|
Eduard Sievers
Eduard Sievers (; 25 November 1850 – 30 March 1932) was a German philologist of the classical and Germanic languages. Sievers was one of the '' Junggrammatiker'' of the so-called "Leipzig School". He was one of the most influential historical linguists of the late nineteenth century. He is known for his recovery of the poetic traditions of Germanic languages such as Anglo-Saxon and Old Saxon, as well as for his discovery of Sievers' law. Biography He was educated at Leipzig and Berlin, and became professor extraordinarius of Germanic and Romance philology at Jena in 1871, receiving a full professorship there five years later. In 1883 he went to Tübingen, and in 1887 to Halle, whence he was called in 1892 to Leipzig. Sievers's analysis Sievers' analysis was a system of five patterns which indicated how the poetic line (or, more specifically, the poetic half-line) was to be emphasized or not, e.g. stressed-unstressed-stressed-unstressed, unstressed-stressed-unstressed-stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CREDENTIAL
A credential is a piece of any document that details a qualification, competence, or authority issued to an individual by a third party with a relevant or ''de facto'' authority or assumed competence to do so. Examples of credentials include academic diplomas, academic degrees, Professional certification, certifications, security clearances, Identity document, identification documents, badges, passwords, user names, key (lock), keys, power of attorney, powers of attorney, and so on. Sometimes publications, such as scientific papers or books, may be viewed as similar to credentials by some people, especially if the publication was peer reviewed or made in a well-known Academic journal, journal or reputable publisher. Types and documentation of credentials A person holding a credential is usually given documentation or secret knowledge (''e.g.,'' a password or key) as proof of the credential. Sometimes this proof (or a copy of it) is held by a third, trusted party. While in some c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Reuter (composer)
Fritz Reuter (9 September 1896 – 4 July 1963) was a German musicologist, music educator, composer and ''Kapellmeister''. Reuter was one of the most important German music educators of the 20th century. After studying music and musicology in Dresden and Leipzig, with Teichmüller, Riemann, Schering and Abert, he received his doctorate in 1922 (Dr. phil.). In 1945, he was appointed Kapellmeister at the Volksoper in Dresden. In 1949, he was appointed as the first professor of music education at a German university (University of Halle). He was also director of institutes at the Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg and the Humboldt University Berlin. In 1955, he was one of the initiators of the first Hallische Musiktage. Life Origin and music studies Born in Löbtau, now part of Dresden, Reuter came from a Saxon artisan family from the Ore Mountains. Günther Noll: ''Fritz Reuter (1896–1963). A tribute on the occasion of his 100th birthday''. In Rudolf-Dieter Kraemer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sievers's Theory Of Anglo-Saxon Meter
Eduard Sievers developed a theory of the meter of Anglo-Saxon alliterative verse, which he published in his 1893 ''Altgermanische Metrik''. Widely used by scholars, it was in particular extended by Alan Joseph Bliss.Bliss, Alan Joseph. ''The metre of 'Beowulf' ''(Oxford: Blackwell, 1958) Sievers' system is a primarily method of categorization rather than a full theory of meter. It does not, in other words, purport to describe the system the '' scops'' actually used to compose their verse, nor does it explain why certain patterns are favoured or avoided. Summary of Sievers' categories A line of Anglo-Saxon verse is made up of two half-lines. Each of these half-lines contains two main stresses (or 'lifts'). Sievers categorized three basic types of half-line that were used. Here a stressed syllable is represented by the symbol '/' and an unstressed syllable by the symbol 'x'. He also noted that three possible types of half-line were not used: */ x x / */ / x x *x x / / However t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
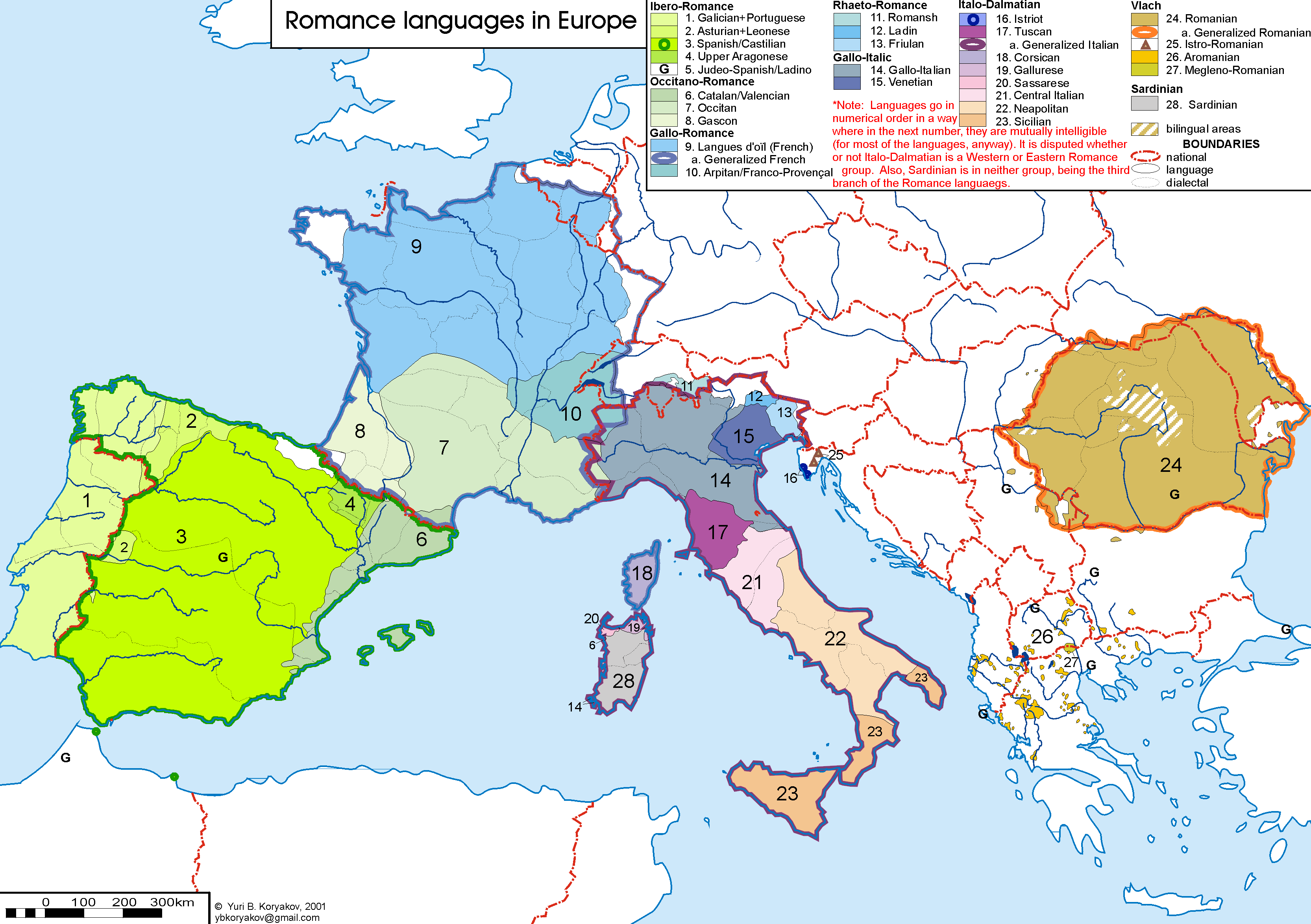
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, highest population within its city limits of any city in the European Union. The city is also one of the states of Germany, being the List of German states by area, third smallest state in the country by area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of Brandenburg, and Brandenburg's capital Potsdam is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.6 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr region, as well as the List of EU metropolitan areas by GDP, fifth-biggest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sievers' Law
Sievers's law in Indo-European linguistics accounts for the pronunciation of a consonant cluster with a glide ( or ) before a vowel as it was affected by the phonetics of the preceding syllable. Specifically, it refers to the alternation between and , and possibly and as conditioned by the weight of the preceding syllable. For instance, Proto-Indo-European (PIE) became Proto-Germanic *''harjaz'', Gothic ''harjis'' "army", but PIE became Proto-Germanic *''hirdijaz'', Gothic ''hairdeis'' "shepherd". It differs from ablaut in that the alternation has no morphological relevance but is phonologically context-sensitive: PIE followed a heavy syllable (a syllable with a diphthong or long vowel, or ending in more than one consonant), but would follow a light syllable (a short vowel followed by a single consonant). History Discovery This situation was first noticed by the Germanic philologist Eduard Sievers (1859–1932), and his aim was to account for certain phenomena i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Saxon
Old Saxon (), also known as Old Low German (), was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). It is a West Germanic language, closely related to the Anglo-Frisian languages. It is documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it gradually evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken throughout modern northwestern Germany, primarily in the coastal regions and in the eastern Netherlands by Saxons, a Germanic tribe that inhabited the region of Saxony. It partially shares Anglo-Frisian's ( Old Frisian, Old English) Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law which sets it apart from Low Franconian and Irminonic languages, such as Dutch, Luxembourgish and German. The grammar of Old Saxon was fully inflected with five grammatical cases ( nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, and instrumental), three grammati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Language
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature dates from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman (a type of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers became dominant in England, their language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Linguistics
Historical linguistics, also known as diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of how languages change over time. It seeks to understand the nature and causes of linguistic change and to trace the evolution of languages. Historical linguistics involves several key areas of study, including the reconstruction of ancestral languages, the classification of languages into families, ( comparative linguistics) and the analysis of the cultural and social influences on language development. This field is grounded in the uniformitarian principle, which posits that the processes of language change observed today were also at work in the past, unless there is clear evidence to suggest otherwise. Historical linguists aim to describe and explain changes in individual languages, explore the history of speech communities, and study the origins and meanings of words ( etymology). Development Modern historical linguistics dates to the late 18th century, having originally grown o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junggrammatiker
The Neogrammarians (, , ) were a German school of linguists, originally at the University of Leipzig, in the late 19th century who proposed the Neogrammarian hypothesis of the regularity of sound change. Overview According to the Neogrammarian hypothesis, a diachronic sound change affects simultaneously all words in which its environment is met, without exception. Verner's law is a famous example of the Neogrammarian hypothesis, as it resolved an apparent exception to Grimm's law. The Neogrammarian hypothesis was the first hypothesis of sound change to attempt to follow the principle of falsifiability according to the scientific method. Subsequent researchers have questioned this hypothesis from two perspectives. First, adherents of lexical diffusion (where a sound change affects only a few words at first and then gradually spreads to other words) believe that some words change others. Second, some believe that it is possible for sound changes to observe grammatical conditioning. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English language, English, is also the world's most List of languages by total number of speakers, widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia, History of Germany#Iron Age, Iron Age Northern Germany and along the North Sea and Baltic coasts. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English language, English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philologist
Philology () is the study of language in oral and written historical sources. It is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics with strong ties to etymology. Philology is also defined as the study of literary texts and oral and written records, the establishment of their authenticity and their original form, and the determination of their meaning. A person who pursues this kind of study is known as a philologist. In older usage, especially British, philology is more general, covering comparative and historical linguistics. Classical philology studies classical languages. Classical philology principally originated from the Library of Pergamum and the Library of Alexandria around the fourth century BC, continued by Greeks and Romans throughout the Roman and Byzantine Empire. It was eventually resumed by European scholars of the Renaissance, where it was soon joined by philologies of other European ( Romance, Germanic, Celtic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |