|
Elbow Joint
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the humerus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
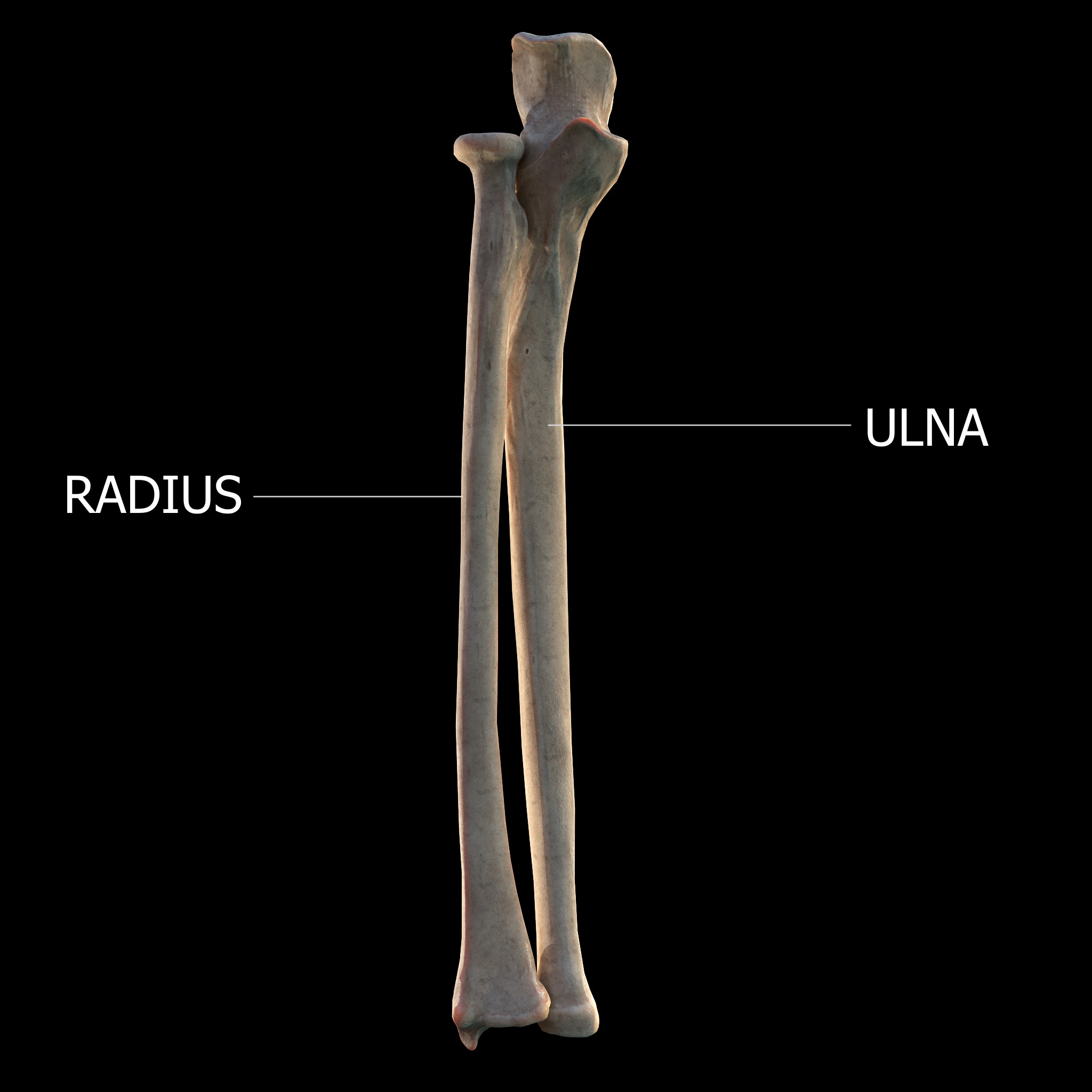
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow ( brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the forearm can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humeroradial Joint
The humeroradial joint is the joint between the head of the radius and the capitulum of the humerus, is a limited ball-and-socket joint, hinge type of synovial joint. Structure The annular ligament binds the head of the radius to the radial notch of the ulna, preventing any separation of the two bones laterally. Therefore, the humeroradial joint is not functionally a ball and socket joint, although the joint surface in itself allows movement in all directions. The annular ligament secures the head of the radius from dislocation, which would otherwise tend to occur, from the shallowness of the cup-like surface on the head of the radius. Without this ligament, the tendon of the biceps brachii would be liable to pull the head of the radius out of the joint. The head of the radius is not in complete contact with the capitulum of the humerus in all positions of the joint. The capitulum occupies only the anterior and inferior surfaces of the lower end of the humerus, so that in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Capsule
In anatomy, a joint capsule or articular capsule is an envelope surrounding a synovial joint. Each joint capsule has two parts: an outer fibrous layer or membrane, and an inner synovial layer or membrane. Membranes Each capsule consists of two layers or membranes: * an outer (fibrous membrane, ''fibrous stratum'') composed of avascular white fibrous tissue * an inner ('''', ''synovial stratum'') which is a secreting layer On the inside of the capsule, articular cartilage covers the end surfaces of the bones that articulate within ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Radioulnar Joint
The proximal radioulnar articulation, also known as the proximal radioulnar joint (PRUJ), is a synovial pivot joint between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. Structure The proximal radioulnar joint is a synovial pivot joint. It occurs between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. The interosseous membrane of the forearm and the annular ligament stabilise the joint. A number of nerves run close to the proximal radioulnar joint, including: *median nerve *musculocutaneous nerve *radial nerve See also * Distal radioulnar articulation * Supination Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochlea Of Humerus
In the human arm, the humeral trochlea is the medial portion of the articular surface of the elbow joint which articulates with the trochlear notch on the ulna in the forearm. Structure In humans and other apes, it is trochleariform (or trochleiform), as opposed to cylindrical in most monkeys and conical in some prosimians. It presents a deep depression between two well-marked borders; it is convex from before backward, concave from side to side, and occupies the anterior, lower, and posterior parts of the extremity. The trochlea has the capitulum located on its lateral side and the medial epicondyle on its medial. It is directly inferior to the coronoid fossa anteriorly and to the olecranon fossa posteriorly. In humans, these two fossae, the most prominent in the humerus, are occasionally transformed into a hole, the supratrochlear foramen, which is regularly present in, for example, dogs. Carrying angle When viewed from in front or behind, the trochlea looks roughly cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length, and all three angles are equal. Because of these properties, the equilateral triangle is a regular polygon, occasionally known as the regular triangle. It is the special case of an isosceles triangle by modern definition, creating more special properties. The equilateral triangle can be found in various tilings, and in polyhedrons such as the deltahedron and antiprism. It appears in real life in popular culture, architecture, and the study of stereochemistry resembling the molecular known as the trigonal planar molecular geometry. Properties An equilateral triangle is a triangle that has three equal sides. It is a special case of an isosceles triangle in the modern definition, stating that an isosceles triangle is defined at least as having two equal sides. Based on the modern definition, this leads to an equilateral triangle in which one of the three sides may be considered its base. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
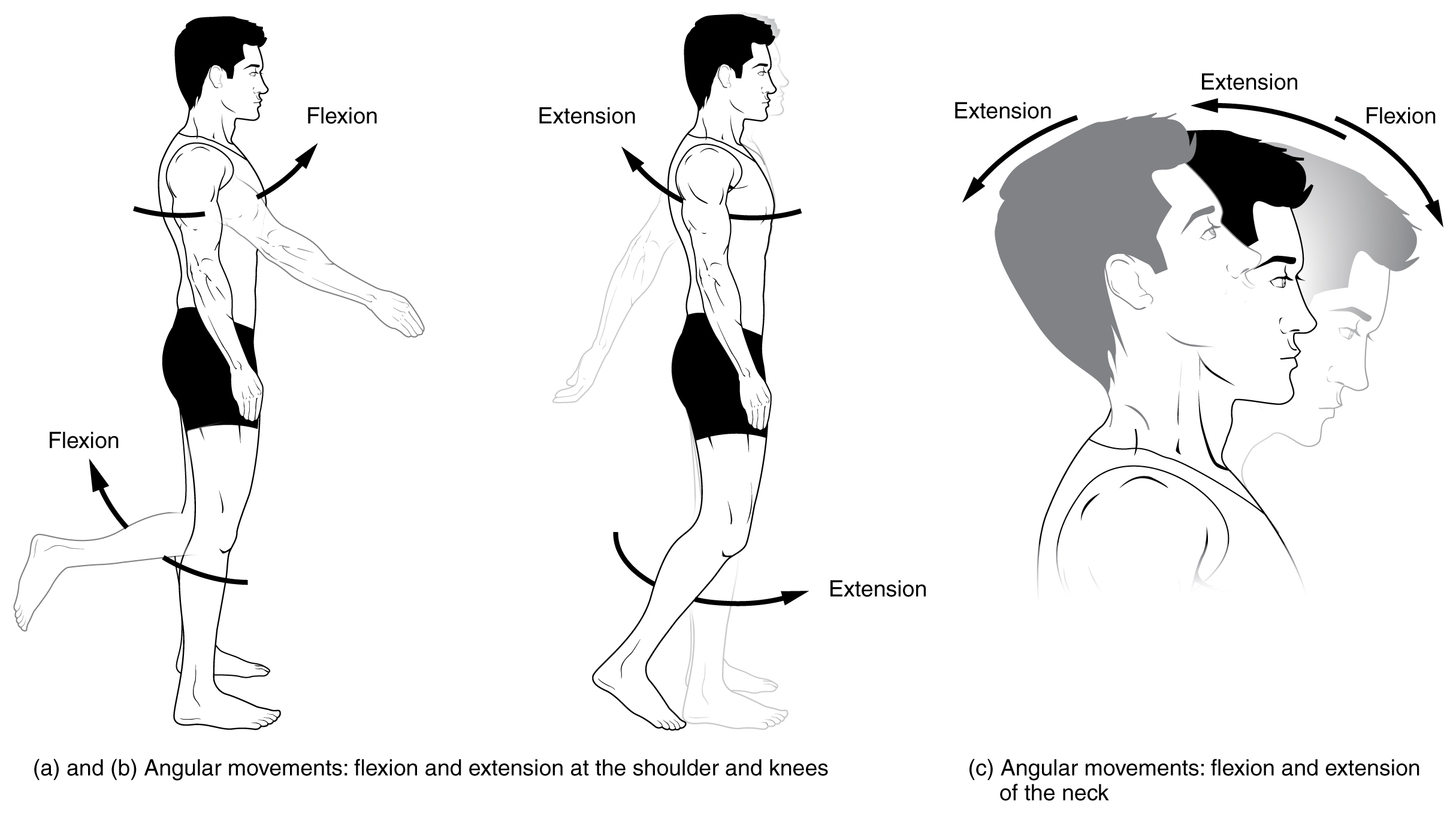
Flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomy, Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Position
Anatomical terminology is a specialized system of terms used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals, such as doctors, surgeons, and pharmacists, to describe the structures and functions of the body. This terminology incorporates a range of unique terms, prefixes, and suffixes derived primarily from Ancient Greek and Latin. While these terms can be challenging for those unfamiliar with them, they provide a level of precision that reduces ambiguity and minimizes the risk of errors. Because anatomical terminology is not commonly used in everyday language, its meanings are less likely to evolve or be misinterpreted. For example, everyday language can lead to confusion in descriptions: the phrase "a scar above the wrist" could refer to a location several inches away from the hand, possibly on the forearm, or it could be at the base of the hand, either on the palm or dorsal (back) side. By using precise anatomical terms, such as "proximal," "distal," "palmar," or " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supination
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomy, Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Notch
The radial notch of the ulna (lesser sigmoid cavity) is a narrow, oblong, articular depression on the lateral side of the coronoid process; it receives the circumferential articular surface of the head of the radius. It is concave from before backward, and its prominent extremities serve for the attachment of the annular ligament. Additional images File:Gray333.png, Annular ligament of radius, from above. References External links * *elbow/elbowbones/bones3at the Dartmouth Medical School The Geisel School of Medicine is the medical school of Dartmouth College located in Hanover, New Hampshire. The fourth oldest medical school in the United States, it was founded in 1797 by New England physician Nathan Smith. It is one of the sev ...'s Department of Anatomy Upper limb anatomy Ulna {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximal Radioulnar Joint
The proximal radioulnar articulation, also known as the proximal radioulnar joint (PRUJ), is a synovial pivot joint between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. Structure The proximal radioulnar joint is a synovial pivot joint. It occurs between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. The interosseous membrane of the forearm and the annular ligament stabilise the joint. A number of nerves run close to the proximal radioulnar joint, including: *median nerve *musculocutaneous nerve *radial nerve See also * Distal radioulnar articulation * Supination Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ... Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |