|
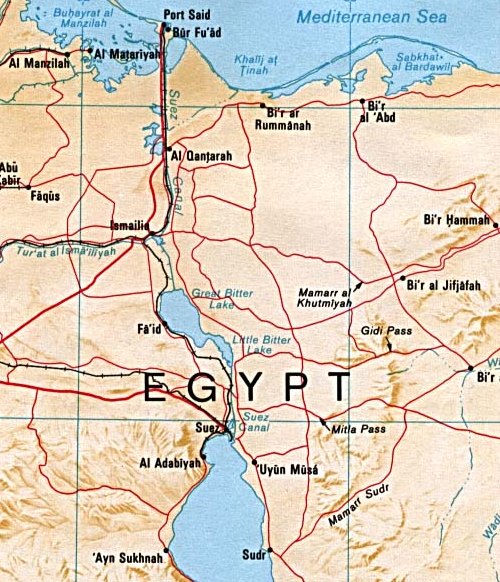
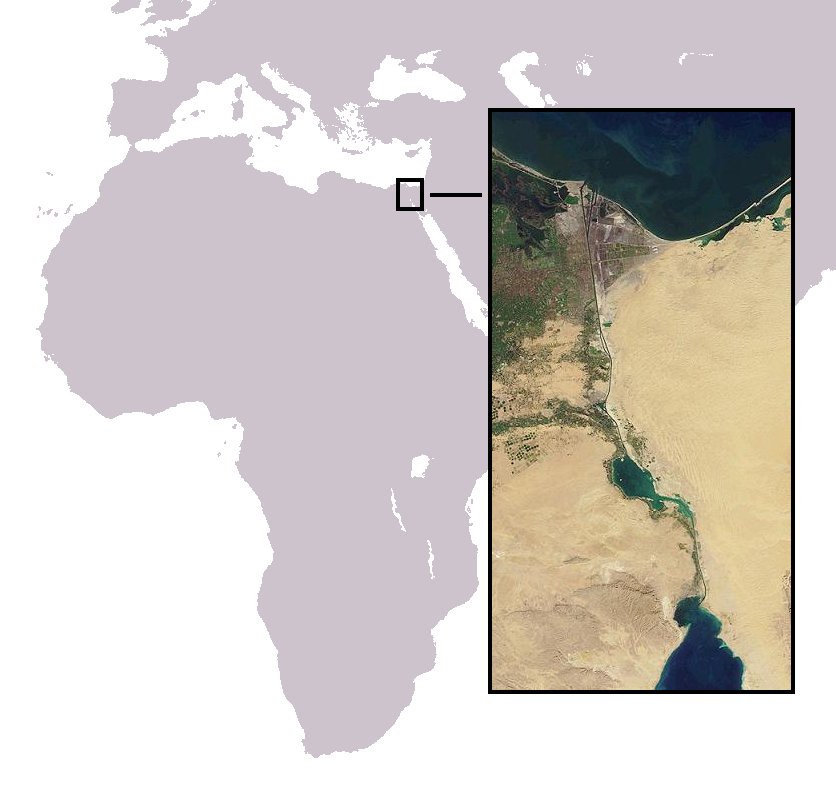
El Matareya, Dakahlia
El Matareya (also spelled Matarieh or la Matarée) ( ). Is a coastal town, is a region ('' markaz'') in Egypt. Located in the Dakahlia Governorate, it is located south of Port Said, nicknamed the fishing town. It lies on the Lake Manzala coast in the northeastern part of the country. The region should not be confused with the district of El Matareya in Cairo. El Matareya has a population of around 300,000 inhabitants, and consists of two main districts: El-Ghasna and El-Okbiyine. It was announced as a separate city in the 1930s, with many villages following in it. History The city consisted of two main islands named El-Ghasna and El-Okbiyine. They were distinct islands until 1903 when the government issued a decree to unite both islands under the name El Matareya city. Transportation between the two islands was via wooden boats until the waterway separating the islands was dried up. The first brick houses in the city were built in the 1750s with the roofs being made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns In Egypt
0-9 * 10th of Ramadan * 15th of May (city), 15th of May * 6th of October (city), 6th of October A * Abu El Matamir * Abu Hummus * Abu Tesht * Abu Tig * Akhmim * Al Khankah * Alexandria * Arish * Ashmoun * Aswan * Awsim * Ain Sokhna B * Badr, Egypt, Badr * Baltim * Banha * Basyoun * Biyala * Belqas * Beni Mazar * Beni Suef * Beni Ebeid * Biba, Egypt, Biba * Bilbeis * Birket El Sab * Borg El Arab * Borg El Burullus * Bush, Egypt, Bush C * Cairo D * Dahab * Dairut * Damanhur * Damietta * Dar El Salam * Daraw * Deir Mawas * Dekernes * Dendera * Desouk * Diarb Negm * Dishna, Egypt, Dishna E * Edfu * Edku * El Alamein * El Ayyat * El Badari, Egypt, El Badari * El Badrashein * El Bagour * El Balyana * El Basaliya * El Bayadiya * El Dabaa * El Delengat * El Fashn * El Gamaliya * El Ghanayem * El Hamool * El Hamam * El Hawamdeya * El Husseiniya * El Idwa * El Kanayat * El Mahalla El Kubra * El Mahmoudiyah * Ptolemais Hermiou, El Mansha * El Manzala * El Mara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbas II Of Egypt
Abbas Helmy II (also known as ''ʿAbbās Ḥilmī Pāshā'', ; 14 July 1874 – 19 December 1944) was the last Khedive of Egypt and the Sudan, ruling from 8January 1892 to 19 December 1914. In 1914, after the Ottoman Empire joined the Central Powers in World War I, the nationalist Khedive was removed by the British, then ruling Egypt, in favour of his more pro-British uncle, Hussein Kamel, marking the ''de jure'' end of Egypt's four-century era as a province of the Ottoman Empire, which had begun in 1517. Early life Abbas II (full name: Abbas Hilmy), the great-great-grandson of Muhammad Ali, was born in Alexandria, Egypt on 14 July 1874. In 1887 he was ceremonially circumcised together with his younger brother Mohammed Ali Tewfik. The festivities lasted for three weeks and were carried out with great pomp. As a boy he visited the United Kingdom, and he had a number of British tutors in Cairo including a governess who taught him English. In a profile of Abbas II, the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb also includes the territorial dispute, disputed territory of Western Sahara. As of 2018, the region had a population of over 100 million people. The Maghreb is usually defined as encompassing much of the northern part of Africa, including a large portion of the Sahara Desert, but excluding Egypt and the Sudan, which are considered to be located in the Mashriq — the eastern part of the Arab world. The traditional definition of the Maghreb — which restricted its scope to the Atlas Mountains and the coastal plains of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya — was expanded in modern times to include Mauritania and the disputed territory of Western Sahara. During the era of al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula (711–1492), the Maghreb's inhabita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorish Architecture
Moorish architecture is a style within Islamic architecture that developed in the western Islamic world, including al-Andalus (the Iberian Peninsula) and what is now Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia (part of the Maghreb). Scholarly references on Islamic architecture often refer to this architectural tradition in terms such as architecture of the Islamic West or architecture of the Western Islamic lands. This architectural tradition integrated influences from pre-Islamic Roman, Byzantine, and Visigothic architectures, from ongoing artistic currents in the Islamic Middle East, and from North African Berber traditions. Major centers of artistic development included the main capitals of the empires and Muslim states in the region's history, such as Córdoba, Kairouan, Fes, Marrakesh, Seville, Granada and Tlemcen. While Kairouan and Córdoba were some of the most important centers during the 8th to 10th centuries, a wider regional style was later synthesized and shared across the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansoura
Mansoura (; ', , rural: ) is a city in Egypt located on the eastern bank of the Damietta branch of the Nile river. The city is the capital of the Dakahlia Governorate and has a population of 621,953 as of 2021. Etymology ''Mansoura'' in Arabic means "victorious". The city is named after the Battle of Mansurah (1250), El Mansoura Battle (1250) against Louis IX of France during the Seventh Crusade. History Mansoura was established in 1219 by al-Kamil of the Ayyubid dynasty upon a Phatmetic branch of Nile, the Nile on a place of several older villages like Al-Bishtamir () and Kafr al-Badamas (, from , "river, canal"). After the Egyptians defeated the Crusaders during the Seventh Crusade, it was named ''Mansoura'' (aka. "The Victorious"). In the Seventh Crusade, the Capetian dynasty, Capetians were defeated and put to flight; between fifteen and thirty thousand of their men fell on the battlefield. Louis IX of France was captured in the main Battle of Fariskur (1250), Battle of Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrénées-Atlantiques
Pyrénées-Atlantiques (; Gascon language, Gascon Occitan language, Occitan: ''Pirenèus Atlantics''; ) is a Departments of France, department located in the Regions of France, region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine in the southwest corner of metropolitan France. Named after the Pyrenees mountain range and the Atlantic Ocean, it covers the French Basque Country and the Béarn. It is divided in Arrondissements of the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department, three arrondissements and its Prefectures in France, prefecture is Pau, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Pau. In 2019, it had a population of 682,621.Populations légales 2019: 64 Pyrénées-Atlantiques INSEE History Originally named Basses-Pyrénées, it was one of the 83 departments of France created during the French Revolution, o ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anwar Sadat
Muhammad Anwar es-Sadat (25 December 1918 – 6 October 1981) was an Egyptian politician and military officer who served as the third president of Egypt, from 15 October 1970 until Assassination of Anwar Sadat, his assassination by fundamentalist army officers on 6 October 1981. Sadat was a senior member of the Free Officers Movement (Egypt), Free Officers who overthrew King Farouk I in the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, and a close confidant of President Gamal Abdel Nasser, under whom he served as Vice President of Egypt, vice president twice and whom he succeeded as president in 1970. In 1978, Sadat and Menachem Begin, Prime Minister of Israel, signed a peace treaty in cooperation with United States President Jimmy Carter, for which they were recognized with the Nobel Peace Prize. In his 11 years as president, he changed Egypt's trajectory, departing from many political and economic tenets of Nasserism, reinstituting a multi-party system, and launching the Infitah economic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of Attrition
The War of Attrition (; ) involved fighting between Israel and Egypt, Jordan, the Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) and their allies from 1967 to 1970. Following the 1967 Six-Day War, no serious diplomatic efforts were made to resolve the issues at the heart of the Arab–Israeli conflict. The 1967 Arab League summit formulated in September the "Khartoum Resolution, three no's" policy, barring peace, International recognition of Israel, recognition, or negotiations with Israel. Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser believed that only military initiative would compel Israel or the international community to facilitate a full Israeli withdrawal from Sinai Peninsula, Sinai, and hostilities soon resumed along the Suez Canal. These initially took the form of limited artillery duels and small-scale incursions into Sinai, but by 1969, the Egyptian Army judged itself prepared for larger-scale operations. On March 8, 1969, Nasser proclaimed the official launch of the War of Attri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
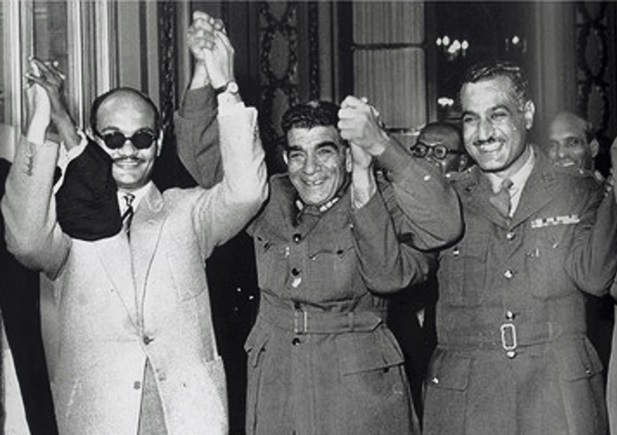
Salah Salem
Salah Salem () (September 25, 1920 – February 18, 1962) was an Egyptian military officer and politician who was a prominent member of the Free Officers Movement (Egypt), Free Officers Movement that orchestrated the Egyptian Revolution of 1952. Early life and military career Salem was born in 1920 to an Egyptian family in Sinkat, Sudan, Sinkat, Sudan, which was a colony ran by Egypt and Britain under a Condominium (international law), condominium, at the time. He was raised in the Hilmiyyat Gadida neighborhood of Cairo, where he was educated at the Ibrahimiyyeh School. In 1938, he graduated from the Egyptian Military Academy, Royal Egyptian Military Academy. He, along with four other future members of the Free Officers Movement (Egypt), Free Officers, was ranked in the top 10 percent of his classes at the General Staff College by 1947. He graduated from college in 1948. That same year, Salem served in the Egyptian and Sudanese army in the Palestine War as an infantry officer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdel Hakim Amer
Mohamed Abdel Hakim Amer (, ; 11 December 1919 – 13 September 1967), better known as Abdel Hakim Amer, was an Egyptian military officer and politician. Amer served in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, and played a leading role in the military coup that overthrew King Farouk in 1952. After leading Egyptian forces in the 1956 Suez war, he was appointed Minister for Defense by President Gamal Abdel Nasser and was Egyptian Vice President between 1958 and 1965. Early life and education Amer was born in Samalut, in the El Minya on 11 December 1919. He was from an affluent family, and his father was a land owner and village mayor. His uncle Mohammed Haidar Pasha served as the minister of war during the reign of King Farouk. After finishing school, Amer attended the Egyptian Military Academy and graduated in 1938. He was commissioned into the Egyptian Army in 1939. Military career Amer served in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, took part in the 1952 Revolution and commanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamal Abdel Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein (15 January 1918 – 28 September 1970) was an Egyptian military officer and revolutionary who served as the second president of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the Egyptian revolution of 1952 and introduced Land reform in Egypt, far-reaching land reforms the following year. Following a 1954 Attempted assassination of Gamal Abdel Nasser, assassination attempt on his life by a Muslim Brotherhood member, he cracked down on the organization, put President Mohamed Naguib under house arrest and assumed executive office. He was 1956 Egyptian referendum, formally elected president in June 1956. Nasser's popularity in Egypt and the Arab world skyrocketed after his Suez Canal Authority, nationalization of the Suez Canal and his political victory in the subsequent Suez Crisis, known in Egypt as the ''Tripartite Aggression''. Calls for Arab Union, pan-Arab unity under his leadership increased, culminating with the formation of the United Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripartite Aggression
The Suez Crisis, also known as the Second Arab–Israeli War, the Tripartite Aggression in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel, was a British–French–Israeli invasion of Egypt in 1956. Israel invaded on 29 October, having done so with the primary objective of re-opening the Straits of Tiran and the Gulf of Aqaba as the recent tightening of the eight-year-long Egyptian blockade further prevented Israeli passage. After issuing a joint ultimatum for a ceasefire, the United Kingdom and France joined the Israelis on 5 November, seeking to depose Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser and regain control of the Suez Canal, which Nasser had earlier nationalised by transferring administrative control from the foreign-owned Suez Canal Company to Egypt's new government-owned Suez Canal Authority. Shortly after the invasion began, the three countries came under heavy political pressure from both the United States and the Soviet Union, as well as from the United Nations, eventual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |