|
Eatonville, Nova Scotia
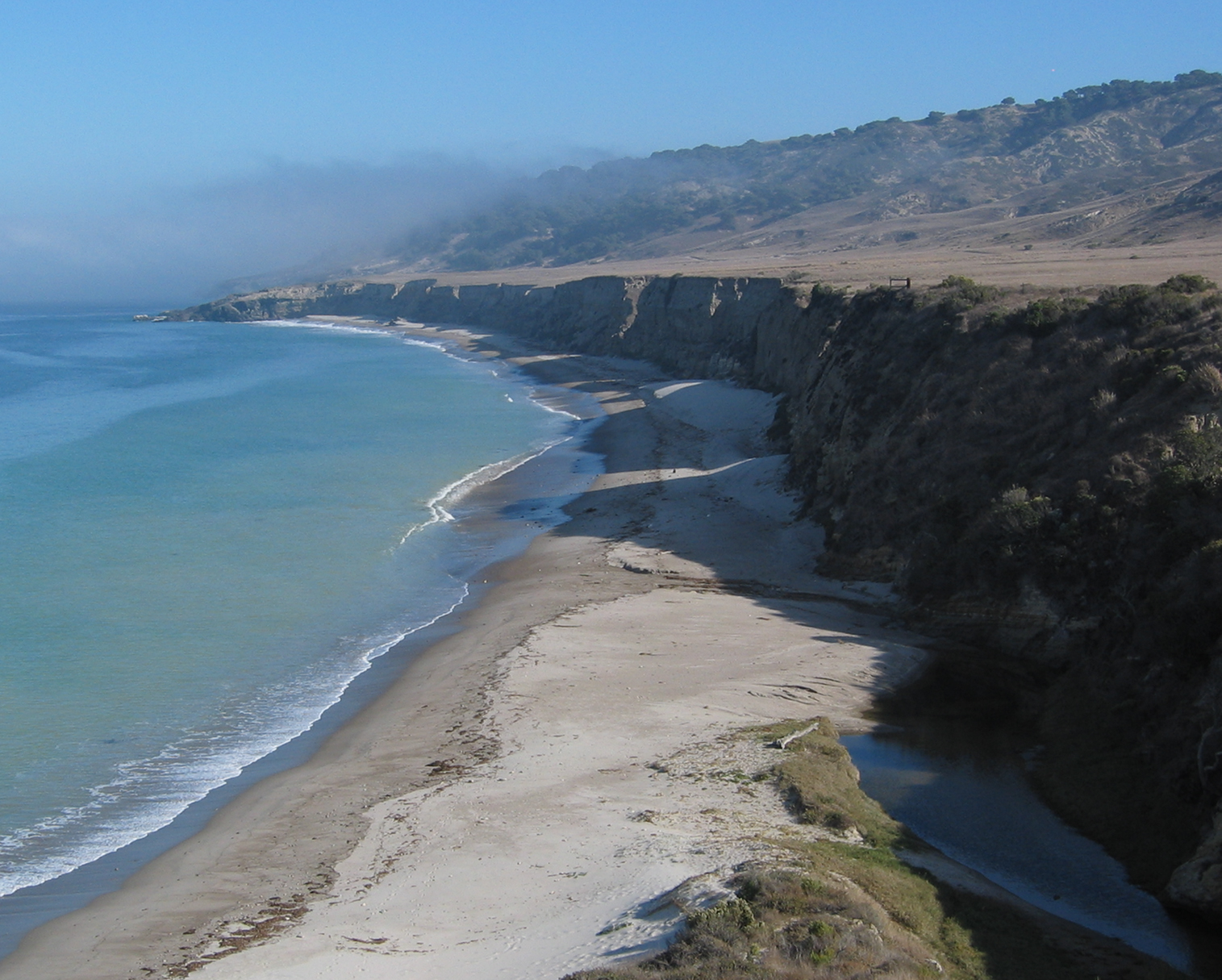
Eatonville is a former lumber and shipbuilding village in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia. It includes a large tidal harbour at the mouth of the Eatonville Brook beside several dramatic sea stacks known as the "Three Sisters". It was founded in 1826 and abandoned in the 1940s. The site of the village is now part of Cape Chignecto Provincial Park. Early history The complex geology of Eatonville Harbour and powerful erosion forces of the Bay of Fundy tides created a series of dramatic sea stacks, stone arches and caves. Three of the sea stacks are closely grouped and known as the "Three Sisters". According to a Mi'kmaw legend, they were created by the mythical figure Glooscap when he turned a pack of dogs pursuing a moose into the stone towers. The fleeing moose became the Isle Haute and can be seen in the distance from the frozen stone forms of the Three Sisters. Settlers established a small sawmill on crown land at the tidal harbour beside the sea stacks about 1826. Early famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church.-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''village'', from Latin ''villāticus'', ultimately from Latin ''villa'' (English ''vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
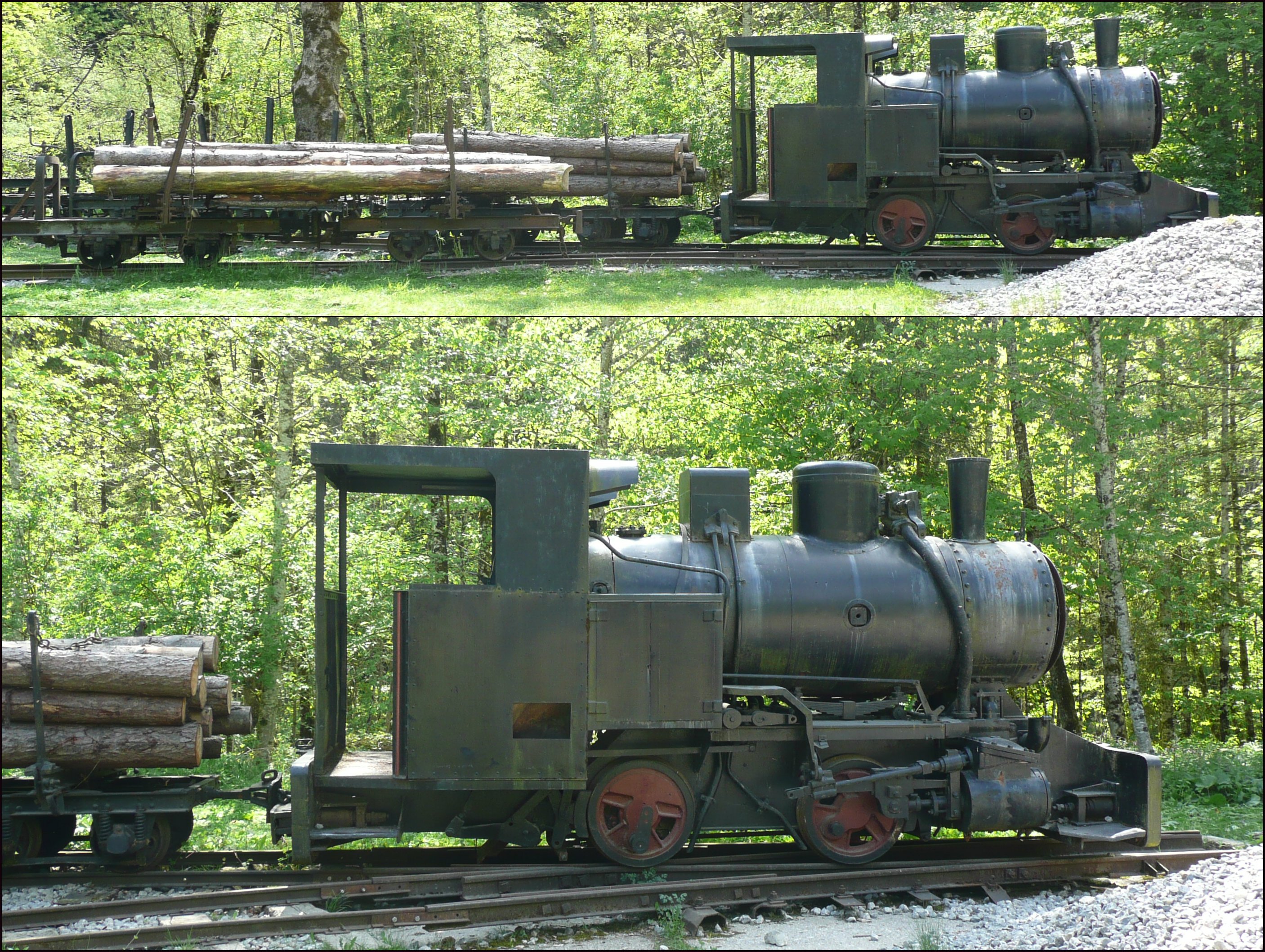
Tramway (industrial)
Tramways are lightly laid industrial railways, often not intended to be permanent. Originally, rolling stock could be pushed by humans, pulled by animals (especially horses and mules), cable-hauled by a stationary engine, or pulled by small, light locomotives. Tramways can exist in many forms; sometimes simply tracks temporarily placed on the ground to transport materials around a factory, mine or quarry. Many use narrow-gauge railway technology, but because tramway infrastructure is not intended to support the weight of vehicles used on railways of wider track gauge, the infrastructure can be built using less substantial materials, enabling considerable cost savings. The term "tramway" is not used in North America, but is commonly used in the United Kingdom and elsewhere where British railway terminology and practices influenced management practices, terminologies and railway cultures, such as Australia, New Zealand, and those parts of Asia, Africa and South America that c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debert
Debert ( ; 2006 pop: 1,471) is an unincorporated farming community in Nova Scotia, Canada. Located in the central-western part of Colchester County, it is approximately west of Truro. The community has two churches ( United Baptist Church and United Church of Canada), Royal Canadian Legion (Branch 106), a skating rink, a community centre, two vehicle repair garages, one convenience store, and a volunteer fire department. Debert is situated near coal and iron ore deposits that were mined in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Debert became a station stop on the Halifax-Montreal mainline of the Intercolonial Railway in the 1870s. This railway line continues to this day under the ownership of Canadian National Railway (CN Rail), with passenger service provided by Via Rail, but without a stop at Debert. Military history During the Second World War Debert was the location of a Canadian Army base named Debert Military Camp and an adjoining Royal Canadian Air Force station named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geopark
A geopark is a protected area with internationally significant geology within which Sustainability, sustainable development is sought and which includes tourism, conservation, education and research concerning not just geology but other relevant sciences. In 2005, a European Geopark was defined as being: "a territory with a particular geological heritage and with a sustainable territorial development....the ultimate aim of a European Geopark is to bring enhanced employment opportunities for the people who live there." Today the geopark is virtually synonymous with the UNESCO geopark, which is defined and managed under the voluntary authority of UNESCO's International Geoscience Programme, International Geoscience and Geoparks Programme (IGGP). UNESCO provides a standard for geoparks and a certification service to territories that apply for it. The service is available to member states of UNESCO. The list of members is not the same as the member states of the United Nations. Memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CFB Greenwood
Canadian Forces Base Greenwood , or CFB Greenwood, is a Canadian Forces Base located east of Greenwood, Nova Scotia. It is primarily operated as an air force base by the Royal Canadian Air Force and is one of two bases in the country using the CP-140 Aurora and CP-140A Arcturus anti-submarine/maritime patrol and surveillance aircraft, the other being CFB Comox. Its primary RCAF lodger unit is 14 Wing, commonly referred to as 14 Wing Greenwood. RAF Station Greenwood The relatively fog-free climate of the farming hamlet of Greenwood was selected by the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and Royal Air Force for an airfield as part of the British Commonwealth Air Training Plan (BCATP), following the signing of that formal agreement on December 17, 1939. The airfield for RAF Station Greenwood was constructed between 1940 and 1942 with the first training units arriving as part of No. 36 Operational Training Unit (OTU) on March 9, 1942. Early training aircraft types included the Lockh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raised Beach
A raised beach, coastal terrace,Pinter, N (2010): 'Coastal Terraces, Sealevel, and Active Tectonics' (educational exercise), from 2/04/2011/ref> or perched coastline is a relatively flat, horizontal or gently inclined surface of marine origin,Pirazzoli, PA (2005a): 'Marine Terraces', in Schwartz, ML (ed) ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science.'' Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 632–633 mostly an old abrasion platform which has been lifted out of the sphere of wave activity (sometimes called "tread"). Thus, it lies above or under the current sea level, depending on the time of its formation.Strahler AH; Strahler AN (2005): ''Physische Geographie.'' Ulmer, Stuttgart, 686 p.Leser, H (ed)(2005): ‚''Wörterbuch Allgemeine Geographie.'' Westermann&Deutscher Taschenbuch Verlag, Braunschweig, 1119 p. It is bounded by a steeper ascending slope on the landward side and a steeper descending slope on the seaward side (sometimes called "riser"). Due to its generally flat shape, it is often used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunkhouse
A bunkhouse is a barracks-like building that historically was used to house working cowboys on ranches, or loggers in a logging camp in North America. As most cowboys were young single men, the standard bunkhouse was a large open room with narrow beds or cots for each individual and little privacy. The bunkhouse of the late 19th century was usually heated by a wood stove and personal needs were attended to in a cookhouse and an outhouse. Background While the modern bunkhouse today is still in existence on some large ranches that are too far away from towns for an easy daily commute, it now has electricity, central heating and modern indoor plumbing. In the United Kingdom, a bunkhouse provides accommodation with fewer facilities than a larger, staffed youth hostel. Bunkhouses are found in mountainous areas, such as the Scottish Highlands, as well as rural areas in England and Wales, for example at All Stretton. Bunkhouses are very different from hotels: bunkhouses often just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
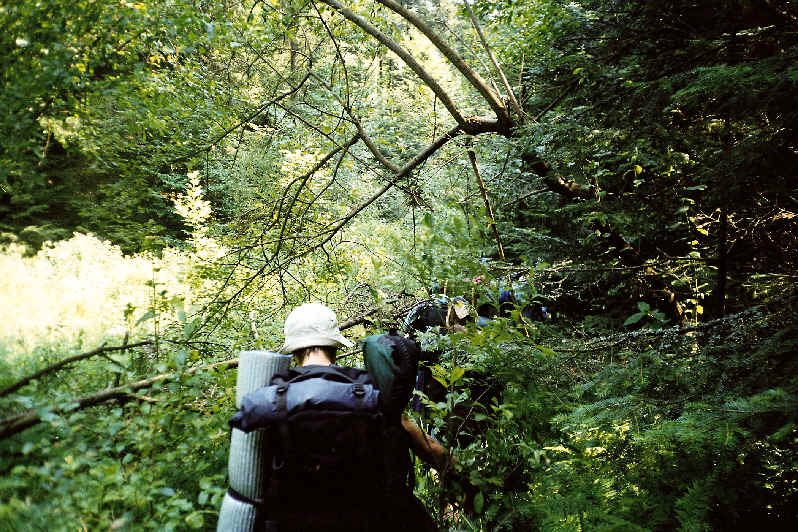
Backpacking (wilderness)
Backpacking is the outdoor recreation of carrying gear on one's back while hiking for more than a day. It is often an extended journey and may involve camping outdoors. In North America, tenting is common, where simple shelters and mountain huts, widely found in Europe, are rare. In New Zealand, hiking is called Tramping in New Zealand, tramping, and tents are used alongside a nationwide network of huts. Hill walking is equivalent in Britain (but this can also refer to a day walk), though backpackers make use of a variety of accommodation, in addition to camping. Backpackers use simple huts in South Africa. Trekking and bushwalking are other words used to describe such multi-day trips. The terms walking tour or Long distance path , long distance hike are also used. Backpacking backpacking (travel), as a method of travel is a different activity, which mainly uses public transport during a journey that can last months. It is, however, similar to bikepacking, bicycle touring, Canoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eatonville Centre , United States
{{disambig ...
Eatonville may refer to: * Eatonville, Florida, United States * Eatonville, Minnesota, United States, an alternative name for the former Dakota village Ḣeyate Otuŋwe * Eatonville, Mississippi, United States * Eatonville, Ontario, a neighbourhood of the city of Toronto, Canada * Eatonville, Nova Scotia, Canada, a ghost town * Eatonville, Washington Eatonville is a town in Pierce County, Washington, United States. It is south of Tacoma, Washington, Tacoma. The population was 2,845 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The town motto is "Better Together." History For centuries, Nis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Paper Company
The Scott Paper Company was a manufacturer and marketer of sanitary tissue products with operations in 22 countries. Its products were sold under a variety of well-known brand names, including ''Scott Tissue'', ''Cottonelle'', ''Baby Fresh'', ''Scottex'' and ''Viva''. Consolidated sales of its consumer and commercial products totalled approximately $3.6 billion in 1994. The company was acquired by the Kimberly-Clark, Kimberly-Clark Corporation in 1995. History Scott Paper was founded in 1879 in Philadelphia by brothers Edward Irvin Scott, E. Irvin Scott and Clarence Scott, and is often credited as being the first to market toilet paper sold on a roll. They began marketing paper towels in 1907, and Facial tissue, paper tissues in the 1930s. In 1927, Scott purchased a Nova Scotian pulp mill, and thus began a long series of acquisitions. It joined with The Mead Corporation in 1936 to form Brunswick Pulp & Paper Company, which used their pulp mill in Georgia, US, Georgia to suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
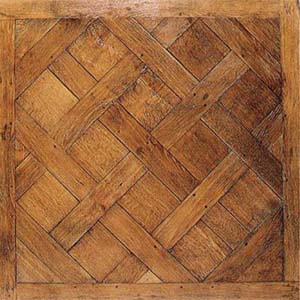
Parquetry
Parquet (; French for "a small compartment") is a geometric mosaic of wood pieces used for decorative effect in flooring. Parquet patterns are often entirely geometrical and angular—squares, triangles, Lozenge (shape), lozenges—but may contain curves. The most popular parquet flooring pattern is herringbone pattern, herringbone. Etymology The word derives from the Old French ''parchet'' (the diminutive of ''parc''), literally meaning "''a small enclosed space''". History Large diagonal squares known as ''parquet de Palace of Versailles, Versailles'' were introduced in 1684 as ''parquet de menuiserie'' ("woodwork parquet") to replace the marble flooring that required constant washing, which tended to rot the joists beneath the floors. Such ''parquets en losange'' were noted by the Swedish architect Daniel Cronström at Versailles and at the Grand Trianon in 1693. Materials Woods contrasting in color and grain, such as oak, walnut, cherry, tilia, lime, pine, maple etc. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Yarmouth, Nova Scotia
New Yarmouth is an abandoned farming and forestry community which is now part of the Cape Chignecto Provincial Park in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia near the village of Advocate, Nova Scotia, Advocate. Geography New Yarmouth occupies a plateau 244 metres (800 feet) above West Advocate, Nova Scotia, Advocate overlooking Advocate Bay, a branch of the Bay of Fundy. The highest point in Cape Chignecto Provincial Park is located on a summit of 275 metres (900 feet) just north of the New Yarmouth fire tower. McGahey Brook and Mill Brook have their source at New Yarmouth, draining south to Advocate Bay through deep ravines, while Copp Hollow Brook also begins at New Yarmouth, draining to the north. An abandoned log pond and several beaver ponds are found near the source of these brooks. History Land at New Yarmouth was first granted to United Empire Loyalist, Loyalist John Hall in 1785 and later granted to Alexander and John Grant in 1819 although neither family appear to have se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |