|
Eoceratops
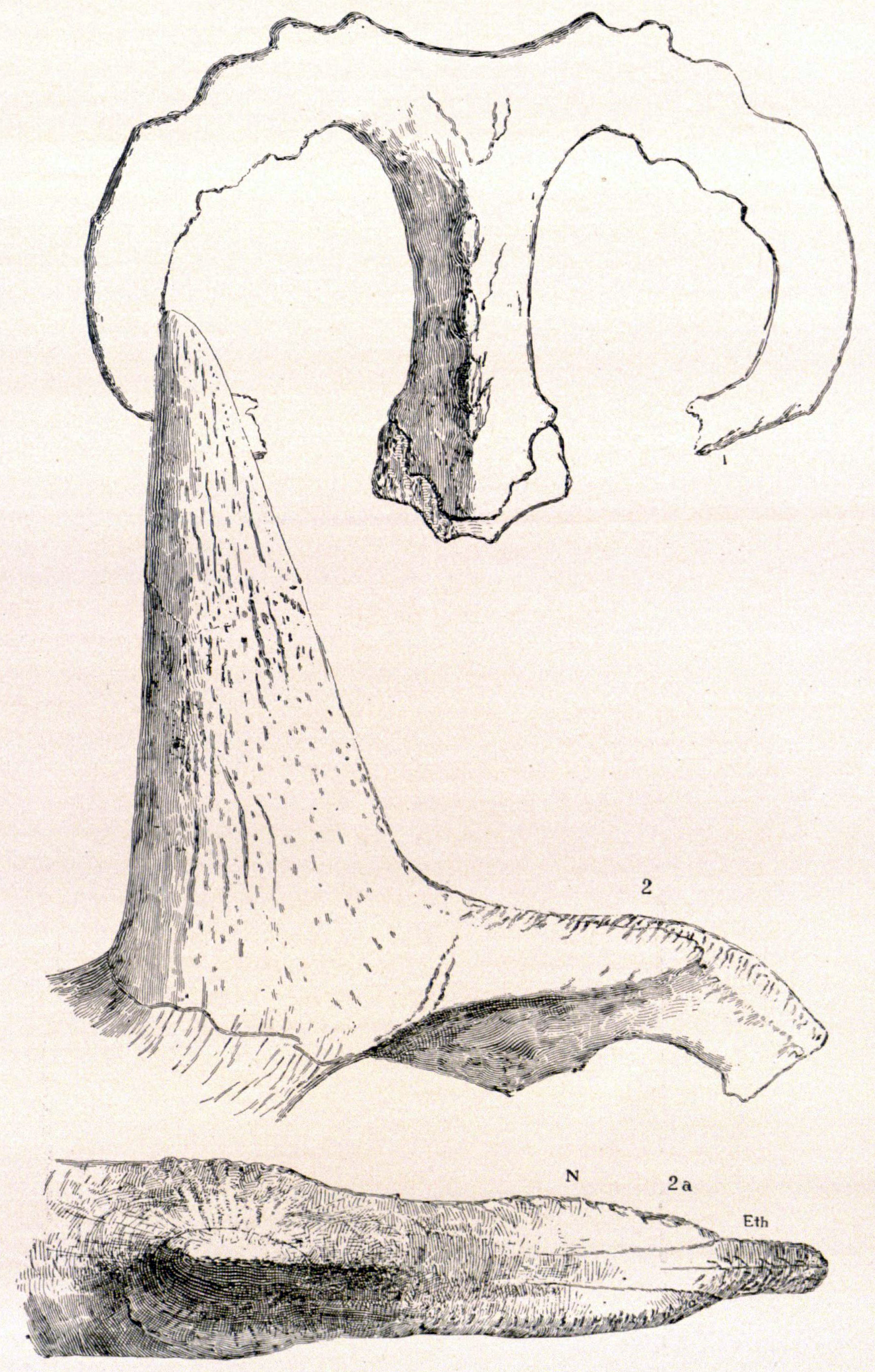
''Chasmosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period in North America. Its given name means 'opening lizard', referring to the large openings ( fenestrae) in its frill (Greek ''chasma'', meaning 'opening', 'hollow', or 'gulf'; and ''sauros'', meaning 'lizard'). With a length of and a weight of —or anywhere from 2,200 to nearly 5,000 lbs., give or take—''Chasmosaurus'' was of a slightly smaller to ‘average’ size, especially when compared to larger ceratopsians (such as ''Triceratops'', which were about the size of an African bush elephant). It was initially to be called ''Protorosaurus'', but this name had been previously published for another animal. All of the excavated specimens of ''Chasmosaurus'' were collected at the Dinosaur Park Formation, Dinosaur Provincial Park, Alberta, Canada. Referred specimens of ''C. russelli'' come from the lower beds of the formation, while ''C. belli'' comes from the middle and upper beds. Discovery an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonius
''Monoclonius'' (meaning "single sprout") is an extinct dubious genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur found in the Late Cretaceous layers of the Judith River Formation in Montana, United States, and the uppermost rock layers of the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta, Canada dated to between 75 and 74.6 million years ago. ''Monoclonius'' was first named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1876. Later, much taxonomic confusion was caused by the discovery of '' Centrosaurus'', a very similar genus of ceratopsian that is known from much better remains. Today, typical ''Monoclonius'' specimens are usually believed to be juvenile ''Centrosaurus'' or subadults, in many cases of other genera such as ''Centrosaurus''. Those specimens that remain under the name ''Monoclonius'' are mostly too incomplete or immature to be confidently matched with adult specimens from the same time and place. This is especially true of the type species, ''Monoclonius crassus''. Therefore, ''Monoclonius'' is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Lambe
Lawrence Morris Lambe (August 27, 1863 – March 12, 1919) was a Canadian geologist, palaeontologist, and ecologist from the Geological Survey of Canada (GSC). His published work, describing the diverse and plentiful dinosaur discoveries from the fossil beds in Alberta, did much to bring dinosaurs into the public eye and helped usher in the ''Golden Age of Dinosaurs'' in the province. During this period, between the 1880s and World War I, dinosaur hunters from all over the world converged on Alberta. ''Lambeosaurus'', a well-known hadrosaur, was named after him as a tribute, in 1923. In addition to paleontology, Lambe discovered a number of invertebrate species ranging from Canada to the Pacific Northwest. Lambe's contemporary discoveries were published in works such as ''Sponges From the Atlantic Coast of Canada'' and ''Catalogue of the recent marine sponges of Canada and Alaska''. Early life and education Lambe was born in Montreal on August 27, 1863. Lambe studied at the Roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of Chasmosaurinae, chasmosaurine Ceratopsia, ceratopsian dinosaur that lived during the late Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 68 to 66 million years ago on the island continent of Laramidia, now forming western North America. It was one of the last-known non-avian dinosaurs and lived until the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago. The name ''Triceratops'', which means 'three-horned face', is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words () meaning 'three', () meaning 'horn', and () meaning 'face'. Bearing a large bony neck frill, frill, three horns on the skull, and a large, four-legged body, exhibiting convergent evolution with bovines and rhinoceroses, ''Triceratops'' is one of the most recognizable of all dinosaurs and the best-known ceratopsian. It was also one of the largest, measuring around long and weighing up to . It shared the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1915 In Paleontology
Arthropods Newly named insects Archosauromorphs Newly named pseudosuchians Dinosaurs * Charles H. Sternberg's crew excavated a ''Corythosaurus'' from quarry 243 in Dinosaur Provincial Park, Alberta, Canada. The specimen would later be displayed at the Calgary Zoo. * Matthew observed that fossils of hadrosaur Dinosaur egg, eggs and hatchlings were absent in coastal areas and suggested that hadrosaurs may have preferred nesting grounds further inland. He believed that these inland nesting grounds were actually where hadrosaurs first evolved and therefore to breed, hadrosaurs retraced their ancestors route back to their place of origin. After hatching, the young hadrosaurs would spend some time inland maturing before migrating out to more coastal areas. New taxa Anapsids Turtles Synapsids Non-mammalian Paleontologists * Death of Eberhard Fraas. References {{portal, Paleontology [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76.5 and 74.4 million years ago. It was deposited in alluvial plain, alluvial and coastal plain environments, and it is bounded by the nonmarine Oldman Formation below it and the marine (ocean), marine Bearpaw Formation above it.Eberth, D.A. 2005. The geology. In: Currie, P.J., and Koppelhus, E.B. (eds), ''iarchive:dinosaurprovinci0000unse, Dinosaur Provincial Park: A Spectacular Ancient Ecosystem Revealed''. Indiana University Press: Bloomington and Indianapolis, p.54-82. . The Dinosaur Park Formation contains dense concentrations of dinosaur skeletons, both articulated and disarticulated, which are often found with preserved remains of soft tissues. Remains of other animals such as fish, turtles, and crocodilians, as well as plant re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenestra (anatomy)
A fenestra (fenestration; : fenestrae or fenestrations) is any small opening or pore, commonly used as a term in the biological sciences. It is the Latin word for "window", and is used in various fields to describe a pore in an anatomical structure. Biological morphology In morphology, fenestrae are found in cancellous bones, particularly in the skull. In anatomy, the round window and oval window are also known as the ''fenestra rotunda'' and the ''fenestra ovalis''. In microanatomy, fenestrae are found in endothelium of fenestrated capillaries, enabling the rapid exchange of molecules between the blood and surrounding tissue. The elastic layer of the tunica intima is a fenestrated membrane. In surgery, a fenestration is a new opening made in a part of the body to enable drainage or access. Plant biology and mycology In plant biology, the perforations in a perforate leaf are also described as fenestrae, and the leaf is called a fenestrate leaf. The leaf window is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Bush Elephant
The African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), also known as the African savanna elephant, is a species of elephant native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of three extant elephant species and, along with the African forest elephant, one of two extant species of African elephant. It is the largest living terrestrial animal, with fully grown bulls reaching an average shoulder height of and a body mass of ; the largest recorded specimen had a shoulder height of and an estimated body mass of . The African bush elephant is characterised by its long prehensile trunk with two finger-like processes; a convex back; large ears which help reduce body heat; and sturdy tusks that are noticeably curved. The skin is grey with scanty hairs, and bending cracks which support thermoregulation by retaining water. The African bush elephant inhabits a variety of habitats such as forests, grasslands, woodlands, wetlands and agricultural land. It is a mixed herbivore feeding mostly on grasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta, Canada
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, the Northwest Territories to its north, and the U.S. state of Montana to its south. Alberta and Saskatchewan are the only two landlocked Canadian provinces. The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly humid continental climate, continental climate, but seasonal temperatures tend to swing rapidly because it is so arid. Those swings are less pronounced in western Alberta because of its occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area, at , and the fourth most populous, with 4,262,635 residents. Alberta's capital is Edmonton; its largest city is Calgary. The two cities are Alberta's largest Census geographic units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Provincial Park
Dinosaur Provincial Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site situated 220 kilometres (137 mi) east of Calgary, Alberta, Canada; or northeast of Brooks. The park is situated in the Red Deer River valley, which is noted for its striking badland topography, and abundance of dinosaur fossils. The park is well-known for being one of the richest dinosaur fossil locales in the world. Fifty-eight dinosaur species have been discovered at the park and more than 500 specimens have been removed and exhibited in museums around the globe. The renowned fossil assemblage of nearly 500 species of life, from microscopic fern spores to large carnivorous dinosaurs, justified its becoming a World Heritage Site in 1979. Dinosaur Provincial Park Visitor Centre The Dinosaur Provincial Park Visitor Centre features exhibits about dinosaurs, fossils, and the geology and natural history of the park. There is a video theatre, fossil prep lab area, and a gift shop. Public programs are offered in the summer. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period (geology)
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (a scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardised international units of geological time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |