|
Elizabeth Barrett
Elizabeth Barrett Browning (née Moulton-Barrett; 6 March 1806 – 29 June 1861) was an English poet of the Victorian era, popular in Britain and the United States during her lifetime and frequently anthologised after her death. Her work received renewed attention following the feminist scholarship of the 1970s and 1980s, and greater recognition of women writers in English. Born in County Durham, the eldest of 12 children, Elizabeth Barrett wrote poetry from the age of eleven. Her mother's collection of her poems forms one of the largest extant collections of juvenilia by any English writer. At 15, she became ill, suffering intense head and spinal pain for the rest of her life. Later in life, she also developed lung problems, possibly tuberculosis. She took laudanum for the pain from an early age, which is likely to have contributed to her frail health. In the 1840s, Elizabeth was introduced to literary society through her distant cousin and patron John Kenyon. Her first adult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Life
{{disambiguation ...
Early life may refer to: Biology In relation to Earthly history of life * RNA world, early in the history of terrestrial life *Ediacaran period, early in the history of terrestrial life * Cambrian Explosion period, early in the history of terrestrial life In relation to biological organisms *Zygote, at the start of an organism's life *Embryo, early in an organism's life *Foetus, early in an animal's life, occurring before birth *Larva, an early stage in many animal life forms before maturity *Child, early human life Other uses * '' My Early Life'' (book), 1930 autobiography by Winston Churchill See also * Early Life Stage test * * * Early Stage (other) * Life (other) Life is the characteristic that distinguishes organisms from inorganic substances and dead objects. Life or The Life may also refer to: Human life * Human life (other) * Human condition, the characteristics, events, and situations of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poet Laureate Of The United Kingdom
The British poet laureate is an honorary position appointed by the monarch of the United Kingdom on the advice of the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime minister. The role does not entail any specific duties, but there is an expectation that the holder will write verse for significant national occasions. The laureateship dates to 1616 when a pension was provided to Ben Jonson, but the first official laureate was John Dryden, appointed in 1668 by Charles II of England, Charles II. On the death of Alfred, Lord Tennyson, who held the post between November 1850 and October 1892, there was a break of four years as a mark of respect; Tennyson's laureate poems "Ode on the Death of the Duke of Wellington" and "The Charge of the Light Brigade (poem), The Charge of the Light Brigade" were particularly cherished by the Victorian public. Four poets—Thomas Gray, Samuel Rogers, Walter Scott and Philip Larkin—turned down the laureateship. Historically appointed for an unfixed term a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
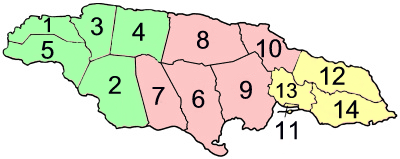
Cambridge, Jamaica
Cambridge is a town in Jamaica. It is the main township of the parish of St James, nestled in mountains, fifteen (15) miles south east of the City of Montego Bay and its hub is historic Wilmot Max Ramsay Square (Jamaica Gleaner, Thursday, 23 October 1986). Cambridge is located in the County of Cornwall. The chief "fruit-basket" of the parish, Cambridge is also the capital of the upper St James region. Cambridge students go to traditional high schools—Cornwall College Cornwall College may refer to: * The Cornwall College Group, in Cornwall and Devon, England * Cornwall College, Jamaica * Cornwall Collegiate and Vocational School, Cornwall, Ontario, Canada {{Disambiguation ... (boys), Mt Alvernia (girls) and Montego Bay High School for Girls—all sited in the City of Montego Bay, the St James Parish Capital. There are a Basic, an Infant, a Primary and a Secondary High Schools in Cambridge with "the proposed Marco Brown Public Library." Cantabrigians worship at, prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall County, Jamaica
Cornwall is the westernmost of the three historic counties into which Jamaica is divided. It is the least populated county of the country. It has no current-day administrative significance. It includes Montego Bay, the island's second largest city by area. ''The county of Cornwall is shown in green'' History Jamaica's three counties were established in 1758 to facilitate the holding of courts along the lines of the British county court system. Cornwall, the westernmost, was named after the westernmost county of England. Savanna-la-Mar was its county town In Great Britain and Ireland, a county town is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county, and the place where public representatives are elected to parliament. Following the establishment of county councils in .... Parishes References {{Authority control Counties of Jamaica 1758 establishments in the British Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint James Parish, Jamaica
St. James is a suburban parish, located on the north-west end of the island of Jamaica in the county of Cornwall. Its capital is Montego Bay (derived from the Spanish word ''manteca'' (lard) because many wild hogs were found there, from which lard was made). Montego Bay was officially named the second city of Jamaica, behind Kingston, in 1981, although Montego Bay became a city in 1980 through an act of the Jamaican Parliament. The parish is the birthplace of the Right Excellent Samuel Sharpe (died 1833), one of Jamaica's seven National Heroes. History When the Spanish occupied Jamaica, Montego Bay was an export point for lard, which was obtained from wild hogs in the forests. In many of the early maps of Jamaica, Montego Bay was listed as "Bahia de Manteca" (Lard Bay). The parish was given the name "St. James" in honour of King James II by Sir Thomas Modyford, the island's first English Governor. At the beginning of the English rule, the parish was one of the poorest; i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were the territories in the West Indies under British Empire, British rule, including Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, the Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Bermuda, Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Honduras, British Guiana and Trinidad and Tobago. The Kingdom of England first English overseas possessions, established colonies in the region during the 17th century. Financed by valuable extractive commodities such as sugar production, the colonies were also at the centre of the Atlantic slave trade, with around 2.3 million slaves being brought to the British West Indies. The colonies also served as bases to project the power of the British Empire through the Royal Navy and Britain's Merchant Marine, and to expand and protect British overseas trade. Before the decolonization of the Americas in the later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
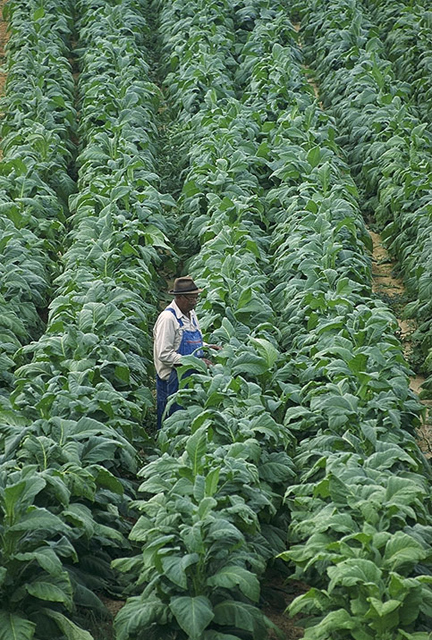
Slave Plantation
A slave plantation is an agricultural farm that uses enslaved people for labour. The practice was abolished in most places during the 19th century. Slavery Planters embraced the use of slaves mainly because indentured labor became expensive. Some indentured servants were also leaving to start their farms as land was widely available. Colonists in the Americas tried using Native Americans for labor, but they were susceptible to European diseases and died in large numbers. The plantation owners then turned to enslaved Africans for labor. In 1665, there were fewer than 500 Africans in Virginia but by 1750, 85 percent of the 235,000 slaves in the Thirteen Colonies lived in the southern colonies, Virginia included. Africans made up 40 percent of the South's population. According to the 1840 United States census, one out of every four families in Virginia owned slaves. There were over 100 plantation-owners who owned over 100 slaves. The number of slaves in the 15 States was jus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Of Jamaica
The Crown Colony of Jamaica and Dependencies was a British colony from 1655, when it was Invasion of Jamaica (1655), captured by the The Protectorate, English Protectorate from the Spanish Empire. Jamaica became a British Empire, British colony from 1707 and a Crown colony in 1866. The Colony was primarily used for sugarcane production, and experienced many slave rebellions over the course of British rule. Jamaica was granted independence in 1962. History 17th century English conquest In late 1654, English leader Oliver Cromwell launched the ''Western Design'' armada against Spanish West Indies, Spain's colonies in the Caribbean. In April 1655, Robert Venables, General Robert Venables led the armada in an attack on Spain's fort at Santo Domingo, Hispaniola. However, the Spanish repulsed this poorly-executed attack, known as the Siege of Santo Domingo (1655), Siege of Santo Domingo, and the English troops were soon decimated by disease, injured badly or possibly killed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurora Leigh
''Aurora Leigh'' is an 1856 verse novel by Elizabeth Barrett Browning. The poem is written in blank verse and encompasses nine books (the woman's number, the number of the Sibylline Books). It is a first-person narration, from the point of view of Aurora; its other heroine, Marian Erle, is an abused self-taught child of itinerant parents. The poem is set in Florence, Malvern, London and Paris. The work references Biblical and classical history and mythology, as well as modern novels, such as '' Corinne ou l'Italie'' by Anne Louise Germaine de Staël and the novels of George Sand. In Books 1–5, Aurora narrates her past, from her childhood to the age of about 27; in Books 6–9, the narrative has caught up with her, and she reports events in diary form. The author styled the poem "a novel in verse", and referred to it as "the most mature of my works, and the one into which my highest convictions upon Life and Art have entered". The scholar Deirdre David asserts that Barrett Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonnets From The Portuguese
''Sonnets from the Portuguese'', written and published first in 1850, is a collection of 44 love sonnets written by Elizabeth Barrett Browning. The collection was acclaimed and popular during the poet's lifetime and it remains so today. Despite what the title implies, the sonnets are entirely Browning's own, and not translated from Portuguese. The first line of Sonnet 43 has become one of the most famous in English poetry: "How do I love thee? Let me count the ways." Title Barrett Browning was initially hesitant to publish the poems, believing they were too personal. However, her husband Robert Browning insisted they were the best sequence of English-language sonnets since Shakespeare's time and urged her to publish them. To offer the couple some privacy, she decided to publish them as if they were translations of foreign sonnets. She initially planned to title the collection "''Sonnets translated from the Bosnian''", but Robert Browning proposed that she claim their sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emily Dickinson
Emily Elizabeth Dickinson (December 10, 1830 – May 15, 1886) was an American poet. Little-known during her life, she has since been regarded as one of the most important figures in American poetry. Dickinson was born in Amherst, Massachusetts, into a prominent family with strong ties to its community. After studying at the Amherst Academy for seven years in her youth, she briefly attended the Mount Holyoke Female Seminary before returning to her family's home in Amherst. Evidence suggests that Dickinson lived much of her life in isolation. Considered an eccentric by locals, she developed a penchant for white clothing and was known for her reluctance to greet guests or, later in life, even to leave her bedroom. Dickinson never married, and most of her friendships were based entirely upon correspondence. Although Dickinson was a prolific writer, her only publications during her lifetime were one letter and 10 of her nearly 1,800 poems. The poems published then were usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic who is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales involving mystery and the macabre. He is widely regarded as one of the central figures of Romanticism and Gothic fiction in the United States and of early American literature. Poe was one of the country's first successful practitioners of the short story, and is generally considered to be the inventor of the detective fiction genre. In addition, he is credited with contributing significantly to the emergence of science fiction. He is the first well-known American writer to earn a living exclusively through writing, which resulted in a financially difficult life and career.. Poe was born in Boston. He was the second child of actors David Poe Jr., David and Eliza Poe, Elizabeth "Eliza" Poe. His father abandoned the family in 1810, and when Eliza died the following year, Poe was taken in by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |