|
Endocervix
The cervical canal is the spindle-shaped, flattened canal of the cervix which connects the vagina to the main cavity of the uterus in most mammals. Anatomy The cervical canal communicates with the uterine cavity via the internal orifice of the uterus (or internal os) and with the vagina via the external orifice of the uterus (ostium of uterus or external os). The internal orifice of the uterus is an interior narrowing of the uterine cavity. It corresponds to a slight constriction known as the ''isthmus'' that can be seen on the surface of the uterus about midway between the apex and base. The external orifice of the uterus is a small, depressed, somewhat circular opening on the rounded extremity of the cervix, opening to the vagina. Through this aperture, the cervical cavity communicates with that of the vagina. The external orifice is bounded by two lips, an anterior and a posterior. The anterior is shorter and thicker, though it projects lower than the posterior because of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervix is approximately 4 cm long with a diameter of approximately 3 cm and tends to be described as a cylindrical shape, although the front and back walls of the cervix are contiguous. The size of the cervix changes throughout a woman's life cycle. For example, women in the fertile years of their reproductive cycle tend to have larger cervixes than postmenopausal women; likewise, women who have produced offspring have a larger cervix than those who have not. In relation to the vagina, the part of the cervix that opens to the uterus is called the ''internal os'' and the opening of the cervix in the vagina is called the ''external os''. Between them is a conduit commonly called the cervic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
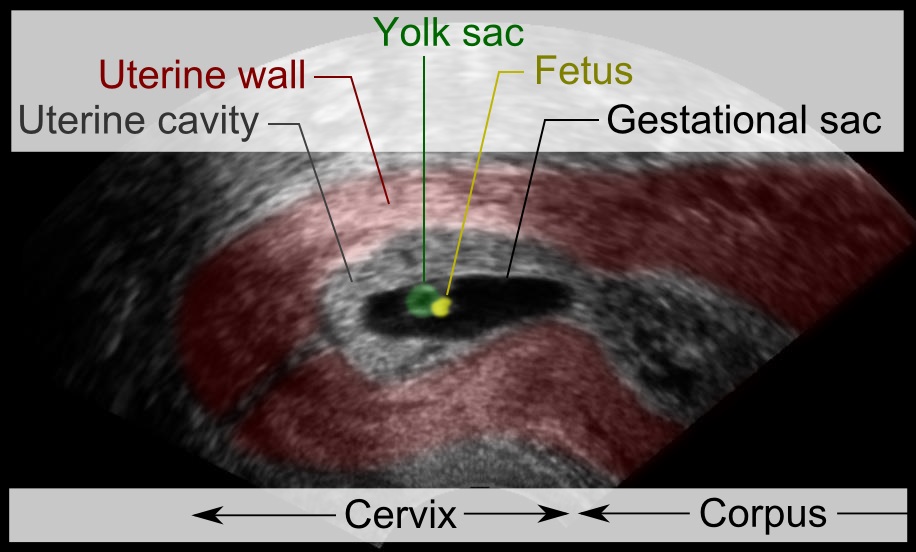
Cervical Pregnancy
A cervical pregnancy is an ectopic pregnancy that has implanted in the uterine endocervix. Such a pregnancy typically aborts within the first trimester, however, if it is implanted closer to the uterine cavity – a so-called cervico-isthmic pregnancy – it may continue longer. Placental removal in a cervical pregnancy may result in major hemorrhage. Diagnosis The diagnosis is made in asymptomatic pregnant women either by inspection seeing a bluish discolored cervix or, more commonly, by obstetric ultrasonography. A typical non-specific symptom is vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. Ultrasound will show the location of the gestational sac in the cervix, while the uterine cavity is "empty". Cervical pregnancy can be confused with a miscarriage when pregnancy tissue is passing through the cervix. Histologically the diagnosis has been made by Rubin's criteria on the surgical specimen: cervical glands are opposite the trophoblastic tissue, the trophoblastic attachment is below the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
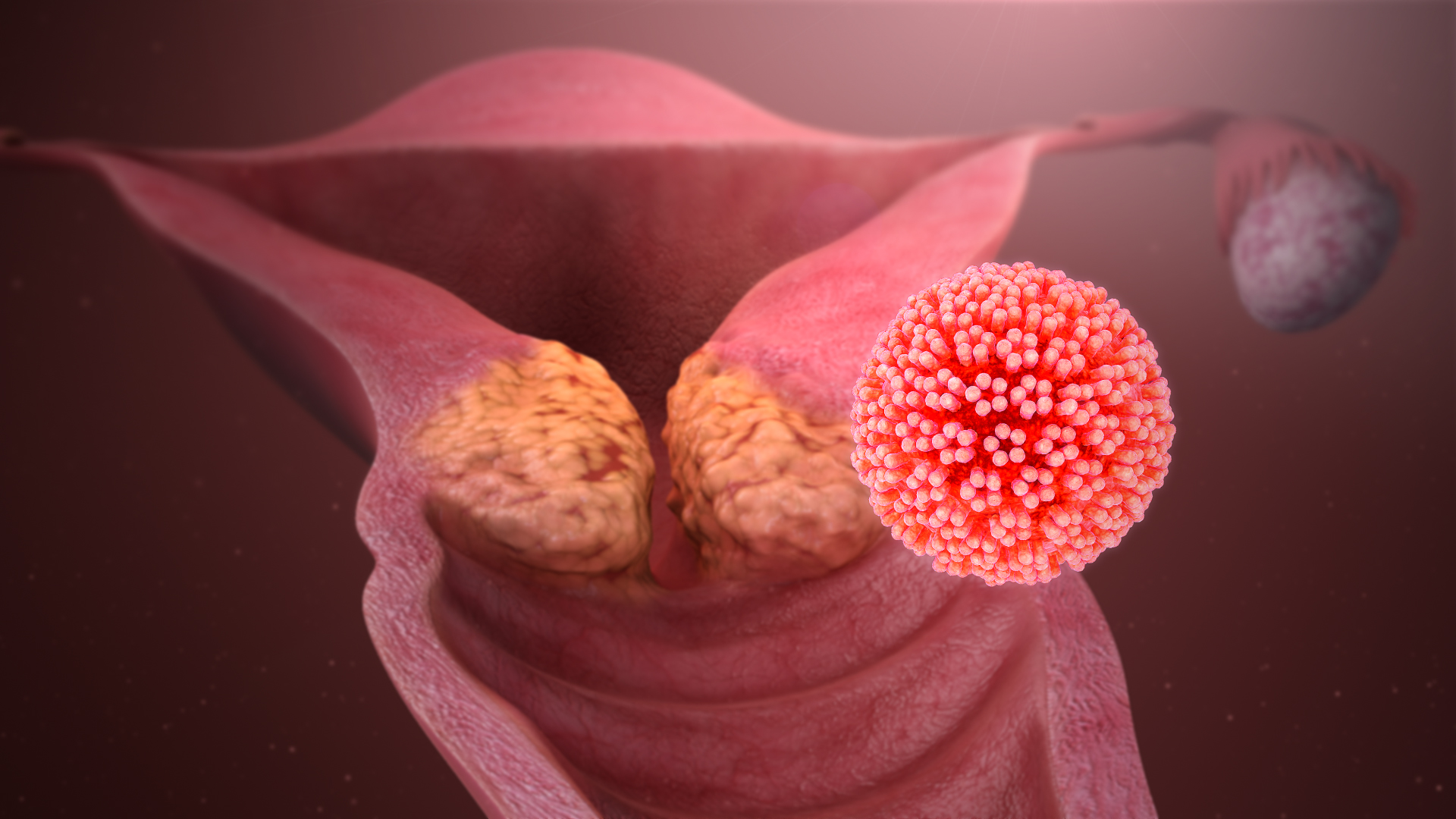
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. All warts are caused by HPV. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervical cancer, cervix, vulva cancer, vulva, vaginal cancer, vagina, penis cancer, penis, anal cancer, anus, oropharyngeal cancer, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV, and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of all cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by the ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vimentin
Vimentin is a structural protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VIM'' gene. Its name comes from the Latin ''vimentum'' which refers to an array of flexible rods. Vimentin is a Intermediate filament#Type III, type III intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed in mesenchymal cells. Intermediate filament, IF proteins are found in all Animal, animal cells as well as bacteria. Intermediate filaments, along with tubulin-based microtubules and actin-based microfilaments, comprise the cytoskeleton. All IF proteins are expressed in a highly developmentally-regulated fashion; vimentin is the major cytoskeletal component of mesenchymal cells. Because of this, vimentin is often used as a marker of mesenchymally-derived cells or cells undergoing an Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during both normal development and Metastasis, metastatic progression. Structure The assembly of the fibrous vimentin filament that forms the cytosk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone Receptor
The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone. In humans, PR is encoded by a single ''PGR'' gene residing on chromosome 11q22, it has two isoforms, PR-A and PR-B, that differ in their molecular weight. The PR-B is the positive regulator of the effects of progesterone, while PR-A serve to antagonize the effects of PR-B. Mechanism Progesterone is necessary to induce activation of the progesterone receptors. When no binding hormone is present the carboxyl terminal inhibits transcription. Binding to a hormone induces a structural change that removes the inhibitory action. Progesterone antagonists prevent the structural reconfiguration. After progesterone binds to the receptor, restructuring with dimerization follows and the complex enters the nucleus and binds to DNA. There transcription takes place, resulting in formation of messenge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen Receptor
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are proteins found in cell (biology), cells that function as receptor (biochemistry), receptors for the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). There are two main classes of ERs. The first includes the intracellular estrogen receptors, namely ERα and ERβ, which belong to the nuclear receptor family. The second class consists of membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), such as GPER (GPR30), ER-X, and Gq-mER, Gq-mER, which are primarily G protein-coupled receptors. This article focuses on the nuclear estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ). Upon activation by estrogen, intracellular ERs undergo protein targeting, translocation to the nucleus where they bind to specific DNA sequences. As DNA-binding transcription factors, they regulate the activity of various genes. However, ERs also exhibit functions that are independent of their DNA-binding capacity. These non-genomic actions contribute to the diverse effects of estrogen signaling in cells. Estrogen receptors (ERs) b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P16 (gene)
p16 (also known as p16INK4a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, CDKN2A, multiple tumor suppressor 1 and numerous other synonyms), is a protein that slows cell division by slowing the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S phase, thereby acting as a tumor suppressor. It is encoded by the ''CDKN2A'' gene. A deletion (the omission of a part of the DNA sequence during replication) in this gene can result in insufficient or non-functional p16, accelerating the cell cycle and resulting in many types of cancer. p16 can be used as a biomarker to improve the histological diagnostic accuracy of grade 3 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). p16 is also implicated in the prevention of melanoma, oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma, cervical cancer, vulvar cancer and esophageal cancer. p16 was discovered in 1993. It is a protein with 148 amino acids and a molecular weight of 16 kDa that comprises four ankyrin repeats. The name of p16 is derived from its molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoembryonic Antigen
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) describes a set of highly-related glycoproteins involved in cell adhesion. CEA is normally produced in gastrointestinal tissue during fetal development, but the production stops before birth. Consequently, CEA is usually present at very low levels in the blood of healthy adults (about 2–4 ng/mL). However, the serum levels are raised in some types of cancer, which means that it can be used as a tumor marker in clinical tests. Serum levels can also be elevated in heavy smoking, smokers. CEA are Glycosylphosphatidylinositol, glycosyl phosphatidyl inositol (GPI) cell-surface-anchored glycoproteins whose specialized Sialyl-Lewis X, sialo Fucosylation, fucosylated glycoforms serve as functional colon carcinoma L-selectin and E-selectin ligands, which may be critical to the metastatic dissemination of colon carcinoma cells. Immunologically they are characterized as members of the CD66 cluster of differentiation. The proteins include CD66a, CD66b, CD6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
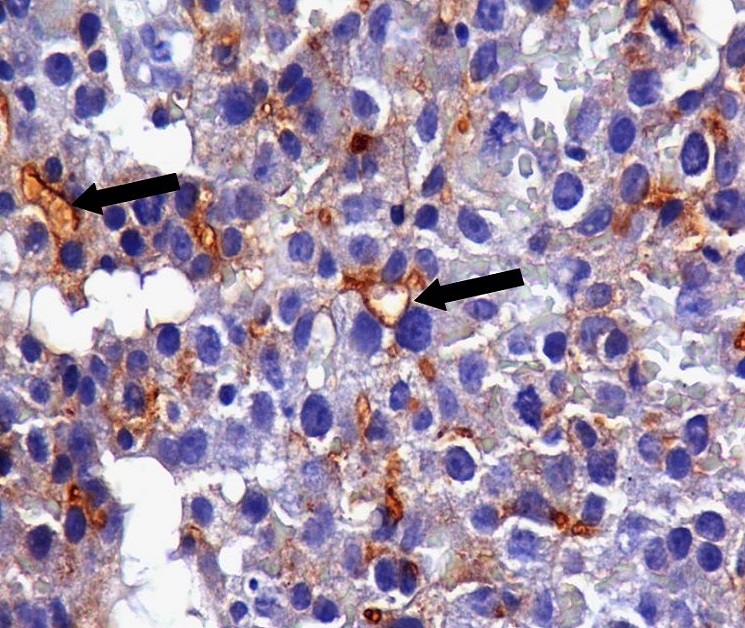
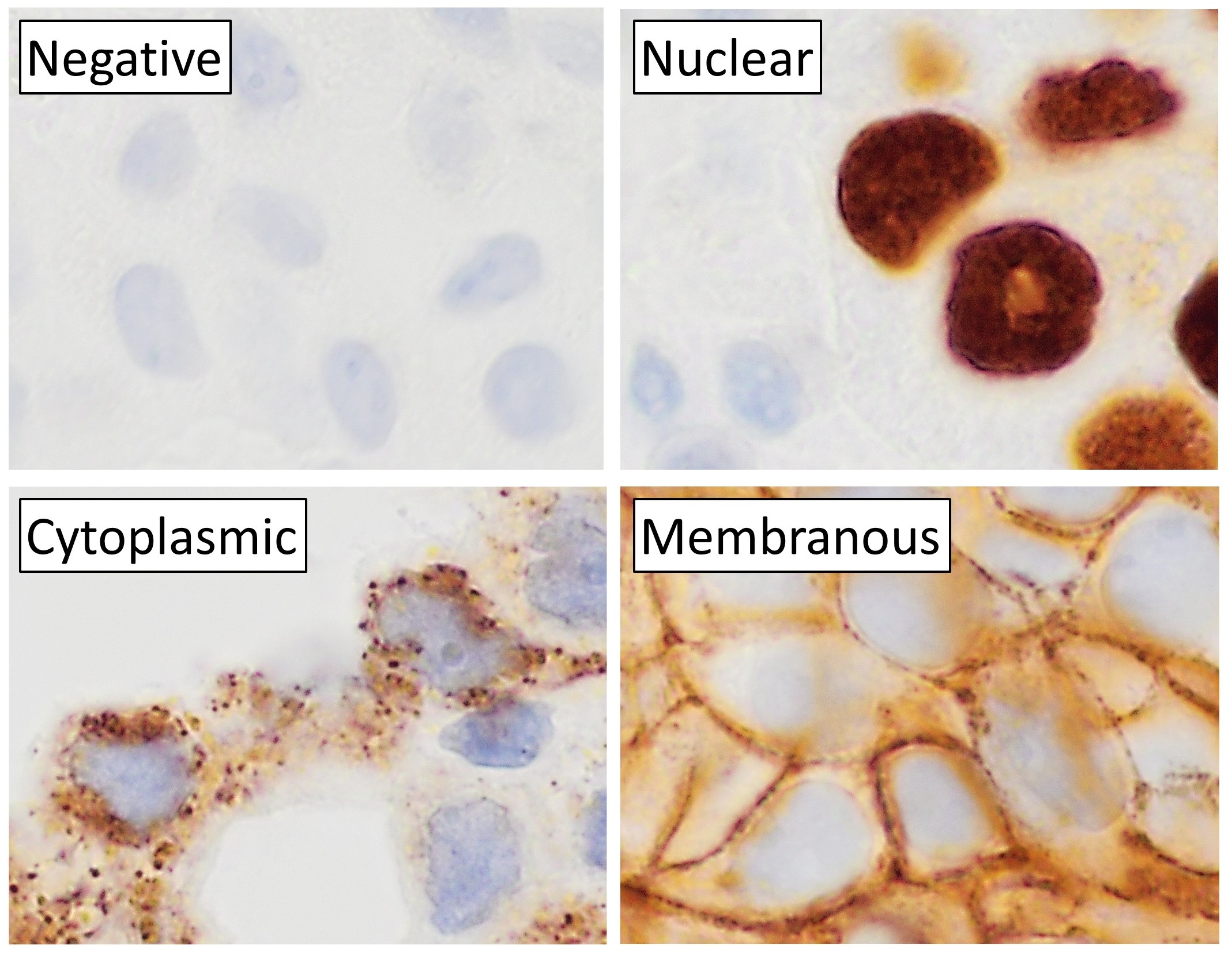
Immunohistochemical Staining
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett Coons, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in paraffin, but also cryopreservated (frozen) tissue. Based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is a cancer that arises from the endometrium (the epithelium, lining of the uterus or womb). It is the result of the abnormal growth of cells (biology), cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first sign is most often vaginal bleeding not associated with a menstrual period. Other symptoms include dysuria, pain with urination, dyspareunia, pain during sexual intercourse, or pelvic pain. Endometrial cancer occurs most commonly after menopause. Approximately 40% of cases are related to obesity. Endometrial cancer is also associated with excessive estrogen exposure, hypertension, high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus, diabetes. Whereas taking estrogen alone increases the risk of endometrial cancer, taking both estrogen and a progestogen in combination, as in most birth control pills, decreases the risk. Between two and five percent of cases are related to genes inherited from the parents. Endometrial cancer is sometimes called "uterin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, fetal development of one or more Fertilized egg, fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains uterine gland, glands in its endometrium, lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. (The term ''uterus'' is also applied to analogous structures in some non-mammalian animals.) In humans, the lower end of the uterus is a narrow part known as the Uterine isthmus, isthmus that connects to the cervix, the anterior gateway leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes at the uterine horns; the rounded part, the fundus, is above the openings to the fallopian tubes. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the utero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |