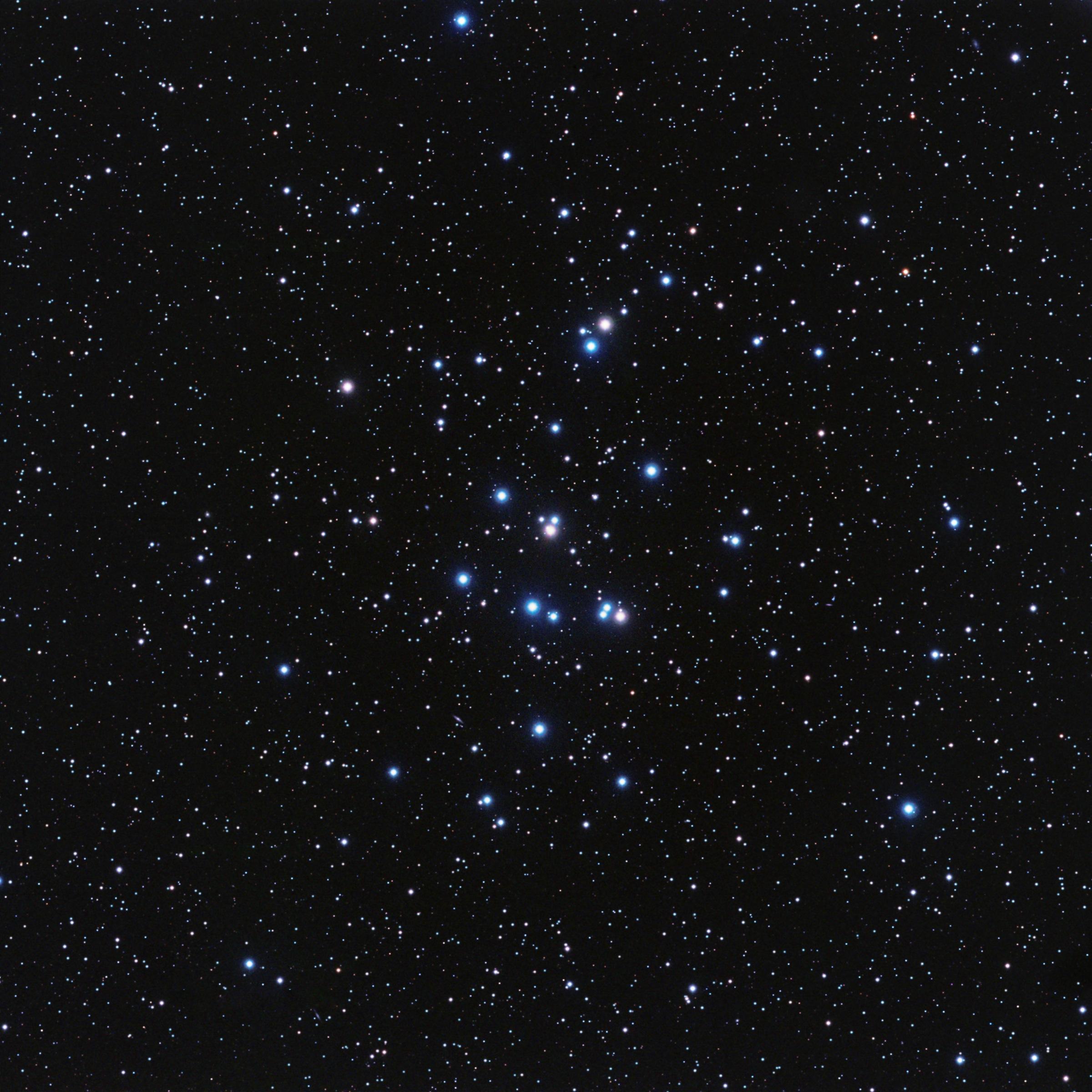
Epsilon Cancri
Epsilon Cancri is a white-hued multiple star system in the zodiac constellation of Cancer. Its name is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from ε Cancri, and abbreviated Epsilon Cnc or ε Cnc. This is the brightest member of the Beehive Cluster (or Praesepe) with an apparent visual magnitude of +6.29, which is near the lower limit of visibility with the naked eye. The annual parallax shift of as seen from Earth yields a distance estimate of approximately from the Sun. The system is moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +30 km/s. The outer pair has the designation WDS J08405+1933. The primary star is designated Epsilon Cancri and the secondary is HD 73711. Epsilon Cancri is itself a spectroscopic binary with components designated Aa (also named Meleph) and Ab. HD 73711 is also suspected of being a spectroscopic binary. Nomenclature ''ε Cancri'' ( Latinised to ''Epsilon Cancri'') is the system's Bayer designation, which originally referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer (constellation)
Cancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as one. Cancer is a medium-size constellation with an area of 506 square degrees and its stars are rather faint, its brightest star Beta Cancri having an apparent magnitude of 3.5. It contains ten stars with known exoplanet, planets, including 55 Cancri, which has five: one Super-Earth, super-Earth and four gas giants, one of which is in the habitable zone and as such has expected temperatures similar to Earth. At the (angular) heart of this sector of our celestial sphere is Beehive Cluster, Praesepe (Messier 44), one of the closest open clusters to Earth and a popular target for amateur astronomers. Characteristics Cancer is a medium-sized constellation that is bordered by Gemini (constellation), Gemini to the west, Lynx (constellation), Lynx to the north, Leo Minor to the northeast, Leo (constellation), Leo to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * Circular orbit: * Elliptic orbit: * Parabolic trajectory: * Hyperbolic trajectory: The eccentricity is given by e = \sqrt where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bright Star Catalogue Objects
Bright may refer to: Common meanings *Bright, an adjective meaning giving off or reflecting illumination; see Brightness *Bright, an adjective meaning someone with intelligence People * Bright (surname) * Bright (given name) *Bright, the stage name of Thai actor, musician, model, host and entrepreneur Vachirawit Chivaaree Places Australia * Bright, Victoria, a town * Electoral district of Bright in South Australia Canada * Bright Parish, New Brunswick Northern Ireland * Bright, County Down, a village and parish in County Down United States * Bright, Indiana, a census-designated place * Bright, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Bright, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community Arts and entertainment Music * Bright (American band), an experimental pop group from Brooklyn, New York ** ''Bright'' (Bright (American band) album), 1996 album * Bright (Japanese band), a dance vocal band from Japan ** ''Bright'' (Bright (Japanese band) album), 2012 album * "Bright" (song), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Objects
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include: pharmaceuticals, consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the EURO STOXX 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer (1825–1880) and dyer Friedrich Weskott (1821–1876). The company was established as a dyestuffs producer, but the versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand its business into other areas. In 1899, Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. Aspirin is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2021, it was the 34th most commonly prescribed medication in the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Star Systems
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravity, gravitational attraction. It may sometimes be used to refer to a single star. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). Terminology A star system of two stars is known as a ''binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. Systems with four or more components are rare, and are much less commonly found than those with 2 or 3. Multiple-star systems are called ''triple'', ''ternary'', or ''trinary'' if they contain three stars; ''quadruple'' or ''quaternary'' if they contain four stars; ''quintuple'' or ''quintenary'' with five stars; ''sextuple'' or ''sextenary'' with six stars; ''septuple'' or ''septenary'' with seven stars; and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-type Giants
A type or type A may refer to: Science * A-type asteroid, a type of relatively uncommon inner-belt asteroids * A type blood, a type in the ABO blood group system * A-type inclusion, a type of cell inclusion * A-type potassium channel, a type of voltage-gated potassium channel * A type proanthocyanidin, a specific type of flavonoids * A-type star, a class of stars * Type A climate, a type in the Köppen climate classification * Type A flu, a type of influenza virus * Type A evaluation of uncertainty, an uncertainty in measurement that can be inferred, for example, from repeated measurement * Type A personality, a personality type in the Type A and Type B personality theory * Hemophilia type A, a type of haemophilia * A-type granite a type of granite rock * Adenosine receptor Technology * Type A Dolby Noise Reduction, a type of Dolby noise-reduction system * Type A plug (see also NEMA connector) * Type A submarine, a class of submarines in the Imperial Japanese Navy which se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Line
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the #Absorption spectrum, absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared spectroscopy, Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or dwarf stars, and positions of stars on and off the band are believed to indicate their physical properties, as well as their progress through several types of star life-cycles. These are the most numerous true stars in the universe and include the Sun. Color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. After condensation and ignition of a star, it generates thermal energy in its dense stellar core, core region through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. During this stage of the star's lifetime, it is located on the main sequence at a position determined primarily by its mass but also based on its chemical composition and age. The cores of main-sequence stars are in hydros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Am Star
An Am star or metallic-line star is a type of chemically peculiar star of spectral type A whose spectrum has strong and often variable absorption lines of metals such as zinc Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ..., strontium, zirconium, and barium, and deficiencies of others, such as calcium and scandium. The original definition of an Am star was one in which the star shows "an apparent surface underabundance of calcium, Ca (and/or scandium, Sc) and/or an apparent overabundance of the iron group, Fe group and heavier elements". The unusual relative abundances cause the spectral type assessed from the Calcium K lines to be systematically earlier than one assessed from other metallic lines. Typically, a spectral type judged solely from hydrogen lines is intermediate. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemically Peculiar Star
In astrophysics, chemically peculiar stars (CP stars) are stars with distinctly unusual Metallicity, metal abundances, at least in their surface layers. Classification Chemically peculiar stars are common among hot main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) stars. These hot peculiar stars have been divided into four main classes on the basis of their spectra, although two classification systems are sometimes used: * non-magnetic metallic-lined star, metallic-lined (Am, CP1) * Ap and Bp stars, magnetic (Ap, CP2) * non-magnetic mercury-manganese star, mercury-manganese (HgMn, CP3) * Helium-weak star, helium-weak (He-weak, CP4). The class names provide a good idea of the peculiarities that set them apart from other stars on or near the main sequence. The Am stars (CP1 stars) show weak lines of singly ionized Calcium, Ca and/or Scandium, Sc, but show enhanced abundances of heavy metals. They also tend to be slow rotators and have an effective temperature between 7000 and . The Ap stars (CP2 st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Spectrum
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, infrared and radio waves that radiate from stars and other celestial objects. A stellar spectrum can reveal many properties of stars, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance and luminosity. Spectroscopy can show the velocity of motion towards or away from the observer by measuring the Doppler shift. Spectroscopy is also used to study the physical properties of many other types of celestial objects such as planets, nebulae, galaxies, and active galactic nuclei. Background Astronomical spectroscopy is used to measure three major bands of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum: visible light, radio waves, and X-rays. While all spectroscopy looks at specific bands of the spectrum, different methods are required to acquire the signal depending on the freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |