|
Embedded Java
Embedded Java refers to versions of the Java program language that are designed for embedded systems. Since 2010 embedded Java implementations have come closer to standard Java, and are now virtually identical to the Java Standard Edition. Since Java 9 customization of the Java Runtime through modularization removes the need for specialized Java profiles targeting embedded devices. History Although in the past some differences existed between embedded Java and traditional PC based Java, the only difference now is that embedded Java code in these embedded systems is mainly contained in constrained memory, such as flash memory. A complete convergence has taken place since 2010, and now Java software components running on large systems can run directly with no recompilation at all on design-to-cost mass-production devices (such as consumers, industrial, white goods, healthcare, metering, smart markets in general) CORE embedded Java API for a unified Embedded Java ecosystem In or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded World 2014 Oracle Java (02)
Embedded or embedding (alternatively imbedded or imbedding) may refer to: Science * Embedding, in mathematics, one instance of some mathematical object contained within another instance ** Graph embedding * Embedded generation, a distributed generation of energy, also known as decentralized generation * Self-embedding, in psychology, an activity in which one pushes items into one's own flesh in order to feel pain * Embedding, in biology, a part of sample preparation for microscopes * Embeddedness, in economics and economic sociology, refers to the degree to which economic activity is constrained by non-economic institutions. Computing * Embedded system, a special-purpose system in which the computer is completely encapsulated by the device it controls * Embedding, installing media into a text document to form a compound document ** , a HyperText Markup Language (HTML) element that inserts a non-standard object into the HTML document * Web embed, an element of a host web pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users and Windows Me for home users. Development of Windows XP began in the late 1990s under the codename "Windows Neptune, Neptune", built on the Architecture of Windows NT#Kernel, Windows NT kernel and explicitly intended for mainstream consumer use. An updated version of Windows 2000 was also initially planned for the business market. However, in January 2000, both projects were scrapped in favor of a single OS codenamed "Whistler", which would serve as a single platform for both consumer and business markets. As a result, Windows XP is the first consumer edition of Windows not based on the Windows 95 kernel or MS-DOS. Upon its release, Windows XP received critical acclaim, noting increased performance and stability (especially compared to Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Platform
Java is a set of computer software and specifications that provides a software platform for developing application software and deploying it in a cross-platform computing environment. Java is used in a wide variety of computing platforms from embedded devices and mobile phones to enterprise servers and supercomputers. Java applets, which are less common than standalone Java applications, were commonly run in secure, Sandbox (computer security), sandboxed environments to provide many features of native applications through being embedded in HTML pages. Writing in the Java (programming language), Java programming language is the primary way to produce code that will be deployed as Java byte code, byte code in a Java virtual machine (JVM); byte code compilers are also available for other languages, including Ada (programming language), Ada, JavaScript, Kotlin (programming language), Kotlin (Google's preferred Android language), Python (programming language), Python, and Ruby (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STM32
STM32 is a family of 32-bit microcontroller and microprocessor integrated circuits by STMicroelectronics. STM32 microcontrollers are grouped into related series that are based around the same 32-bit ARM processor core: Cortex-M0, Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, Cortex-M33, or Cortex-M55. Internally, each microcontroller consists of ARM processor core(s), flash memory, static RAM, a debugging interface, and various peripherals. In addition to its microcontroller lines, STMicroelectronics has introduced microprocessor (MPU) offerings such as the MP1 and MP2 series into the STM32 family. These processors are based around single or dual ARM Cortex-A cores combined with an ARM Cortex-M core. Cortex-A application processors include a memory management unit (MMU), enabling them to run advanced operating systems such as Linux. Overview The STM32 family of the microcontroller ICs is based on various 32-bit RISC ARM Cortex-M cores. STMicroelectronics licenses the ARM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JamaicaVM
The JamaicaVM is a virtual machine and build environment for developing and running realtime Java programs. It includes a deterministic garbage collector and implements the RTSJ.Fridtjof Siebert, "Realtime Garbage Collection in the JamaicaVM 3.0", JTRES 2007, 26–28 September 2007, Vienna, Austria It is designed for use in both realtime and embedded systems. It provides the base runtime environment for JamaicaCAR. See also * Real-time Java Real-time Java is a catch-all term for a combination of technologies that enables programmers to write programs that meet the demands of real-time systems A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a s ... * Embedded Java References External links JamaicaVM {{DEFAULTSORT:Jamaicavm Java virtual machine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azul Systems
Azul Systems, Inc. (also known as Azul) is a company that develops and distributes runtimes ( JDK, JRE, JVM) for executing Java-based applications. The company was founded in March 2002. Azul Systems has headquarters in Sunnyvale, California. History Azul Systems was founded by Scott Sellers (now President & CEO), Gil Tene (CTO), and Shyam Pillalamarri. Initially founded as a hardware appliance company, Azul's Java Compute Appliances (JCAs) were designed to massively scale up the usable computing resources available to Java applications. The first compute appliances, offered in April 2005, were the Vega 1-based models. With the introduction of Azul Platform Prime in 2010, the company transitioned to producing software-only products. It retired its hardware appliance Vega product lines in 2013. Stephen DeWitt previously held the position of CEO. On April 1, 2020, Azul announced that it had closed a strategic growth equity investment led by London-based Vitruvian Partners and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-Time Specification For Java
Real-time Java is a catch-all term for a combination of technologies that enables programmers to write programs that meet the demands of real-time systems in the Java programming language. Java's sophisticated memory management, native support for threading and concurrency, type safety, and relative simplicity have created a demand for its use in many domains. Its capabilities have been enhanced to support real-time computational needs: * Real-time Java supports a strict priority-based threading model, * because Java threads support priorities, Java locking mechanisms support priority inversion avoidance techniques, such as priority inheritance or the priority ceiling protocol, and * event handling. The initial proposal for an open standard for real-time Java was put forth by Kelvin Nilsen, then serving as a research faculty member at Iowa State University. A follow-on overview paper was published in the ''Communications of the ACM''. The overwhelmingly positive response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun SPOT
Sun SPOT (Sun Small Programmable Object Technology) was a sensor node for a wireless sensor network developed by Sun Microsystems announced in 2007. The device used the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for its networking, and unlike other available sensor nodes, used the Squawk virtual machine, Squawk Java virtual machine. After the acquisition of Sun Microsystems by Oracle Corporation, the SunSPOT platform was supported but its forum was shut down in 2012. A mirror of the old site is maintained for posterity. Hardware The completely assembled device fit in the palm of a hand. Its first processor board included an ARM architecture 32 bit CPU with ARM9, ARM920T core running at 180 MHz. It had 512 KB RAM and 4 MB flash memory. A 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.15.4 radio had an integrated antenna and a USB interface was included. A sensor board included a three-axis accelerometer (with 2G and 6G range settings), temperature sensor, light sensor, 8 tri-color LEDs, analog and dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excelsior JET
Excelsior JET is a now-defunct proprietary Java SE technology implementation built around an ahead-of-time (AOT) Java to native code compiler. The compiler transforms the portable Java bytecode into optimized executables for the desired hardware and operating system (OS). Also included are a Java runtime featuring a just-in-time (JIT) compiler for handling classes that were not precompiled for whatever reason (e.g. third-party plugins or dynamic proxies), the complete Java SE API implementation licensed from Oracle, and a toolkit to aid deployment of the optimized applications. Excelsior JET was developed by Excelsior LLC, headquartered in Novosibirsk, Russia. Overview Excelsior JET passed the "official" test suite (TCK) for Java SE 8, and was certified Java Compatible on macOS and a number of Windows and Linux flavors running on Intel x86, AMD64/Intel 64 and compatible hardware. (The macOS version was 64-bit only.) The Enterprise Edition supported the Equinox OSGi runtime at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIPS Architecture
MIPS (Microprocessor without Interlocked Pipelined Stages) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures (ISA)Price, Charles (September 1995). ''MIPS IV Instruction Set'' (Revision 3.2), MIPS Technologies, Inc. developed by MIPS Computer Systems, now MIPS Technologies, based in the United States. There are multiple versions of MIPS, including MIPS I, II, III, IV, and V, as well as five releases of MIPS32/64 (for 32- and 64-bit implementations, respectively). The early MIPS architectures were 32-bit; 64-bit versions were developed later. As of April 2017, the current version of MIPS is MIPS32/64 Release 6. MIPS32/64 primarily differs from MIPS I–V by defining the privileged kernel mode System Control Coprocessor in addition to the user mode architecture. The MIPS architecture has several optional extensions: MIPS-3D, a simple set of floating-point SIMD instructions dedicated to 3D computer graphics; MDMX (MaDMaX), a more extensive i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple Inc., Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM alliance, AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors. Originally intended for personal computers, the architecture is well known for being used by Apple's desktop and laptop lines from 1994 until 2006, and in several videogame consoles including Microsoft's Xbox 360, Sony's PlayStation 3, and Nintendo's GameCube, Wii, and Wii U. PowerPC was also used for the Curiosity (rover), Curiosity and Perseverance (rover), Perseverance rovers on Mars and a variety of satellites. It has since become a niche architecture for personal computers, particularly with A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
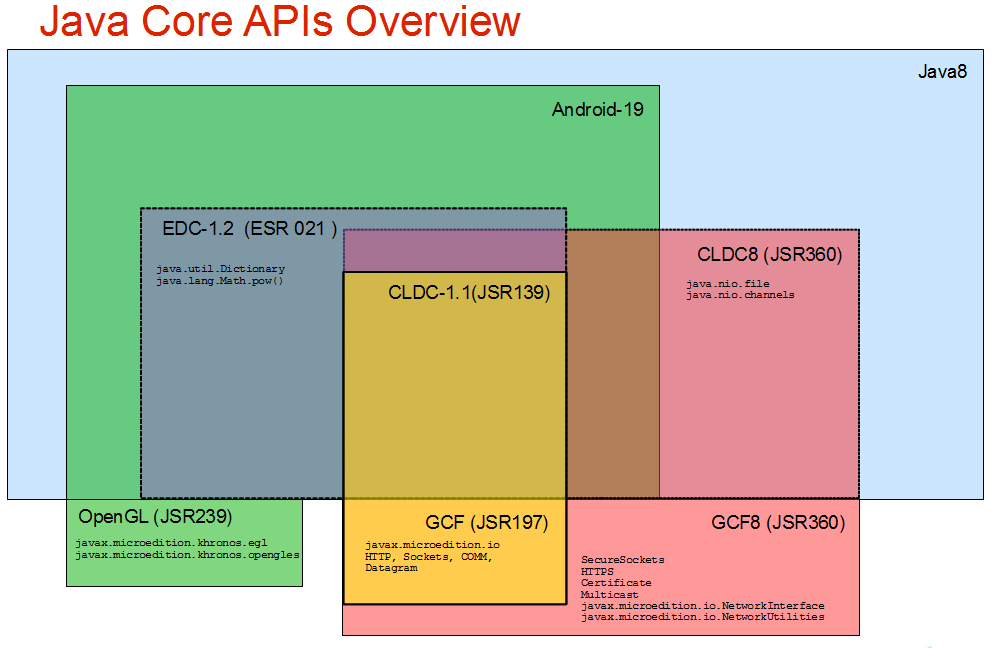
Java Platform, Micro Edition
Java Platform, Micro Edition or Java ME is a computing platform for development and deployment of portable code for embedded and mobile devices (micro-controllers, sensors, gateways, mobile phones, personal digital assistants, TV set-top boxes, printers). Java ME was formerly known as Java 2 Platform, Micro Edition or J2ME. The platform uses the object-oriented Java programming language, and is part of the Java software-platform family. It was designed by Sun Microsystems (now Oracle Corporation) and replaced a similar technology, PersonalJava. In 2013, with more than 3 billion Java ME enabled mobile phones in the market, the platform was in continued decline as smartphones have overtaken feature phones. History The platform used to be popular in feature phones, such as Nokia's Series 40 models. It was also supported on the Bada operating system and on Symbian OS along with native software. Users of Windows CE, Windows Mobile, Maemo, MeeGo and Androi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |