|
EN (cuneiform)
En (Borger 2003 nr. 164 ; Unicode, U+12097 𒂗, see also Ensí) is the Sumer, Sumerian cuneiform for 'lord/lady' or 'priest[ess]'. Originally, it seems to have been used to designate a high priest or priestess of a Sumerian city-state's patron-deity – a position that entailed political power as well. It may also have been the original title of the ruler of Uruk. See Lugal#Lugal, ensi and en, ''Lugal, ensi and en'' for more details. Deities including En as part of their name include dingir, DEnlil, DEnki, DEngurun, and DSin (mythology), Enzu. Enheduanna, Akkadian language, Akkadian 2285 BC – 2250 BC was the first known holder of the title En, here meaning 'Priestess'. Archaic forms The corresponding Emesal, Emesal dialect word was UMUN, which may preserve an archaic form of the word. Earlier Emeg̃ir (the standard dialect of Sumerian) forms can be postulated as *''ewen'' or *''emen'', eventually dropping the middle consonant and becoming the familiar EN. Amarna letters: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform Sign EN, For Lord Or Master (evolution)
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform scripts are marked by and named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions (Latin: ) which form their Grapheme, signs. Cuneiform is the History of writing#Inventions of writing, earliest known writing system and was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). Over the course of its history, cuneiform was adapted to write a number of languages in addition to Sumerian. Akkadian language, Akkadian texts are attested from the 24th century BC onward and make up the bulk of the cuneiform record. Akkadian cuneiform was itself adapted to write the Hittite language in the early second millennium BC. The other languages with significant cuneiform Text corpus, corpora are Eblaite language, Eblaite, Elamit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Language
Akkadian ( ; )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218–280 was an East Semitic language that is attested in ancient Mesopotamia ( Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa, Babylonia and perhaps Dilmun) from the mid- third millennium BC until its gradual replacement in common use by Old Aramaic among Assyrians and Babylonians from the 8th century BC. Akkadian, which is the earliest documented Semitic language, is named after the city of Akkad, a major centre of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (–2154 BC). It was written using the cuneiform script, originally used for Sumerian, but also used to write multiple languages in the region including Eblaite, Hurrian, Elamite, Old Persian and Hittite. The influence of Sumerian on Akkadian went beyond just the cuneiform script; owing to their close proximity, a lengthy span of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
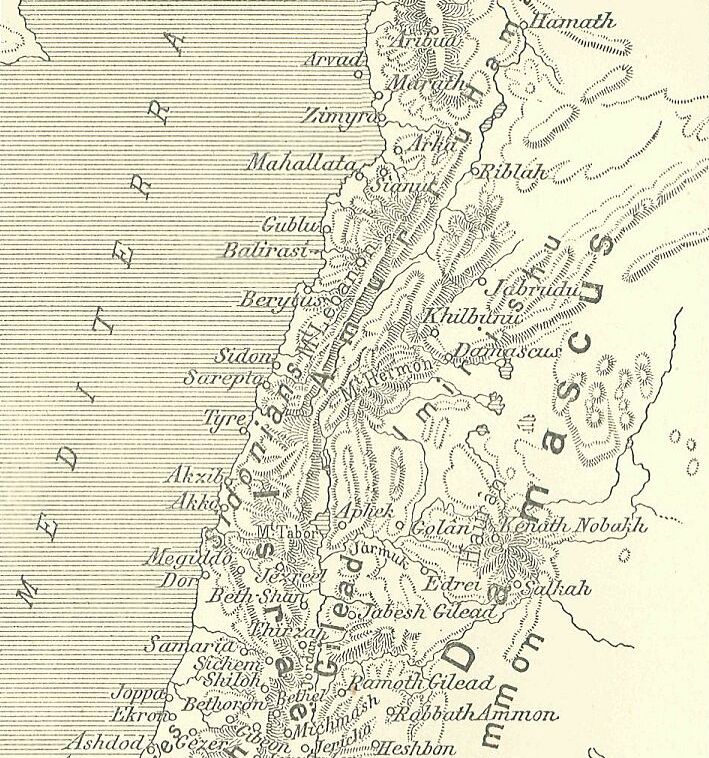
Labayu
Labaya (Labayu or Lib'ayu) was the ruler of Shechem and warlord in the central hill country of southern Canaan during the Amarna Period (c. 1350 BC). He lived contemporaneously with Pharaoh Akhenaten. Labaya is mentioned in several of the Amarna Letters (abbreviated "EA", for 'el Amarna'). He is the author of letters EA 252– 54. Labaya was active over the whole length of Samaria and slightly beyond, as he gave land to Habiru in the vicinity of Šakmu (Shechem) and he and his sons threatened such powerful towns as Jerusalem and Gazru (Gezer) to the south, and Megiddo to the north. Career The Amarna letters give an incomplete look at Labaya's career. In the first of Labaya's letters thus far discovered (EA 252), he defends himself to the Pharaoh against complaints of other city rulers about him, for example, the complaint that he has hired mercenaries from among the Habiru. Labaya further admitted to having invaded Gezer and insulting its king Milkilu. He denied any knowle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abimilku
Abimilki (Amorite language, ''Amorite'': , ''LÚ, LÚa-bi-mil-ki'', ) around 1347 BC held the rank of Prince of Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre (called "Surru" in the letters), during the period of the Amarna letters Text corpus, correspondence (1360–1332 BC). He is the author of ten letters to the Egyptian pharaoh, EA 146–155 (EA (el Amarna), EA for 'el Amarna'). In letter EA 147, Pharaoh Akhenaten confirmed him as ruler of Tyre upon the death of his father, and in EA 149, referred to him with the rank of ''rabisu'' (general). Abimilki is not referenced by name in any other letters of the 382-letter corpus. His name has been linked with the biblical Abimelech. His name means "My father (is) king." Historical background Following the request of Akhenaten to disseminate his political updates in Canaan, Kinaha, some other city states rebelled against this decision. The background was the vacancy in the position of ''rabisu'' in the garrison of Tyre, which Akhenaten staffed with non-Egyptians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johns Hopkins University Press
Johns Hopkins University Press (also referred to as JHU Press or JHUP) is the publishing division of Johns Hopkins University. It was founded in 1878 and is the oldest continuously running university press in the United States. The press publishes books and journals, and operates other divisions including fulfillment and electronic databases. Its headquarters are in Charles Village section of Baltimore, Maryland Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east .... In 2017, after the retirement of Kathleen Keane, who is credited with modernizing JHU Press for the digital age, the university appointed new director Barbara Pope. Overview Daniel Coit Gilman, the first president of Johns Hopkins University, inaugurated the press in 1878. The press began as the university's Public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 282
Amarna letter EA 282 is a relatively short ovate clay tablet Amarna letter, located in the British Museum, no. 29851. The letter contains only 16 lines of cuneiform text, in Akkadian language, Akkadian, with lines 12 to 16 covering half of the tablet's reverse. Of note, the scribe, though the tablet is unparagraphed, inscribed a line along the bottom of the front side below line 11; and likewise, at the start of the letter, a line is inscribed above the top of line 1, on the obverse. (See photo, Obverse Letter EA 282 is from Šuwardata, of Qiltu (typical in the Amarna letters: the "Man-(LÚ (man Sumerogram), LÚ), URU (city Sumerogram), URU-Qiltu-(ki (cuneiform), ki), the "Govern-or" or 'Man of the (URU)-City-(his)'), to the Pharaoh of Egypt, and is from one of the vassal states in Canaan. Visually, the tablet is ovate, with even the inscribed cuneiform signs having ovate form, almost over the entire letter. Consequently, though EA 282 is topical, and tells a story, its first appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 254
Amarna letter EA 254, titled: ''"Neither Rebel nor Delinquent (2)"'', is a moderate length, tall, and mostly flat rectangular clay tablet Amarna letter, (see her. The letter is from Labaya of city-state Šakmu (Shechem today). It is an undamaged letter, in pristine condition, with cuneiform script on almost all surfaces: ''Obverse'', Bottom, ''Reverse'', and Left Side. Letter EA 254 is numbered VAT 335, from the Vorderasiatisches Museum Berlin. The Amarna letters, about 300, numbered up to EA 382, are a mid 14th century BC, about 1360 BC and 30-35 years later, correspondence. The initial corpus of letters were found at Akhenaten's city Akhetaten, in the floor of the Bureau of Correspondence of Pharaoh; others were later found, adding to the body of letters. The letter EA 254: ''"Neither Rebel nor Delinquent (2)"'' EA 254, letter three of three. (Not a linear, line-by-line translation, and English from French.) ''Obverse:'' See here Line drawing (cuneiform), Line drawing : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 252
Amarna letter EA 252, titled: ''Sparing One's Enemies,'' is a square, mostly flat clay tablet letter written on both sides, and the bottom edge. Each text line was written with a horizontal line scribed below the text line, as well as a vertical left margin-line, (beginning of text at left) scribe line on the obverse of the tablet. The letter contains 14 (15) lines on the obverse, continuing on the bottom tablet edge to conclude at line 31 on the reverse, leaving a small space before the final tablet edge. At least 4 lines from the obverse intrude into the text of the reverse (appearing as upside-down cuneiform into the text of the reverse), actually dividing the reverse into a top half and bottom half, and even creating a natural spacing segue to the reverse's text, and the story. Letter EA 252 is authored by Labaya, by the 'Man, city-state' (of) Šakmu ( Shechem today), and written to the Pharaoh. The letter is letter one of three letters authored by him, to the Pharaoh. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bêlu
Bêl (; from ) is a title signifying 'lord' or 'master' applied to various gods in the Mesopotamian religion of Akkad, Assyria, and Babylonia. The feminine form is ''Bêlit'' ('Lady, Mistress') in Akkadian. ''Bel'' is represented in Greek as Belos and in Latin as Belus. ''Belit'' appears in Greek form as Beltis (Βελτις). Linguistically, ''Bel'' is an East Semitic form cognate with the Northwest Semitic Baal with the same meaning. ''Bel'' was especially used for the Babylonian god Marduk in Assyrian and neo-Babylonian personal names or mentioned in inscriptions in a Mesopotamian context. Similarly, ''Bêlit'' mostly refers to Marduk's spouse Sarpanit. Marduk's mother, the Sumerian goddess often referred to in the Sumerian language as Ninhursag, Damkina, and Ninmah, was often known as ''Belit-ili'' ('Lady of the Gods') in Akkadian. Other gods called "Lord" were sometimes identified totally or in part with Bel Marduk. The god Malak-bel of Palmyra is an example, atteste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1350 BC
Events and trends * c. 1352 BC – Amenhotep III (Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt) dies and is succeeded as Pharaoh by Amenhotep IV. * 1350 BC – Yin becomes the new capital of Shang dynasty The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou d ... China. References {{DEFAULTSORT:1350s Bc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |