|
Edward B. Bunn, S.J. Intercultural Center
The Edward B. Bunn, S.J. Intercultural Center commonly known as the Intercultural Center or ICC is a seven-story mixed use building on the main campus of Georgetown University named for Edward B. Bunn. The center was built in 1982 as the Photovoltaic Higher Education National Exemplar Facility in conjunction with a grant from the United States Department of Energy, U.S. Department of Energy. The facility hosts numerous administrative offices, student facilities, and conference spaces, but is best known for its contribution to solar power development. Among the occupants of the building are the Edmund A. Walsh School of Foreign Service, the Center for Contemporary Arab Studies, the Prince Alwaleed Bin Talal Center for Muslim-Christian Understanding, and several departments of Georgetown College (Georgetown University), Georgetown College. History In 1980, Georgetown University applied to the Department of Energy for a grant to fund the construction of an intercultural center that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgetown University
Georgetown University is a private university, private Jesuit research university in Washington, D.C., United States. Founded by Bishop John Carroll (archbishop of Baltimore), John Carroll in 1789, it is the oldest Catholic higher education, Catholic institution of higher education in the United States, the oldest university in Washington, D.C., and the nation's first University charter#Federal, federally chartered university. The university has eleven Undergraduate education, undergraduate and Postgraduate education, graduate schools. Its main campus, located in the Georgetown (Washington, D.C.), Georgetown historic neighborhood, is on a hill above the Potomac River and identifiable by Healy Hall, a National Historic Landmark. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among List_of_research_universities_in_the_United_States#Universities_classified_as_"R1:_Doctoral_Universities_–_Very_high_research_activity", "R1: Doctoral Universities – V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
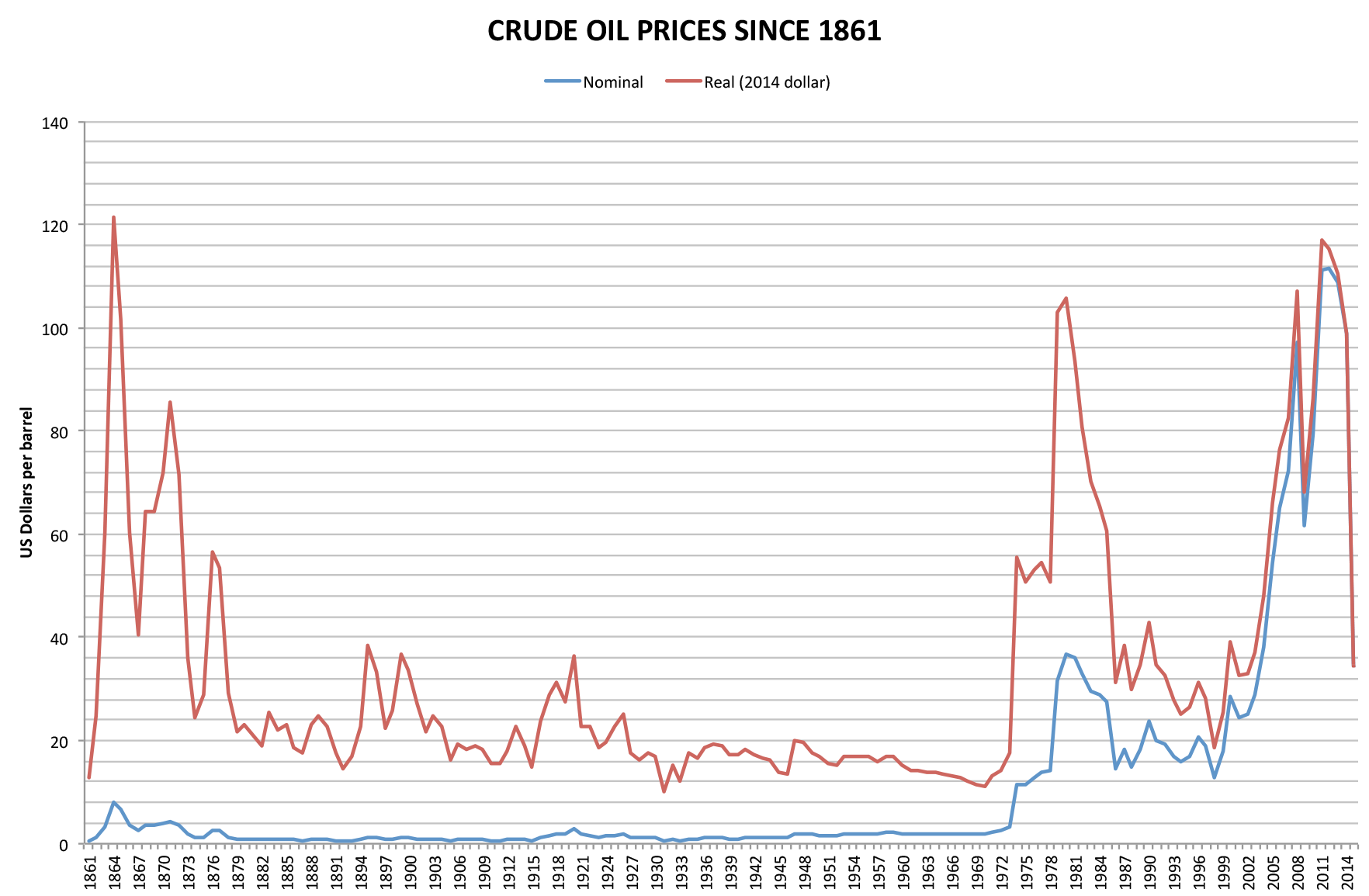
1973 Oil Embargo
In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against countries that had supported Israel at any point during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, which began after Egypt and Syria launched a large-scale surprise attack in an ultimately unsuccessful attempt to recover the territories that they had lost to Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War. In an effort that was led by Faisal of Saudi Arabia, the initial countries that OAPEC targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the United States. This list was later expanded to include Portugal, Rhodesia, and South Africa. In March 1974, OAPEC lifted the embargo, but the price of oil had risen by nearly 300%: from US to nearly US globally. Prices in the United States were significantly higher than the global average. After it was implemented, the embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on the gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University And College Buildings Completed In 1982
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgetown University Buildings
This is a list of buildings on Georgetown University Campuses of Georgetown University, campuses. Georgetown University's undergraduate campus and the medical school campus, together comprising the main campus, and the Law Center campus, are located within Washington, D.C. The Main Campus is located in Georgetown, Washington, D.C. between Canal Road, P Street, and Reservoir Road. The Law Center campus is located in downtown DC on New Jersey Avenue, near Union Station. List of buildings Future buildings *Boathouse, awaiting completion of city environmental survey. *New Henle residential complex, with construction expected to run from May 2023 to July 2025. Former buildings References {{Georgetown University Georgetown University buildings, Lists of university and college buildings in the United States, Georgetown University Lists of buildings and structures in Washington, D.C., Georgetown University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enron
Enron Corporation was an American Energy development, energy, Commodity, commodities, and services company based in Houston, Texas. It was led by Kenneth Lay and developed in 1985 via a merger between Houston Natural Gas and InterNorth, both relatively small regional companies at the time of the merger. Before its bankruptcy on December 2, 2001, Enron employed approximately 20,600 staff and was a major electricity, natural gas, communications, and pulp and paper industry, pulp and paper company, with claimed revenues of nearly $101 billion during 2000. ''Fortune (magazine), Fortune'' named Enron "America's Most Innovative Company" for six consecutive years. At the end of 2001, it was revealed that Enron's reported financial condition was sustained by an institutionalized, systematic, and creatively planned accounting scandals, accounting fraud, known since as the Enron scandal. Enron became synonymous with willful, institutional fraud and systemic Corporate crime, corruptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoco
Amoco ( ) is a brand of filling station, fuel stations operating in the United States and owned by British conglomerate BP since 1998. The Amoco Corporation was an American chemical and petroleum, oil company, founded by Standard Oil Company in 1889 around a oil refinery, refinery in Whiting, Indiana, and was officially the Standard Oil Company of Indiana until 1985. In 1911, it became an independent corporation as part of the break-up of the Standard Oil trust. Incorporated in Indiana, it was headquartered in Chicago. In 1925, Standard Oil of Indiana absorbed the American Oil Company, founded in Baltimore in 1910, and incorporated in 1922, by Louis Blaustein and his son Jacob Blaustein, Jacob. The combined corporation operated or licensed gas stations under both the ''Standard'' name and the ''American'' or ''Amoco'' name (the latter from ''American oil company'') and its logo using these names became a red, white and blue oval with a torch in the center. By the mid-twentiet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reagan National Airport
Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport is a public airport in Arlington County, Virginia, United States, from Washington, D.C. The closest airport to the nation's capital, it is one of two airports owned by the federal government and operated by the Metropolitan Washington Airports Authority (MWAA) that serve the Washington metropolitan area; the other is Dulles International Airport (IAD), located about to the west in Fairfax and Loudoun counties. The airport opened in 1941 and was originally named Washington National Airport. Part of the original terminal is still in use as Terminal 1. The much larger Terminal 2 opened in 1997. In 1998, Congress passed and President Bill Clinton signed a bill renaming the airport in honor of the 40th president of the United States, Ronald Reagan, who was in office from 1981 to 1989. Reagan National serves 98 nonstop destinations . It is a hub for American Airlines. The airport hosts international flights, but has no immigration and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgetown Intercultural Center USGS
Georgetown or George Town may refer to: Places Africa *George, South Africa, formerly known as Georgetown * Janjanbureh, Gambia, formerly known as Georgetown *Georgetown, Ascension Island, main settlement of the British territory of Ascension Island Asia * Georgetown, Prayagraj, India *George Town, Chennai, India *George Town, Penang, capital city of the Malaysian state of Penang Europe * Georgetown, Blaenau Gwent, now part of the town of Tredegar in Wales * Georgetown, Dumfries and Galloway, a location in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland * Es Castell in Minorca, Spain, originally called Georgetown North and Central America Canada * Georgetown, Alberta * Georgetown, Newfoundland and Labrador *Georgetown, Ontario * Georgetown, Prince Edward Island Caribbean * George Town, Bahamas, a village in Exuma District, Bahamas * George Town, Belize, a village in Stann Creek District, Belize *George Town, Cayman Islands, the capital city on Grand Cayman * Georgetown, Saint Vincent and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photovoltaic Panel
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially used for electricity generation and as photosensors. A photovoltaic system employs solar modules, each comprising a number of solar cells, which generate electrical power. PV installations may be ground-mounted, rooftop-mounted, wall-mounted or floating. The mount may be fixed or use a solar tracker to follow the sun across the sky. Photovoltaic technology helps to mitigate climate change because it emits much less carbon dioxide than fossil fuels. Solar PV has specific advantages as an energy source: once installed, its operation does not generate any pollution or any greenhouse gas emissions; it shows scalability in respect of power needs and silicon has large availability in the Earth's crust, although other materials required in P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building-integrated Photovoltaics
Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) are photovoltaic materials that are used to replace conventional building materials in parts of the building envelope such as the roof, skylights, or façades. They are increasingly being incorporated into the construction of new buildings as a principal or ancillary source of electrical power, although existing buildings may be retrofitted with similar technology. The advantage of integrated photovoltaics over more common non-integrated systems is that the initial cost can be offset by reducing the amount spent on building materials and labor that would normally be used to construct the part of the building that the BIPV modules replace. In addition, BIPV allows for more widespread solar adoption when the building's aesthetics matter and traditional rack-mounted solar panels would disrupt the intended look of the building. The term building-applied photovoltaics (BAPV) is sometimes used to refer to photovoltaics that are retrofit – int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |