|
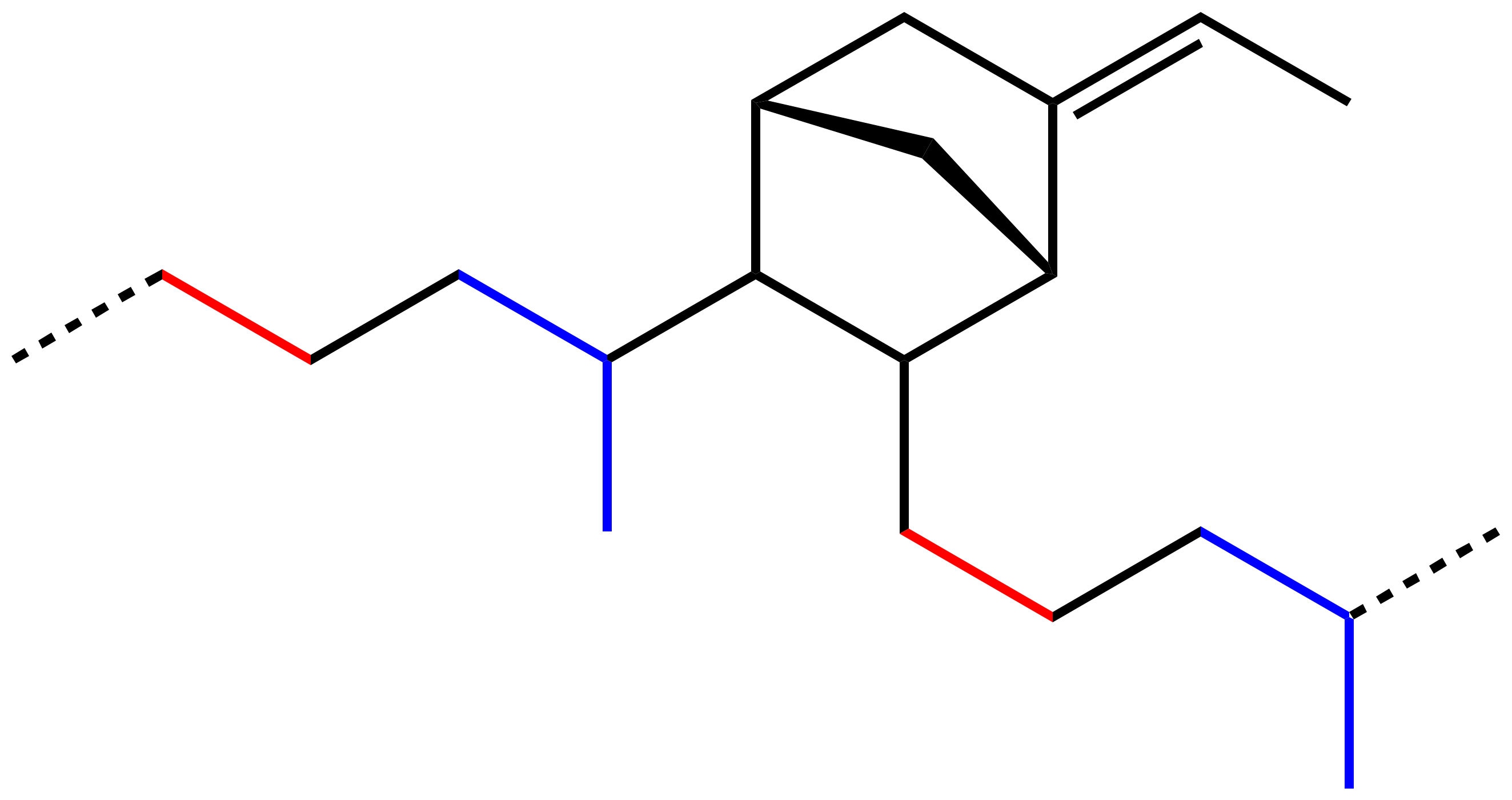
Epdm Rubber
EPDM rubber (ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber) is a type of synthetic rubber that is used in many applications. EPDM is an M-Class rubber under ASTM standard D-1418; the ''M'' class comprises elastomers with a saturated polyethylene chain (the M deriving from the more correct term polymethylene). EPDM is made from ethylene, propylene, and a diene comonomer that enables crosslinking via sulfur vulcanization. Typically used dienes in the manufacture of EPDM rubbers are ethylidene norbornene (ENB), dicyclopentadiene (DCPD), and vinyl norbornene (VNB). Varying diene contents are reported in commercial products, which are generally in the range from 2 to 12%. The earlier relative of EPDM is EPR, ethylene propylene rubber (useful for high-voltage electrical cables), which is not derived from any diene precursors and can be crosslinked only using radical methods such as peroxides. As with most rubbers, EPDM as used is always compounded with fillers such as carbon black and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filler (materials)
Filler materials are particles added to binders (resin, thermoplastics, cement) to make a composite material. Filler materials improve specific properties or make the product cheaper. Coarse filler materials such as construction aggregate and rebar are used in the building industry to make plaster, mortar and concrete. Powdered fillers are mixed in with elastomers and plastics. Worldwide, more than 53 million tons of fillers (with a net worth of ca. US$18 billion) are used every year in the production of paper, plastics, rubber, paints, coatings, adhesives, and sealants. Fillers are produced by more than 700 companies, rank among the world's major raw materials and are contained in a variety of goods for daily consumer needs. The top filler materials used are ground calcium carbonate (GCC), precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC), kaolin, talc, and carbon black. Filler materials can affect the tensile strength, toughness, heat resistance, color, clarity, etc. This can be util ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styrene-butadiene
Styrene-butadiene or styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) describe families of synthetic rubbers derived from styrene and butadiene (the version developed by Goodyear is called Neolite). These materials have good abrasion resistance and good aging stability when protected by additives. In 2012, more than 5.4 million tonnes of SBR were processed worldwide. About 50% of car tires are made from various types of SBR. The styrene/butadiene ratio influences the properties of the polymer: with high styrene content, the rubbers are harder and less rubbery. SBR is not to be confused with the thermoplastic elastomer, styrene-butadiene block copolymer, although being derived from the same monomers. Types SBR is derived from two monomers, styrene and butadiene. The mixture of these two monomers is polymerized by two processes: from solution (S-SBR) or as an emulsion (E-SBR). E-SBR is more widely used. Emulsion polymerization E-SBR produced by emulsion polymerization is initiated by f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers. Currently, rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the Hevea brasiliensis, Pará rubber tree (''Hevea brasiliensis'') or others. The latex is a sticky, milky and white colloid drawn off by making incisions in the bark and collecting the fluid in vessels in a process called "tapping". Manufacturers refine this latex into the rubber that is ready for commercial processing. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, either alone or in combination with other materials. In most of its useful forms, it has a large stretch ratio and high resilience and also is buoyant and water-proof. Industrial demand for rubber-like materials began to out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Transition
The glass–liquid transition, or glass transition, is the gradual and Reversible reaction, reversible transition in amorphous solid, amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within Crystallinity, semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle "glassy" state into a viscous or rubbery state as the temperature is increased. International Organization for Standardization, ISO 11357-2: Plastics – Differential scanning calorimetry – Part 2: Determination of glass transition temperature (1999). An amorphous solid that exhibits a glass transition is called a glass. The reverse transition, achieved by supercooling a viscous liquid into the glass state, is called vitrification. The glass-transition temperature ''T''g of a material characterizes the range of temperatures over which this glass transition occurs (as an experimental definition, typically marked as 100 s of relaxation time). It is always lower than the melting point, melting temperature, ''T''m, of the cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coefficient Of Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions). Substances usually contract with decreasing temperature (thermal contraction), with rare exceptions within limited temperature ranges ('' negative thermal expansion''). Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster, weakening the intermolecular forces between them and therefore expanding the substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. The relative expansion (also called strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. Prediction If an equation of state is available, it can be used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shore A
The Shore durometer is a device for measuring the hardness of a material, typically of polymers. Higher numbers on the scale indicate a greater resistance to indentation and thus harder materials. Lower numbers indicate less resistance and softer materials. The term is also used to describe a material's rating on the scale, as in an object having a "'Shore durometer' of 90." The scale was defined by Albert Ferdinand Shore, who developed a suitable device to measure hardness in the 1920s. It was neither the first hardness tester nor the first to be called a ''durometer'' ( ISV '' duro-'' and '' -meter''; attested since the 19th century), but today that name usually refers to Shore hardness; other devices use other measures, which return corresponding results, such as for Rockwell hardness. Durometer scales There are several scales of durometer, used for materials with different properties. The two most common scales, using slightly different measurement systems, are the AST ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American English, the material is commonly referred to as asphalt or tar. Whether found in natural deposits or refined from petroleum, the substance is classed as a pitch (resin), pitch. Prior to the 20th century, the term asphaltum was in general use. The word derives from the Ancient Greek word (), which referred to natural bitumen or pitch. The largest natural deposit of bitumen in the world is the Pitch Lake of southwest Trinidad, which is estimated to contain 10 million tons. About 70% of annual bitumen production is destined for road surface, road construction, its primary use. In this application, bitumen is used to bind construction aggregate, aggregate particles like gravel and forms a substance referred to as asphalt concrete, which is collo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron-beam Processing
Electron-beam processing or electron irradiation (EBI) is a process that involves using electrons, usually of high energy, to treat an object for a variety of purposes. This may take place under elevated temperatures and nitrogen atmosphere. Possible uses for electron irradiation include sterilization, alteration of gemstone colors, and cross-linking of polymers. Electron energies typically vary from the keV to MeV range, depending on the depth of penetration required. The irradiation dose is usually measured in grays but also in Mrads ( is equivalent to ). The basic components of a typical electron-beam processing device include: an electron gun (consisting of a cathode, grid, and anode), used to generate and accelerate the primary beam; and, a magnetic optical (focusing and deflection) system, used for controlling the way in which the electron beam impinges on the material being processed (the "workpiece"). In operation, the gun's hot cathode emits electrons that are both ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxide
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of Chemical compound, compounds with the structure , where the R's represent a radical (a portion of a complete molecule; not necessarily a free radical) and O's are single oxygen atoms. Oxygen atoms are joined to each other and to adjacent elements through Single bond, single covalent bonds, denoted by dashes or lines. The group in a peroxide is often called the peroxide group, though some nomenclature discrepancies exist. This linkage is recognized as a common polyatomic ion, and exists in many molecules. General structure The characteristic structure of any regular peroxide is the oxygen–oxygen covalent single bond, which connects the two main atoms together. In the event that the molecule has no chemical Substituent, substituents, the peroxide group will have a [−2] Formal charge, net charge. Each oxygen atom has a charge of negative one, as 5 of its Valence electron, valence electrons remain in the outermost Atomic orbital, orbital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulcanization
Vulcanization (British English: vulcanisation) is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include the hardening of other (synthetic) rubbers via various means. Examples include silicone rubber via room temperature vulcanizing and chloroprene rubber (neoprene) using metal oxides. Vulcanization can be defined as the curing of elastomers, with the terms 'vulcanization' and 'curing' sometimes used interchangeably in this context. It works by forming cross-links between sections of the polymer chain which results in increased rigidity and durability, as well as other changes in the mechanical and electrical properties of the material. Vulcanization, in common with the curing of other thermosetting polymers, is generally irreversible. The word was suggested by William Brockedon (a friend of Thomas Hancock who attained the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |