|
Enfilade
Enfilade and defilade are concepts in military tactics used to describe a military formation's exposure to enemy fire. A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be directed along its longest axis. A unit or position is "in defilade" if it uses natural or artificial obstacles to shield or conceal itself from enfilade and hostile fire. The strategies, named by the England, English during the Hundred Years' War, use the French language, French ''wikt:enfiler, enfiler'' ("to put on a string or sling") and ''wikt:défiler, défiler'' ("to slip away or off") spoken by Anglo-Normans, English nobility of the time. Enfilade fire—gunfire directed against an enfiladed formation or position—is also commonly known as "flanking fire". Raking fire is the equivalent term in naval warfare. Strafing, firing on targets from a flying platform, is often done with enfilade fire. It is a very advantageous, and much sought for, position for the attacking force. Enfilade A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench Warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising Trench#Military engineering, military trenches, in which combatants are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. It became archetypically associated with World War I (1914–1918), when the Race to the Sea rapidly expanded trench use on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front starting in September 1914.. Trench warfare proliferated when a Weapons of World War I, revolution in firepower was not matched by similar advances in mobility (military), mobility, resulting in a grueling form of warfare in which the defender held the advantage. On the Western Front in 1914–1918, both sides constructed elaborate trench, underground, and dugout (shelter), dugout systems opposing each other along a front (military), front, protected from assault by barbed wire. The area between opposing trench lines (known as "no man's land") was fully exposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turret-down
In sailing and warfare, to be hull down means that the upper part of a vessel or vehicle is visible, but the main, lower body ( hull) is not; the term hull up means that all of the body is visible. The terms originated with sailing and naval warfare in which the curvature of the Earth causes an approaching vessel to be first visible "sails up". Beginning in the 20th century, ''hull down'' has also been used in armoured warfare. In modern armoured warfare, hull down is a position taken up by an armoured fighting vehicle (AFV) so that its hull (the main part of the vehicle) is behind a crest or other raised ground, but its turret (or a superstructure or roof-mounted weapon) is exposed. Turret down is the position in which the vehicle's crew can observe forward from roof hatches, but the vehicle is completely hidden (usually a few metres further back from a hull-down position). The belly armour should not be exposed, because it is vulnerable to even modest antitank weapons. Ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull-down
In sailing and warfare, to be hull down means that the upper part of a vessel or vehicle is visible, but the main, lower body (Hull (watercraft), hull) is not; the term hull up means that all of the body is visible. The terms originated with sailing and naval warfare in which the curvature of the Earth causes an approaching vessel to be first visible "sails up". Beginning in the 20th century, ''hull down'' has also been used in armoured warfare. In modern armoured warfare, hull down is a position taken up by an armoured fighting vehicle (AFV) so that its hull (the main part of the vehicle) is behind a crest or other raised ground, but its turret (or a superstructure or roof-mounted weapon) is exposed. Turret down is the position in which the vehicle's crew can observe forward from roof hatches, but the vehicle is completely hidden (usually a few metres further back from a hull-down position). The belly armour should not be exposed, because it is vulnerable to even modest antitank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
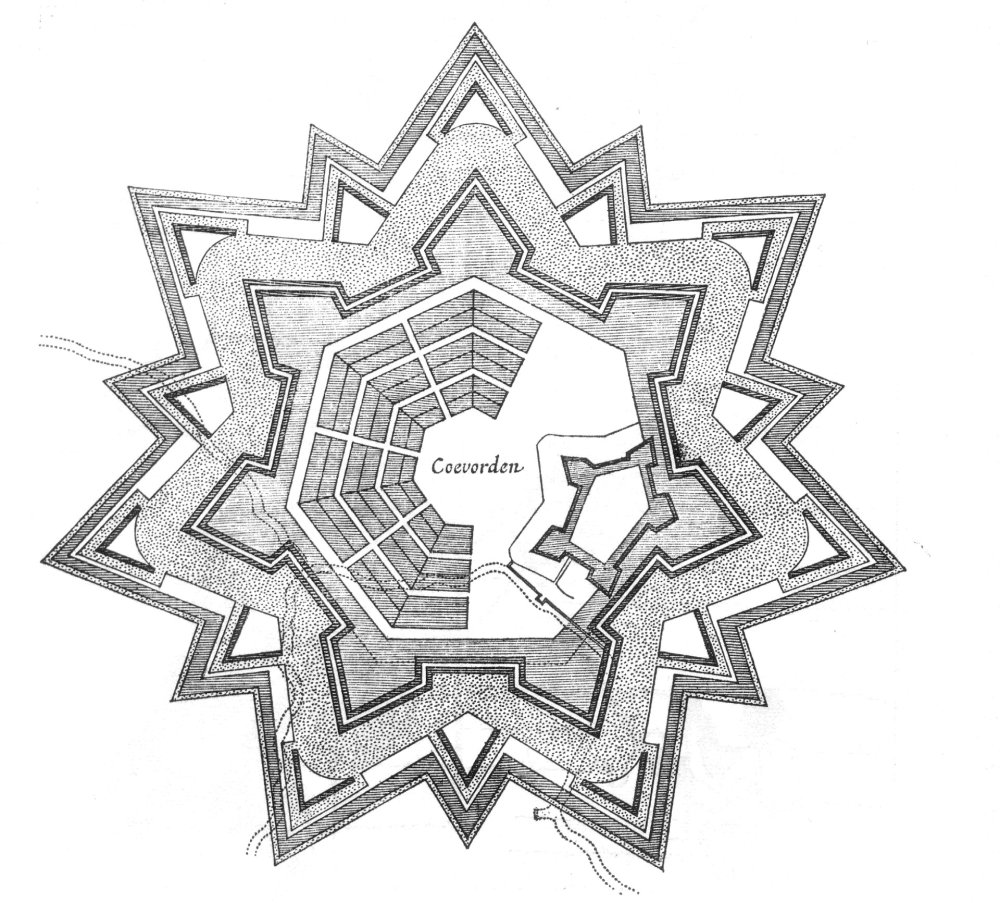
Star Forts
A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, meaning 'Italian outline') is a fortification in a style developed during the early modern period in response to the ascendancy of gunpowder weapons such as cannon, which rendered earlier medieval approaches to fortification obsolete. It appeared in the mid-fifteenth century in Italy. Some types, especially when combined with ravelins and other outworks, resembled the related star fort of the same era. The design of the fort is normally a polygon with bastions at the corners of the walls. These outcroppings eliminated protected blind spots, called "dead zones", and allowed fire along the curtain wall from positions protected from direct fire. Many bastion forts also feature cavaliers, which are raised secondary structures based entirely inside the primary structure. Origins Their predecessors, medieval fortresses, were usually placed on high hills. From there, arrows were shot at the ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient History
Ancient history is a time period from the History of writing, beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian language, Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500, ending with the Early Muslim conquests, expansion of Islam in late antiquity. The three-age system periodises ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages vary between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was Exponential growth, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
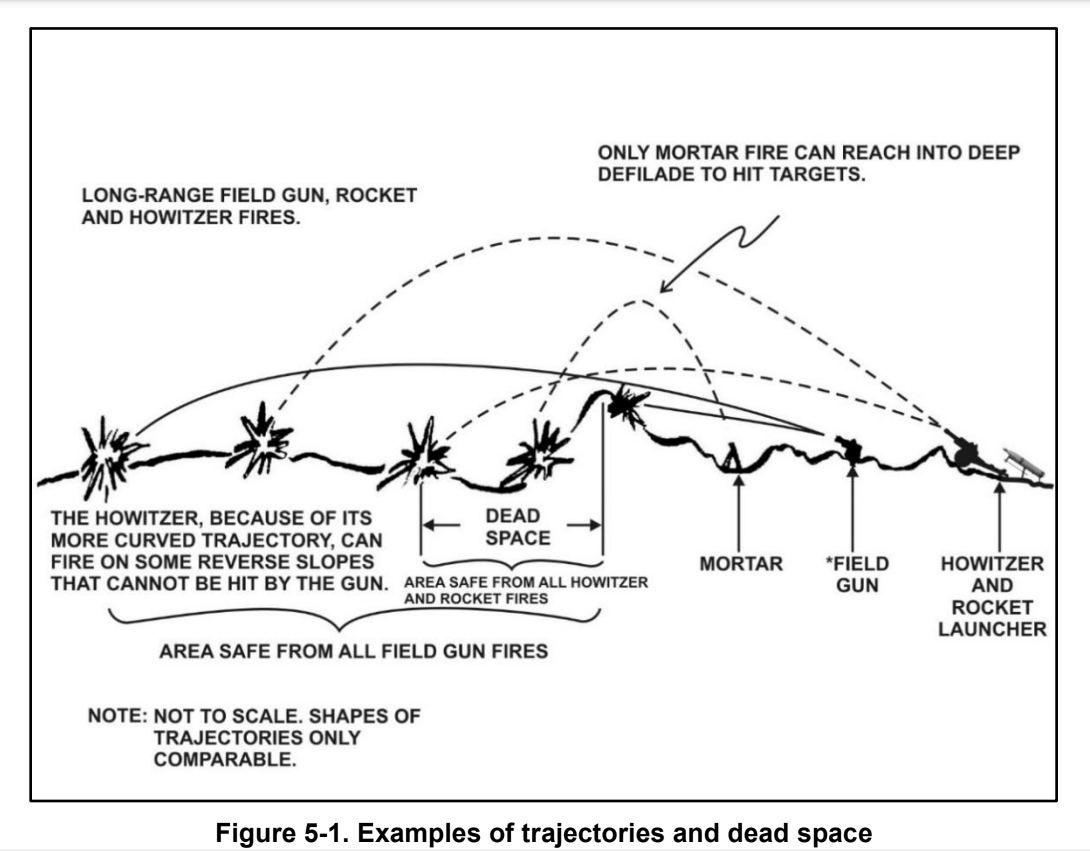
Mortar (weapon)
A mortar today is usually a simple, lightweight, man-portable, Muzzleloader, muzzle-loaded cannon, consisting of a Smoothbore, smooth-bore (although some models use a Rifling, rifled barrel) metal tube fixed to a base plate (to spread out the recoil) with a lightweight bipod mount and a Sight (device), sight. Mortars are typically used as indirect fire weapons for close fire support with a variety of ammunition. Historically mortars were heavy Siege, siege artillery. Mortars launch explosive shell (projectile), shells (technically called Bomb, bombs) in high arching Projectile motion, ballistic trajectories. History Mortars have been used for hundreds of years. The earliest reported use of mortars was in Korea in a 1413 naval battle when Korean gunsmiths developed the ''wan'gu'' (gourd-shaped mortar) (완구, 碗口). The earliest version of the ''wan'gu'' dates back to 1407. Ch'oe Hae-san (1380–1443), the son of Ch'oe Mu-sŏn (1325–1395), is generally credited with inventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indirect Fire
Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by observing the fall of shot and calculating new angles. Description Indirect fire is most commonly used by field artillery and mortars (although field artillery was originally and until after World War I a direct fire weapon, hence the bullet-shields fitted to the carriages of guns such as the famous M1897 75 mm). It is also used with missiles, howitzers, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, naval guns against shore targets, sometimes with machine guns, and has been used with tank and anti-tank guns and by anti-aircraft guns against surface targets. There are two dimensions in aiming a weapon: * In the horizontal plane (azimuth); and * In the vertical plane (elevation), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Slope Defence
A reverse slope defence is a military tactic where a defending force is positioned on the slope of an elevated terrain feature such as a hill, ridge, or mountain, on the side opposite from the attacking force. This tactic both hinders the attacker's ability to observe the defender's positions and reduces the effectiveness of the attacker's long-range weapons such as tanks and artillery. A defending unit usually does not conduct a reverse-slope defence along its entire front, as positioning troops on the forward slope is necessary to control the region in front of the hill. However, when enemy forces are known to have superior long-range direct-fire or indirect-fire weapons, the majority of the defending force can use the hill to limit enemy observation and reduce the effectiveness of the long-range enemy fire. This tactic may even succeed in deceiving the enemy as to the true location and organisation of the main defensive positions. Typically, a smaller unit is still posted on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armored Fighting Vehicle
An armoured fighting vehicle (British English) or armored fighting vehicle (American English) (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by armour, generally combining operational mobility with offensive and defensive capabilities. AFVs can be wheeled or tracked. Examples of AFVs are tanks, armoured cars, assault guns, self-propelled artilleries, infantry fighting vehicles (IFV), and armoured personnel carriers (APC). Armoured fighting vehicles are classified according to their characteristics and intended role on the battlefield. The classifications are not absolute; two countries may classify the same vehicle differently, and the criteria change over time. For example, relatively lightly armed armoured personnel carriers were largely superseded by infantry fighting vehicles with much heavier armament in a similar role. Successful designs are often adapted to a wide variety of applications. For example, the MOWAG Piranha, originally designed as an APC, has been adapted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caponier
A caponier is a type of defensive structure in a fortification. Fire from this point could cover the ditch beyond the curtain wall (fortification), curtain wall to deter any attempt to storm the wall. The word originates from the French ', meaning "chicken coop" (a ''capon'' is a castrated male chicken). In some types of bastioned fortifications, the caponier served as a means of access to the outworks, protecting troops from direct fire; they were often roofless. Although they could be used for firing along the ditch, the flanks of the bastions were the main defence of the ditch by fire. In later polygonal forts, caponiers were often roofed and were not intended as a type of ''covered way'', but as the main way of keeping the ditch clear of a besieger. History Originally the term referred to a covered passageway that traversed the ditch (fortification), ditch outside the curtain of a fortress. Fire from this point could cover the ditch beyond the curtain wall (fortification), cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traverse (archery)
Traverse may refer to: Places * Traverse, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Traverse City, Michigan * Traverse County, Minnesota, a county in Minnesota Other * Traverse (climbing), moving horizontally on a climbing or mountaineering route ** Tyrolean traverse, a climbing rope-technique to cross a chasam * Traverse (fortification), a mass of earth behind a military parapet * Traverse (gunnery), the horizontal field of fire of an artillery piece * ''Traverse'' (magazine), a Northern Michigan regional monthly * TRAVERSE (software), accounting and business software * Traverse (surveying), a method of establishing basic points in the field * Traverse (trench warfare), a development in trench design * Movement of a machine slide on a machine tool * Traverse stage, a style of theatre seating or performance * Traverse Theatre, a writing theatre in Scotland * Traverse Town, a fictional city in some Kingdom Hearts series video games * Chevrolet Traverse, a 2009 sport-utility veh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |