|
Endolymphatic Sac
From the posterior wall of the saccule a canal, the endolymphatic duct, is given off; this duct is joined by the utriculosaccular duct, and then passes along the vestibular aqueduct and ends in a blind pouch, the endolymphatic sac, on the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone, where it is in contact with the dura mater. Studies suggest that the endolymphatic duct and endolymphatic sac perform both absorptive and secretory, as well as phagocytic and immunodefensive, functions. Fittingly, contrast agent uptake in the endolymphatic sac and duct in MRI is inversely correlated to endolymphatic hydrops Endolymphatic hydrops is a disorder of the inner ear. It consists of an excessive build-up of the endolymph fluid, which fills the hearing and balance structures of the inner ear. Endolymph fluid, which is partly regulated by the endolymph sac, ...,J. Gerb, E. Kierig, V. Kirsch, Sandra Becker‐Bense, Rainer Boegle, Thomas Brandt, Marianne Dieterich: ''Contras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccule
The saccule (Latin: sacculus) is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear that detects linear acceleration and head tilting in the vertical plane, and converts these vibrations into electrical impulses to be interpreted by the brain. When the head moves vertically, the sensory cells of the saccule are moved due to a combination of inertia and gravity. In response, the neurons connected to the saccule transmit electrical impulses that represent this movement to the brain. These impulses travel along the vestibular portion of the eighth cranial nerve to the vestibular nuclei in the brainstem. The vestibular system is important for balance, or equilibrium. It includes the saccule, utricle, and the three semicircular canals. The vestibule is the name of the fluid-filled, membranous duct that contains these organs of balance and is in turn encased in the temporal bone of the skull as a part of the inner ear. Structure The saccule, or sacculus, is the smaller of the two vestib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endolymphatic Duct
From the posterior wall of the saccule a canal, the endolymphatic duct, is given off; this duct is joined by the ductus utriculosaccularis, and then passes along the aquaeductus vestibuli and ends in a blind pouch ( endolymphatic sac) on the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone The temporal bone is a paired bone situated at the sides and base of the skull, lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples where four of the cranial bone ..., where it is in contact with the dura mater. Disorders of the endolymphatic duct include Meniere's Disease and Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct. Additional images File:Gray902.png, Transverse section through head of fetal sheep, in the region of the labyrinth. X 30. File:Cross section of semi circular canal svg hariadhi.svg, Transverse section of a human semicircular canal and duct References External links *The Endolymphat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utriculosaccular Duct
The utriculosaccular duct is a part of the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear which connects the two parts of the vestibule, the utricle and the saccule. It continues to the endolymphatic duct and ends in the endolymphatic sac. Importance This structure plays an important role as a duct that serves as a conduit for endolymph between these structures, maintaining proper fluid dynamics essential for vestibular function. Specifically because the utriculosaccular duct carries the endolymphatic fluid to the endolymphatic sac, where it is drained. This system of the endolymphatic fluid prevents excessive fluid build-up in the inner ear, a condition also known as endolymphatic hydrops, which is associated with Ménière´s disease and others vestibular disorders. Further evidence for this physiological drainage mechanism can be seen in contrast-enhanced inner ear MRI Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular Aqueduct
At the posterior lateral wall of the temporal bone is the vestibular aqueduct, which extends to the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. The vestibular aqueduct parallels the petrous apex, in contrast to the cochlear aqueduct, which lies perpendicular to the petrous apex. It transmits a small vein, and contains a tubular prolongation of the membranous labyrinth, the ductus endolymphaticus, which ends in a cul-de-sac, the endolymphatic sac, between the layers of the dura mater within the cranial cavity. Pathology Enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct to greater than 2 mm is associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome, a disease entity that is associated with one-sided hearing loss in children. The diagnosis can be made by high resolution CT or MRI, with comparison to the adjacent posterior semicircular canal The semicircular canals are three semicircular interconnected tubes located in the innermost part of each ear, the inne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrous Portion Of The Temporal Bone
The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word ''petrosus'', meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body. In other mammals, it is a separate bone, the petrosal bone. The petrous bone is important for studies of ancient DNA from skeletal remains, as it tends to contain extremely well-preserved DNA. Base The base is fused with the internal surfaces of the squamous, tympanic, and mastoid parts. Apex The apex, which is rough and uneven, is received into the angular interval between the posterior border of the great wing of the sphenoid bone and the basilar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Bone
The temporal bone is a paired bone situated at the sides and base of the skull, lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples where four of the cranial bones fuse. Each temple is covered by a temporal muscle. The temporal bones house the structures of the ears. The lower seven cranial nerves and the major vessels to and from the brain traverse the temporal bone. Structure The temporal bone consists of four parts—the squamous, mastoid, petrous and tympanic parts. The squamous part is the largest and most superiorly positioned relative to the rest of the bone. The zygomatic process is a long, arched process projecting from the lower region of the squamous part and it articulates with the zygomatic bone. Posteroinferior to the squamous is the mastoid part. Fused with the squamous and mastoid parts and between the sphenoid and occipital bones lies the petrous part, which is shaped li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
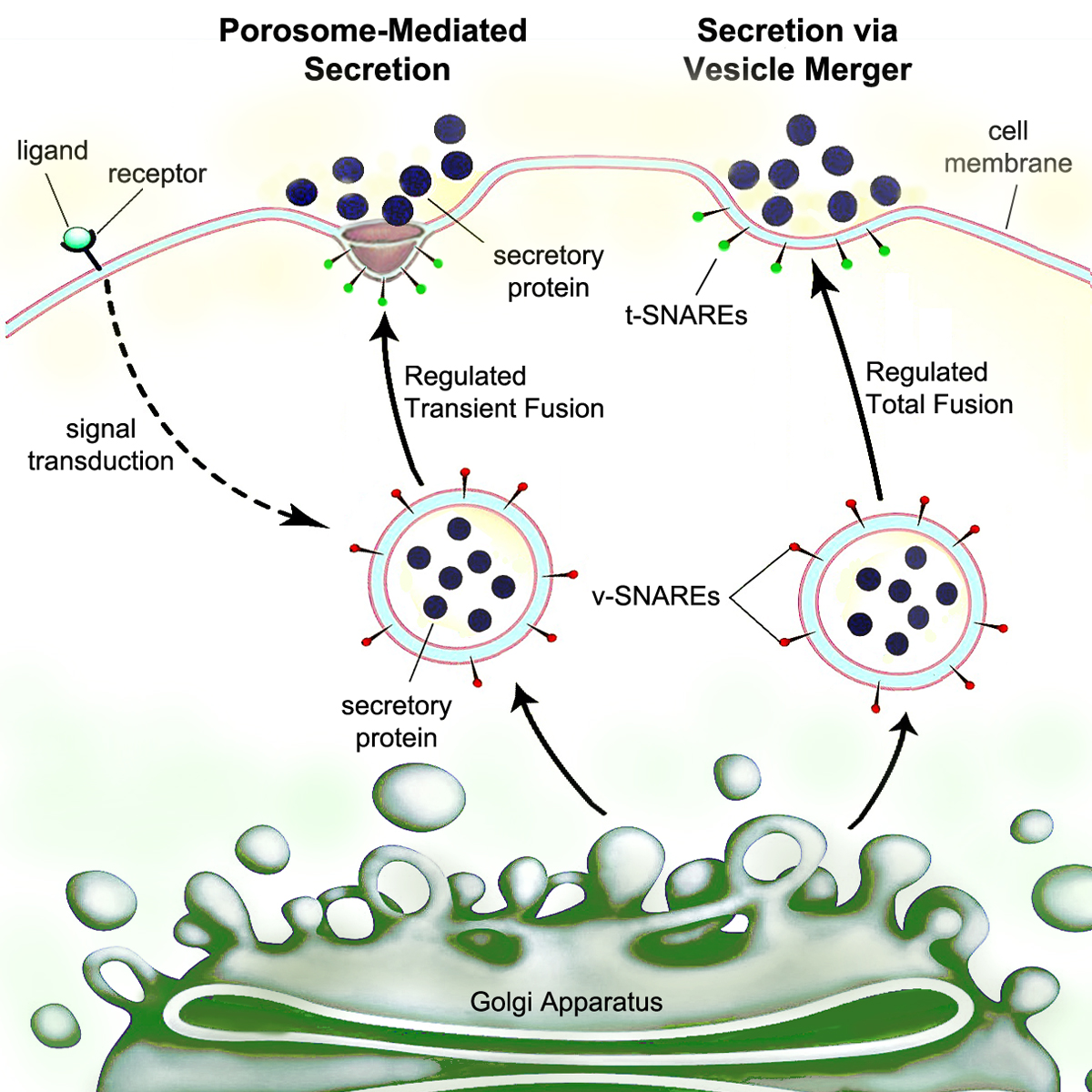
Secretory
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules. For example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast Agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiopharmaceuticals, which emit radiation themselves. In X-ray imaging, contrast agents enhance the radiodensity in a target tissue or structure. In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), contrast agents shorten (or in some instances increase) the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues in order to alter the contrast in the image. Contrast agents are commonly used to improve the visibility of blood vessels and the gastrointestinal tract. The types of contrast agent are classified according to their intended imaging modalities. Radiocontrast media For radiography, which is based on X-rays, iodine and barium are the most common types of contrast agent. Various sorts of iodinated contrast agents exist, with variations occurring between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endolymphatic Hydrops
Endolymphatic hydrops is a disorder of the inner ear. It consists of an excessive build-up of the endolymph fluid, which fills the hearing and balance structures of the inner ear. Endolymph fluid, which is partly regulated by the endolymph sac, flows through the inner ear and is critical to the function of all sensory cells in the inner ear. In addition to water, endolymph fluid contains salts such as sodium, potassium, chloride and other electrolytes. If the inner ear is damaged by disease or injury, the volume and composition of the endolymph fluid can change, causing the symptoms of endolymphatic hydrops. Symptoms The symptoms of endolymphatic hydrops include the feeling of pressure or fullness in the ears, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears) and balance problems. Individuals who have Ménière's disease have a degree of endolymphatic hydrops that is strong enough to trigger the symptoms of this disease, but individuals with endolymphatic hydrops do not always progre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endolymphatic Sac Tumor
An endolymphatic sac tumor (ELST) is a very uncommon papillary epithelial neoplasm arising within the endolymphatic sac or endolymphatic duct. This tumor shows a very high association with Von Hippel–Lindau syndrome (VHL). Classification The ELST has been referred to as adenocarcinoma of endolymphatic sac, Heffner tumor, papillary adenomatous tumor, aggressive papillary adenoma, invasive papillary cystadenoma, and papillary tumor of temporal bone. However, these names are not encouraged as they do not accurately classify the current understanding of the tumor. Signs and symptoms Patients with ELST may present clinically with progressive or fluctuating, one sided sensorineural hearing loss which may mimick Ménière's disease due to the development of tumor associated endolymphatic hydrops. Patients may also experience tinnitus, vertigo, and loss of vestibular function (ataxia). Alternatively, symptom onset may be sudden, due to intralabyrinthine hemorrhage. Patients may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |