|
Endodermis
The endodermis is the innermost layer of cortex in land plants. It is a cylinder of compact living cells, the radial walls of which are impregnated with hydrophobic substances ( Casparian strip) to restrict apoplastic flow of water to the inside. The endodermis is the boundary between the cortex and the stele. In many seedless plants, such as ferns, the endodermis is a distinct layer of cells immediately outside the vascular cylinder (stele) in roots and shoots. In most seed plants, especially woody types, the endodermis is present in roots but not in stems. The endodermis helps regulate the movement of water, ions and hormones into and out of the vascular system. It may also store starch, be involved in perception of gravity and protect the plant against toxins moving into the vascular system. Structure The endodermis is developmentally the innermost portion of the cortex. It may consist of a single layer of barrel-shaped cells without any intercellular spaces or sometimes s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casparian Strip
The Casparian strip is a band-like thickening in the center of the root endodermis (radial and tangential walls of endodermal cells) of vascular plants (Pteridophytes and Spermatophytes). The composition of the region is mainly suberin, lignin and some structural proteins, which are capable of reducing the diffusive apoplastic flow of water and solutes into the stele, its width varies between species. In the root, the Casparian strip is embedded within the cell wall of endodermal cells in the non-growing region of the root behind the root tip.Taiz, L., Zeiger, Eduardo, Møller, Ian Max, & Murphy, Angus. (2015). Plant physiology and development (Sixth ed.). Here, the Casparian strip serves as a boundary layer separating the apoplast of the cortex from the apoplast of the vascular tissue thereby blocking diffusion of material between the two. This separation forces water and solutes to pass through the plasma membrane via a symplastic route in order to cross the endodermis layer. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exodermis
The exodermis is a physiological barrier that has a role in root function and protection. The exodermis is a membrane of variable permeability responsible for the radial flow of water, ions, and nutrients. It is the outer layer of a plant's cortex. The exodermis serves a double function as it can protect the root from invasion by foreign pathogens and ensures that the plant does not lose too much water through diffusion through the root system and can properly replenish its stores at an appropriate rate. Overview and function The exodermis is a specialized type of hypodermis that develops Casparian strips in its cell wall, as well as further wall modifications. The Casparian strip is a band of hydrophobic, corky-like tissue that is found on the outside of the endodermis and the exodermis. Its main function is to prevent solution backflow into the cortex and to maintain root pressure. It is also involved in ensuring that soil is not pulled directly into the root system durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
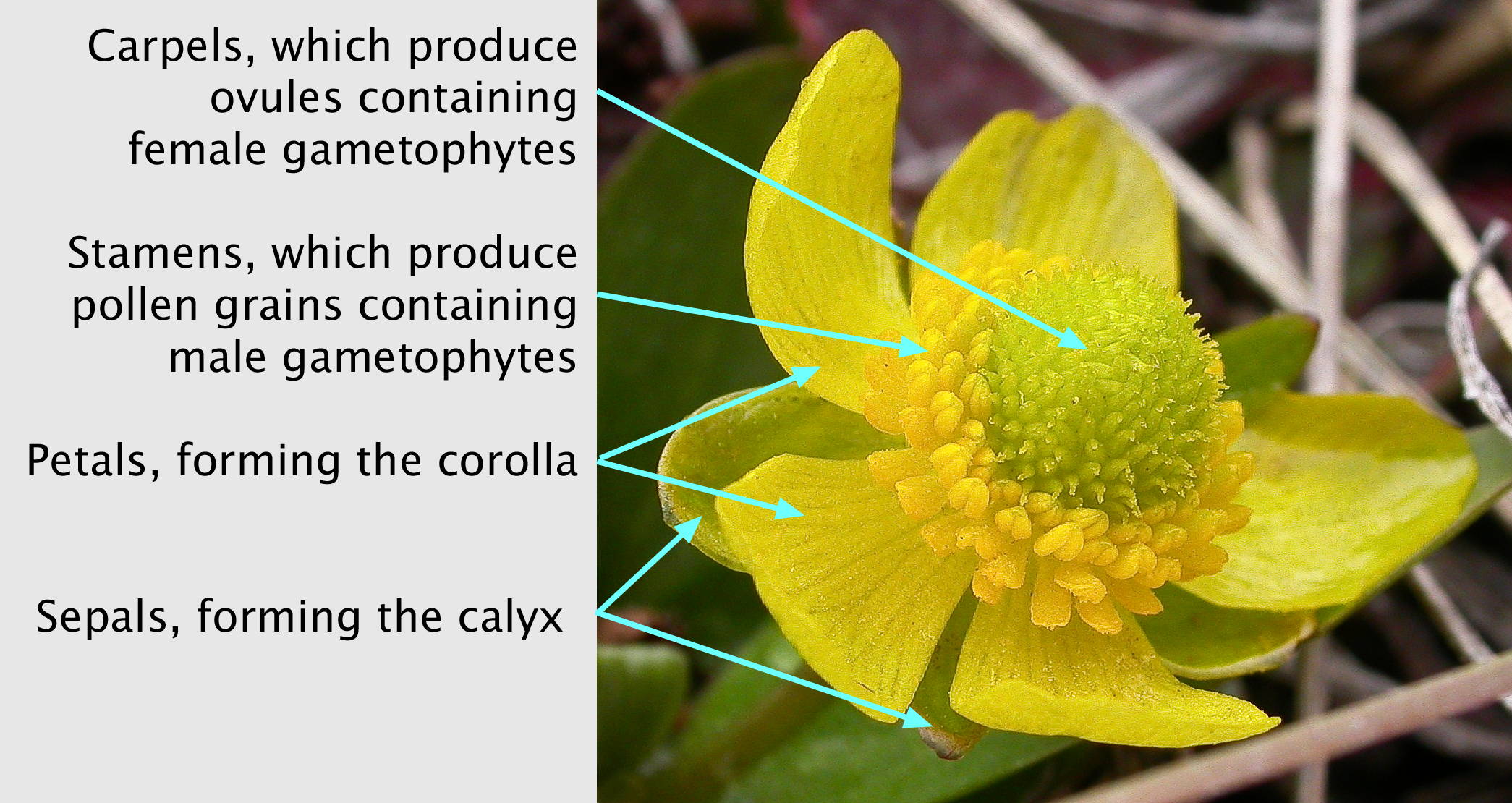
Ranunculus Root Cross Section
''Ranunculus'' is a large genus of about 1750 species of flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae. Members of the genus are known as buttercups, spearworts and water crowfoots. The genus is distributed worldwide, primarily in temperate and montane regions. The familiar and widespread buttercup of gardens throughout Northern Europe (and introduced elsewhere) is the creeping buttercup ''Ranunculus repens'', which has extremely tough and tenacious roots. Two other species are also widespread, the bulbous buttercup ''Ranunculus bulbosus'' and the much taller meadow buttercup ''Ranunculus acris''. In ornamental gardens, all three are often regarded as weeds. Buttercups usually flower in the spring, but flowers may be found throughout the summer, especially where the plants are growing as opportunistic colonizers, as in the case of garden weeds. The water crowfoots (''Ranunculus'' subgenus ''Batrachium''), which grow in still or running water, are sometimes treated in a separa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortex (botany)
In botany, a cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a vascular plant, lying below the epidermis but outside of the vascular bundles. The cortex is composed mostly of large thin-walled parenchyma cells of the ground tissue system and shows little to no structural differentiation. The outer cortical cells often acquire irregularly thickened cell walls, and are called collenchyma cells. Plants Stems and branches In the three dimensional structure of herbaceous stems, the epidermis, cortex and vascular cambium form concentric cylinders around the inner cylindrical core of pith. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts, giving them a green color. They can therefore produce simple carbohydrates through photosynthesis. In woody plants, the cortex is located between the periderm (bark) and the vascular tissue ( phloem, in particular). It is responsible for the transportation of materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Plants
The embryophytes () are a clade of plants, also known as Embryophyta (Plantae ''sensu strictissimo'') () or land plants. They are the most familiar group of photoautotrophs that make up the vegetation on Earth's dry lands and wetlands. Embryophytes have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of freshwater charophyte green algae as a sister taxon of Charophyceae, Coleochaetophyceae and Zygnematophyceae. Embryophytes consist of the bryophytes and the polysporangiophytes. Living embryophytes include hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms (flowering plants). Embryophytes have diplobiontic life cycles. The embryophytes are informally called "land plants" because they thrive primarily in terrestrial habitats (despite some members having evolved secondarily to live once again in semiaquatic/ aquatic habitats), while the related green algae are primarily aquatic. Embryophytes are comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophobe
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thus, prefer other neutral molecules and nonpolar solvents. Because water molecules are polar, hydrophobes do not dissolve well among them. Hydrophobic molecules in water often cluster together, forming micelles. Water on hydrophobic surfaces will exhibit a high contact angle. Examples of hydrophobic molecules include the alkanes, oils, fats, and greasy substances in general. Hydrophobic materials are used for oil removal from water, the management of oil spills, and chemical separation processes to remove non-polar substances from polar compounds. The term ''hydrophobic''—which comes from the Ancient Greek (), "having a fear of water", constructed Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoplast
The ''apoplast '' is the extracellular space outside of plant cell membranes, especially the fluid-filled cell walls of adjacent cells where water and dissolved material can flow and diffuse freely. Fluid and material flows occurring in any extracellular space are called ''apoplastic'' flow or apoplastic transport. The apoplastic pathway is one route by which water and solutes are transported and distributed to different places through tissues and organs, contrasting with the symplastic pathway. To prevent uncontrolled leakage to unwanted places, in certain areas there are barriers to the apoplastic flow: in roots the Casparian strip has this function Outside the plant epidermis of aerial plant parts is a protective waxy film called plant cuticle that protects against drying out, but also waterproofs the plant against external water. The apoplast is important for all the plant's interaction with its environment: The main carbon source (carbon dioxide) needs to be solubil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele (biology)
In a vascular plant, the stele is the central part of the root or Plant stem, stem containing the tissues derived from the procambium. These include vascular tissue, in some cases ground tissue (pith) and a pericycle, which, if present, defines the outermost boundary of the stele. Outside the stele lies the endodermis, which is the innermost cell layer of the cortex. The concept of the stele was developed in the late 19th century by France, French botanists Phillippe Édouard Léon van Tieghem, P. E. L. van Tieghem and H. Doultion as a model for understanding the relationship between the Shoot (botany), shoot and root, and for discussing the evolution of vascular plant morphology. Now, at the beginning of the 21st century, plant molecular biologists are coming to understand the genetics and developmental pathways that govern tissue patterns in the stele. Moreover, physiologists are examining how the anatomy (sizes and shapes) of different steles affect the function of organs. Proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seedless Plants
A cryptogam (scientific name ''Cryptogamae'') is a plant, in the broad sense of the word, or a plant-like organism that share similar characteristics, such as being multicellular, photosynthetic, and primarily immobile, that reproduces via spores rather than through flowers or seeds. This broader definition can include algae, fungi, and certain bacteria (like cyanobacteria), even though they may belong to different biological kingdoms. Taxonomy The name ''Cryptogamae'' () means "hidden reproduction", meaning non-seed bearing plants. Other names, such as "thallophytes", "lower plants", and "spore plants" have occasionally been used. As a group, Cryptogamae are paired with the Phanerogamae or Spermatophyta, the seed plants. At one time, the cryptogams were formally recognised as a group within the plant kingdom. In his system for classification of all known plants and animals, Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) divided the plant kingdom into 24 classes, one of which was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients, and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaf, leaves called megaphylls that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled Fiddlehead fern, fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate (Polypodiidae (plant), Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, Psilotaceae, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid ferns. The fern crown group, consisting of the leptosporangiates and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suberin
Suberin is a lipophilic, complex polyester biopolymer found in plants. It is composed of long-chain fatty acids (called suberin acids) and glycerol. Suberin is interconnected with cutin and lignin and forms a protective barrier in the epidermal and peridermal cell walls of higher plants. Suberin and lignin are considered covalently linked to lipids and carbohydrates, respectively. Lignin is again covalently linked to suberin, and to a lesser extent to cutin, thus construdting a complex macromolecular matrix. Suberin is a major constituent of cork, and is named after the cork oak, '' Quercus suber''. Its main function is as a barrier to movement of water and solutes. Anatomy and physiology Suberin is highly hydrophobic and a somewhat 'rubbery' material. In roots, suberin is deposited in the radial and transverse/tangential cell walls of the endodermal cells. This structure, known as the Casparian strip or Casparian band, functions to prevent water and nutrients taken up by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium, multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of Epithelium#Cell types, columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The thickness of the epidermis varies from 31.2μm for the penis to 596.6μm for the Sole (foot), sole of the foot with most being roughly 90μm. Thickness does not vary between the sexes but becomes thinner with age. The human epidermis is an example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |