|
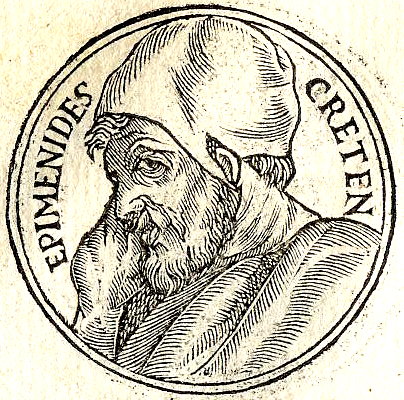
Epimenides
Epimenides of Knossos (or Epimenides of Crete) (; ) was a semi-mythical 7th- or 6th-century BC Greek seer and philosopher-poet, from Knossos or Phaistos. Life While tending his father's sheep, Epimenides is said to have fallen asleep for fifty-seven years in a Cretan cave sacred to Zeus, after which he reportedly awoke with the gift of prophecy (Diogenes Laërtius i. 109–115). Plutarch writes that Epimenides purified Athens after the pollution brought by the Alcmeonidae, and that the seer's expertise in sacrifices and reform of funeral practices were of great help to Solon in his reform of the Athenian state. The only reward he would accept was a branch of the sacred olive, and a promise of perpetual friendship between Athens and Knossos (Plutarch, ''Life of Solon'', 12; Aristotle, '' Ath. Pol''. 1). Athenaeus also mentions him, in connection with the self-sacrifice of the ''erastes'' and ''eromenos'' pair of Aristodemus and Cratinus, who were believed to have given their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus. Zeus is the child of Cronus and Rhea (mythology), Rhea, the youngest of his siblings to be born, though sometimes reckoned the eldest as the others required disgorging from Cronus's stomach. In most traditions, he is married to Hera, by whom he is usually said to have fathered Ares, Eileithyia, Hebe (mythology), Hebe, and Hephaestus.Hard 2004p. 79 At the oracle of Dodona, his consort was said to be Dione (Titaness/Oceanid), Dione, by whom the ''Iliad'' states that he fathered Aphrodite. According to the ''Theogony'', Zeus's first wife was Metis (mythology), Metis, by whom he had Athena.Hesiod, ''Theogony'886900 Zeus was also infamous for his erotic escapades. These resulted in many divine and heroic offspring, including Apollo, Artemis, Hermes, Persephone, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phaistos
Phaistos (, ; Ancient Greek: , , Linear B: ''Pa-i-to''; Linear A: ''Pa-i-to''), also Transliteration, transliterated as Phaestos, Festos and Latin Phaestus, is a Bronze Age archaeological site at modern Faistos, a municipality in south central Crete. It is notable for the remains of a Minoan palace and the surrounding town. Ancient Phaistos was located about east of the Mediterranean Sea and south of Heraklion. Phaistos was one of the largest cities of Minoan Crete. The name Phaistos survives from Ancient Greece, ancient Greek references to a city on Crete of that name at or near the current ruins. History Bronze Age Phaistos was first inhabited around 3600 BCE, slightly later than other early sites such as Knossos. During the Early Minoan period, the site's hills were Terrace (building), terraced and monumental buildings were constructed on them. Like other large Minoan cities, there was a palace that was built in an area that had been used earlier for communal feastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Knossos
Knossos (; , ; Linear B: ''Ko-no-so'') is a Bronze Age archaeological site in Crete. The site was a major centre of the Minoan civilization and is known for its association with the Greek myth of Theseus and the minotaur. It is located on the outskirts of Heraklion, and remains a popular tourist destination. Knossos is considered by many to be the oldest city in Europe. Knossos is dominated by the monumental Palace of Minos. Like other Minoan palaces, this complex of buildings served as a combination religious and administrative centre rather than a royal residence. The earliest parts of the palace were built around 1900 BC in an area that had been used for ritual feasting since the Neolithic. The palace was continually renovated and expanded over the next five centuries until its final destruction around 1350 BC. The site was first excavated by Minos Kalokairinos in 1877. In 1900, Arthur Evans, Sir Arthur Evans undertook more extensive excavations which unearthed most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diogenes Laërtius
Diogenes Laërtius ( ; , ; ) was a biographer of the Greek philosophers. Little is definitively known about his life, but his surviving book ''Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers'' is a principal source for the history of ancient Greek philosophy. His reputation is controversial among scholars because he often repeats information from his sources without critically evaluating it. In many cases, he focuses on insignificant details of his subjects' lives while ignoring important details of their philosophical teachings and he sometimes fails to distinguish between earlier and later teachings of specific philosophical schools. However, unlike many other ancient secondary sources, Diogenes Laërtius tends to report philosophical teachings without trying to reinterpret or expand on them, and so his accounts are often closer to the primary sources. Due to the loss of so many of the primary sources on which Diogenes relied, his work has become the foremost surviving source on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos (; BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath, and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of Plato, Aristotle, and, through them, Western philosophy. Modern scholars disagree regarding Pythagoras's education and influences, but most agree that he travelled to Croton in southern Italy around 530 BC, where he founded a school in which initiates were allegedly sworn to secrecy and lived a communal, ascetic lifestyle. In antiquity, Pythagoras was credited with mathematical and scientific discoveries, such as the Pythagorean theorem, Pythagorean tuning, the five regular solids, the theory of proportions, the sphericity of the Earth, the identity of the morning and evening stars as the planet Venus, and the division of the globe into five climatic zones. He was reputedly the first man to call himself a philosopher ("lover of wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Greek Mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancient Greek religion's view of the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world; the lives and activities of List of Greek deities, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures; and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of mythmaking itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Philosopher
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its methods and assumptions. Historically, many of the individual sciences, such as physics and psychology, formed part of philosophy. However, they are considered separate academic disciplines in the modern sense of the term. Influential traditions in the history of philosophy include Western philosophy, Western, Islamic philosophy, Arabic–Persian, Indian philosophy, Indian, and Chinese philosophy. Western philosophy originated in Ancient Greece and covers a wide area of philosophical subfields. A central topic in Arabic–Persian philosophy is the relation between reason and revelation. Indian philosophy combines the Spirituality, spiritual problem of how to reach Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlighten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aristodemus And Cratinus
In Greek mythology, Aristodemus (Ancient Greek: Ἀριστόδημος) was one of the Heracleidae, son of Aristomachus and brother of Cresphontes and Temenus. He was a great-great-grandson of Heracles and helped lead the fifth and final attack on Mycenae in the Peloponnese. Aristodemus and his brothers complained to the oracle that its instructions had proved fatal to those who had followed them; the oracle had told Hyllas to attack through the narrow passage when the third fruit was ripe. They received the answer that by the "third fruit" the "third generation" was meant, and that the "narrow passage" was not the isthmus of Corinth, but the straits of Rhium. They accordingly built a fleet at Naupactus, but before they set sail, Aristodemus was struck by lightning (or shot by Apollo) and the fleet destroyed, because one of the Heraclidae had slain an Acarnanian soothsayer. His brothers were later able to conquer the Peloponnese. By his wife Argia, daughter of King Autesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
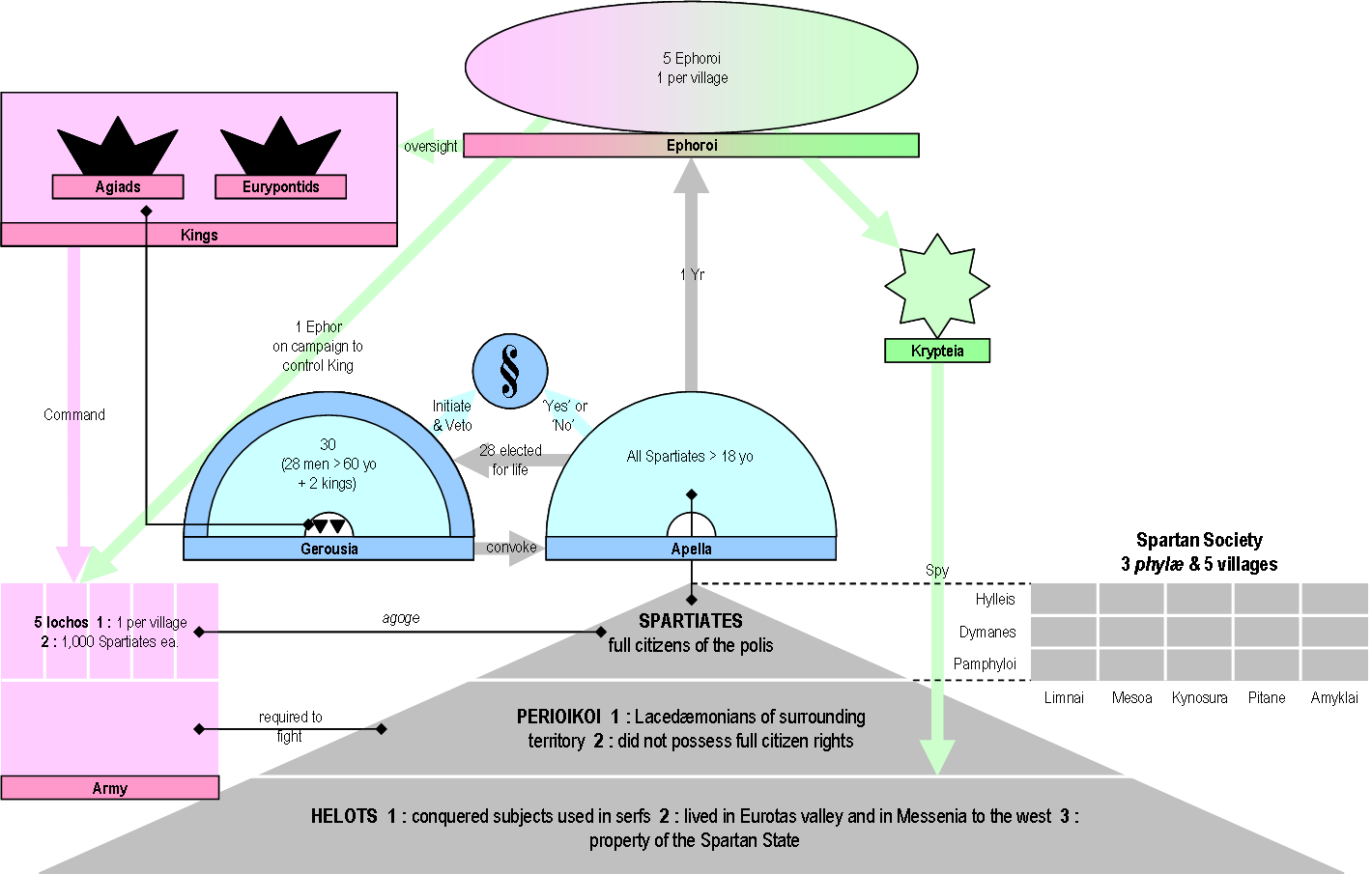
Ephores
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs. The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek ''éphoroi'', plural form of ''éphoros'') comes from the Ancient Greek ''epi'', "on" or "over", and ''horaō'', "to see", i.e., "one who oversees" or "overseer". The ephors were a council of five Spartan men elected annually who swore an oath monthly on the behalf of the state. The Spartan kings, however, would swear on behalf of themselves. The ephors did not have to kneel before the Kings of Sparta, and were held in high esteem by the citizens because of the importance of their powers and because of the holy role that they earned throughout their functions.Donald Kagan, ''The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War''. p. 29. Ithaca/New York 1969, . Several other Greek city-states with a Spartan ancestry also had ephors, such as Taras or Cyrene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
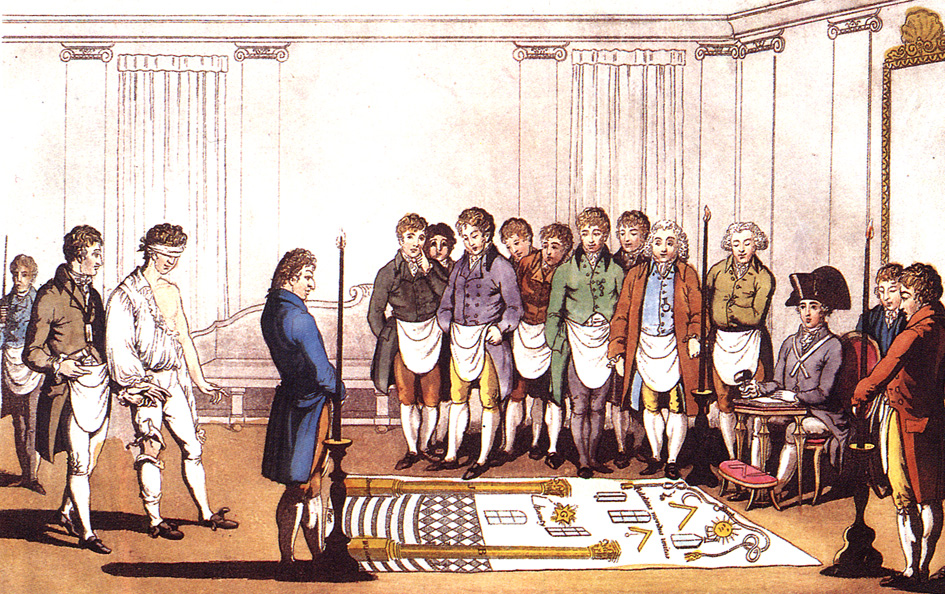
Initiation
Initiation is a rite of passage marking entrance or acceptance into a group or society. It could also be a formal admission to adulthood in a community or one of its formal components. In an extended sense, it can also signify a transformation in which the initiate is 'reborn' into a new role. Examples of initiation ceremonies might include Christian baptism or confirmation, Jewish bar or bat mitzvah, acceptance into a fraternal organization, secret society or religious order, or graduation from school or recruit training. A person taking the initiation ceremony in traditional rites, such as those depicted in these pictures, is called an ''initiate''. Characteristics William Ian Miller notes the role of ritual humiliation in comic ordering and testing. Mircea Eliade discussed initiation as a principal religious act by classical or traditional societies. He defined initiation as "a basic change in existential condition", which liberates man from profane time and histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan" (meaning ) in both respective native languages and most other languages. The region is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the southwest, European Russia to the northwest, China and Mongolia to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the south, and Siberia to the north. Together, the five Central Asian countries have a total population of around million. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians, and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. As the result of Turkic migration, Central Asia also became the homeland for the Kazakhs, Kyrgyzs, Volga Tatars, Tatars, Turkmens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |