|
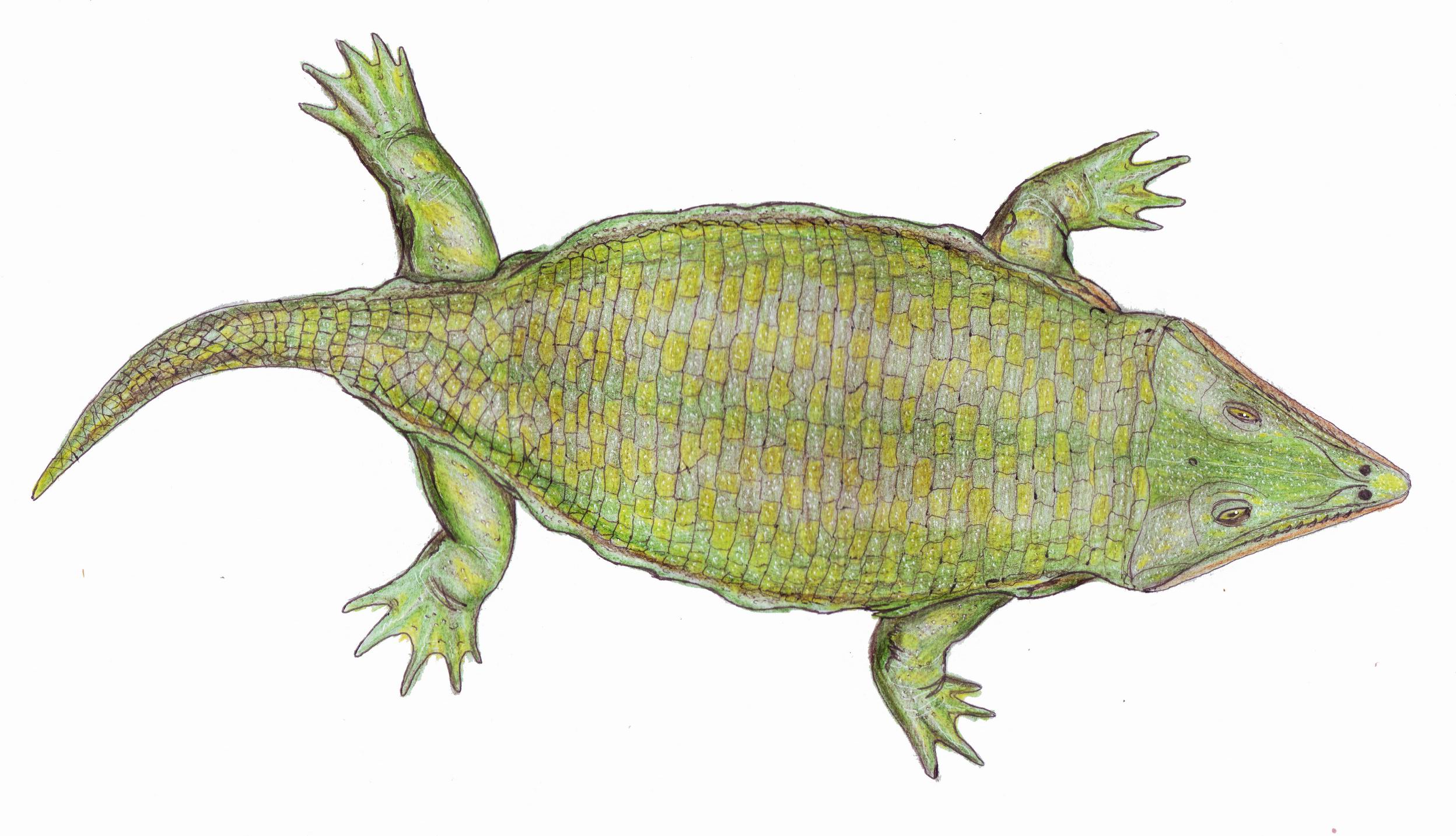
Elfridia
''Elfridia'' is a poorly known extinct genus of microsaur within the family Gymnarthridae. History of study ''Elfridia'' was named in 1985 by American paleontologist David Thayer based on material collected from Carboniferous exposures of the Swisshelm Mountains in Arizona. The genus name is derived from the nearby town of Elfridia, and the species name, ''E. bulbidens,'' is with respect to the bulbous teeth of the animal (''bulbi-'' for 'bulbous' and ''-dens'' for 'tooth'). It is one of the oldest known 'microsaurs' and one of the few from the American southwest region. Anatomy The holotype of ''Elfridia'' is a left mandible. Several other tooth-bearing fragments and isolated postcranial elements are assigned to this taxon. It is diagnosed by having lingually recurved tips of the teeth that are positioned asymmetrically on the labial portion. There are nine to ten teeth on the mandible with a greatly enlarged tooth along the mid-length of the tooth row. Relationships Thay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prehistoric Amphibians
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomina dubia''), or were not formally published ('' nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuditanomorpha
Tuditanomorpha is a suborder of microsaur lepospondyls. Tuditanomorphs lived from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Permian and are known from North America and Europe. Tuditanomorphs have a similar pattern of bones in the skull roof. Tuditanomorphs display considerable variability, especially in body size, proportions, dentition, and presacral vertebral count. Currently there are seven families of tuditanomorphs, with two being monotypic. Tuditanids, gymnarthrids, and pantylids first appear in the Lower Pennsylvanian. Goniorhynchidae, Hapsidopareiontidae, Ostodolepidae, and Trihecatontidae appear in the Late Pennsylvanian and Early Permian. Classification Suborder Tuditanomorpha *Family Goniorhynchidae **'' Rhynchonkos'' *Family Gymnarthridae **'' Cardiocephalus'' **'' Elfridia'' **'' Euryodus'' **'' Leiocephalikon'' **'' Pariotichus'' **'' Sparodus'' *Family Hapsidopareiontidae **'' Hapsidopareion'' **'' Llistrofus'' **'' Ricnodon'' **'' Saxonerpeton'' *Family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' (" coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiocephalus
''Cardiocephalus'' is an extinct genus of lepospondyl amphibian from the Permian period. It was a member of the family Gymnarthridae Gymnarthridae is an extinct family of tuditanomorph microsaurs. Gymnarthrids are known from Europe and North America and existed from the Late Carboniferous through the Early Permian. Remains have been found from the Czech Republic, Nova Scotia .... References External links''Cardiocephalus'' fossil pictures. Gymnarthrids Cisuralian amphibians of North America Fossil taxa described in 1904 {{Lepospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euryodus
''Euryodus'' is an extinct genus of microsaur within the family Gymnarthridae. References See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted g ... Gymnarthrids {{Lepospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elfrida, Arizona
Elfrida is a census-designated place in Cochise County, Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 459. Description Elfrida is located on U.S. Route 191, northwest of Douglas and north of McNeal. Elfrida has the United States Postal Service Zip Code of 85610. Elfrida is home to Valley Union High School grades 9–12 and Elfrida Elementary School grades K–8. Chiricahua Community Health Centers was founded in Elfrida in 1986. Elfrida Community Center is north of the center crossroads. Elfrida gained a library, ''circa'' March 2000. The Elfrida Library is part of the Cochise County Library District. The Elfrida Fire Department is south of the center crossroads. Demographics Climate According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Elfrida has a semi-arid climate, abbreviated "BSk" on climate maps. See also * List of census-designated places in Arizona The 2010 Census defines 360 census-designated places or CDPs within the state of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swisshelm Mountains
The Swisshelm Mountains are a small mountain range adjacent to the southwest corner of the Chiricahua Mountains of eastern Cochise County, Arizona. They are separated from the Pedrogosa Mountains to the southeast, the Chiricahuas to the northeast, and by Leslie Creek, bordering the south and east; the area is now notable for the Leslie Canyon National Wildlife Refuge. The mountain range is named for John Swisshelm, a miner, a local settler of the late 1800s. Range The range is a north-south range, with three notable peaks. In the south, Swisshelm Mountain is the highest at . In the north, an unnamed peak is 5225 ft, and is adjacent to ''Whitewater Draw'' of the lower stretch of Rucker Creek. A second unnamed peak is in the northeast, at 5847 ft and also adjacent to Rucker Creek. Leslie Creek forms the eastern and southern border of the Swisshelm Mountains. The Chiricahuas are directly adjacent eastwards; the Pedregosa Mountains are southeast and are drained by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordate
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit metameric segmentation. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |