|
EMD FP9
The EMD FP9 is an American , B-B dual-service passenger and freight-hauling diesel locomotive that was produced between February 1954 and December 1959 by General Motors Electro-Motive Division, and General Motors Diesel. Final assembly was at GM-EMD's La Grange, Illinois plant, except for Canadian orders, which were assembled by Canadian subsidiary GMD at London, Ontario. The FP9 was essentially EMD's F9 locomotive extended by four feet to give greater steam generator and water capacity for hauling passenger trains. A total of 90 cab-equipped lead A units were built; unlike the freight series, no cabless booster B units were sold. Regular F9B units were sometimes used with FP9 A units, since they, lacking cabs, had more room for water and steam generators. The FP9 and its predecessor, the FP7, were offshoots of GM-EMD's highly successful F-unit series of cab unit diesel locomotives. Original buyers Locomotives built by EMD at La Grange, Illinois Locomotives built by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackenzie Northern Railway
The Mackenzie Northern Railway is a Canadian railway operating in Alberta and the Northwest Territories. It is the northernmost trackage of the contiguous North American railway network. Since being purchased by CN in 2006, it has been officially known as the Meander Subdivision. History The majority of the tracks which the Mackenzie Northern Railway uses were built by the federal government as the Great Slave Lake Railway, running from a point on the Northern Alberta Railways (NAR) at Grimshaw, Alberta, to the southern shores of Great Slave Lake at Hay River, Northwest Territories. The undertaking started in 1961 with a proposal to Parliament, and the line opened in 1964. This railroad was part of John Diefenbaker's vision for the north, and facilitated shipment of lead-zinc ore from the Pine Point Mine. The Great Slave Railway's operation was entrusted to Canadian National Railway in 1966, which had been operating the line on behalf of the federal government since it opene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Generator (railroad)
A steam generator is a type of boiler used to produce steam for climate control and potable water heating in railroad passenger cars. The output of a railroad steam generator is low pressure, saturated steam that is passed through a system of pipes and conduits throughout the length of the train. Steam generators were developed when diesel locomotives started to replace steam locomotives on passenger trains. In most cases, each passenger locomotive was fitted with a steam generator and a feedwater supply tank. The steam generator used some of the locomotive's diesel fuel supply for combustion. When a steam generator-equipped locomotive was not available for a run, a so-called "heating car" fitted with one or two steam generators was inserted between the last locomotive in the consist and the rest of the train. Steam generators would also be fitted to individual cars to enable them to be heated independently of any locomotive supply. In Ireland, Córas Iompair Éireann used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of GMD Locomotives
The following is a list of locomotives produced by General Motors Diesel (GMD), and its corporate successor Electro-Motive Canada (EMC). The NF-110 and NF-210 locomotive models were narrow gauge locomotives for use on Canadian National Railway's Newfoundland Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ... lines, as are the New Zealand DF class for use by Tranz Rail. References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Gmd Locomotives * General Motors engines GMD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of GM-EMD Locomotives
The following is a list of locomotives produced by the Electro-Motive Corporation (EMC), and its successors General Motors Electro-Motive Division (GM-EMD) and Electro-Motive Diesel (EMD). Streamlined power cars and early experimental locomotives EMC participated in the construction of a number of motorized railcars, integrated streamliner trainsets, and experimental locomotives in the 1930s. Most of these were short production runs (one, two, or four units) that were used by a single railroad. These consisted of Winton prime movers and General Electric generating, control, and transmission components inside a carbody whose assembly was subcontracted to another manufacturer, since EMC did not commence regular road locomotive production until 1937. Switchers (SW/NW/SC/NC/MP) The "S" designation originally stood for six hundred horsepower and the "N" designation for nine hundred horsepower, although they were used for the more general designation of smaller and larger engine models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001. Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, the railway owns approximately of track in seven provinces of Canada and into the United States, stretching from Montreal to Vancouver, and as far north as Edmonton. Its rail network also serves Minneapolis–St. Paul, Milwaukee, Detroit, Chicago, and Albany, New York, in the United States. The railway was first built between eastern Canada and British Columbia between 1881 and 1885 (connecting with Ottawa Valley and Georgian Bay area lines built earlier), fulfilling a commitment extended to British Columbia when it entered Confederation in 1871; the CPR was Canada's first transcontinental railw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIA FP9ARM
The Via Rail FP9ARM was a re-manufactured version of a GMD FP9A Diesel passenger locomotive, rebuilt between 1983 and 1985 by Canadian National Railways at their Pointe St-Charles shops. History In the early 1980s, Via was suffering from reliability problems with its motive power. While an order for GMD F40PHs was expected to be announced, Via needed to something in the interim to improve service on its routes. Via Rail had a surplus of steam-heated GMD Via FP9A units built in the 1950s and so fifteen of these units were chosen to be re-manufactured. The first twelve units, 6300–6311, were re-manufactured at the CN Pointe St-Charles shops in Montreal while the final three, 6312–6314, were re-manufactured at the CN shops in Moncton, New Brunswick. As part of the re-manufacturing many original components were replaced or upgraded - the original 16-567C engines were rebuilt with 645E series power assemblies, and the Woodward governor was revised, thereby raising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
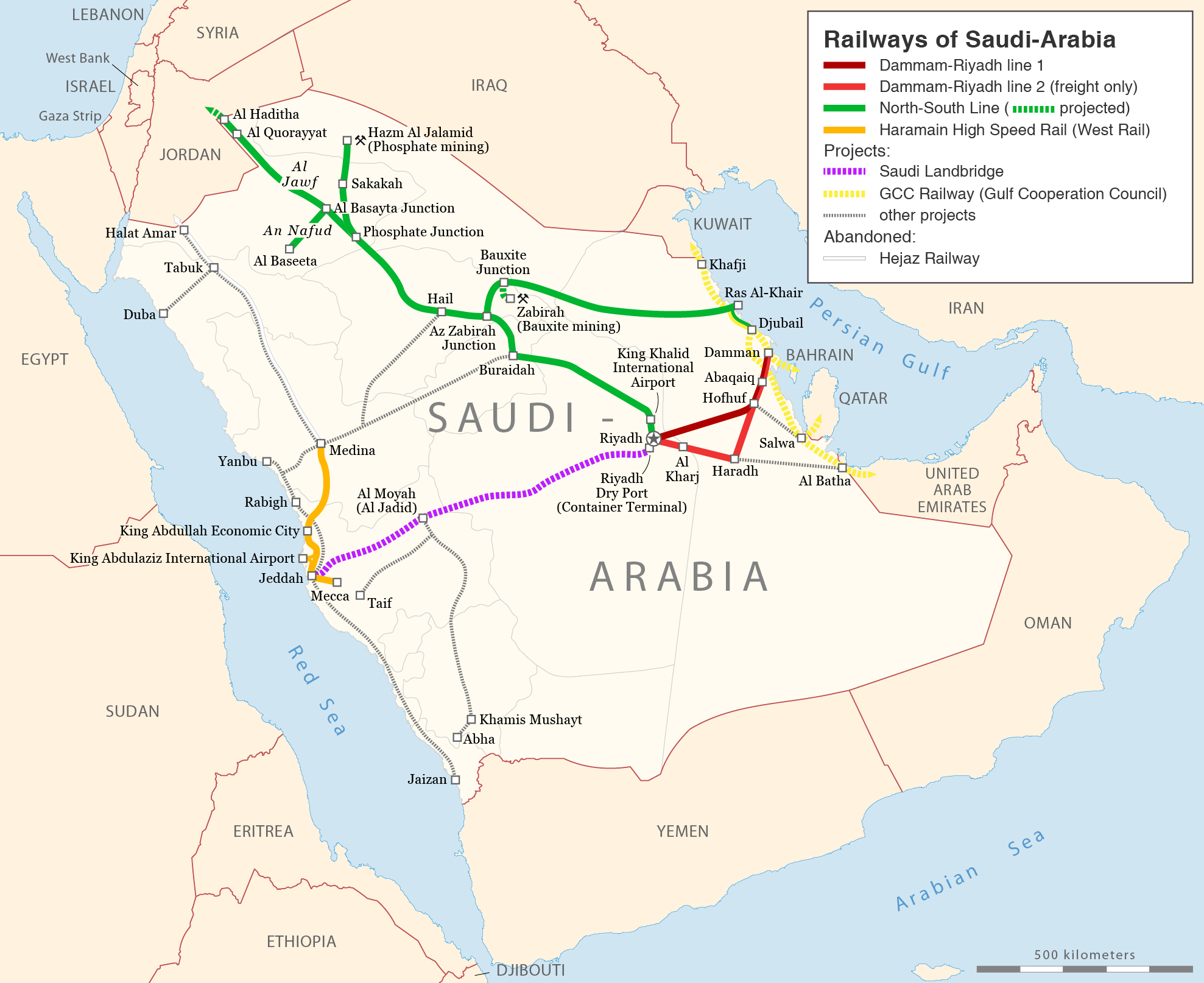
Saudi Government Railways
The Saudi Railways Organization (SRO) ( ar, المؤسسة العامة للخطوط الحديدية) is one of two state-owned companies that operates Saudi Arabia's rail network along with Saudi Railway Company. The SRO operates a network of railways with a total length of approximately 1,380 kilometers. The network consists of two main lines. A 449 km passenger line that links Dammam with Riyadh, and a 556 km freight line that connects the King Abdul Aziz Port in Dammam with Riyadh. There are plans to extend the network to the Red Sea port of Jeddah and, eventually to the borders of Jordan, Yemen, and perhaps all the way to Egypt. Approval to merge Saudi Railways Organization and Saudi Railway Company was announced in February 2021. History The first railway in Arabia was the Hejaz Railway, constructed by the Ottoman Empire from the Damascus to Medina. This narrow gauge railway opened in 1908, but closed in 1920 due to the Arab Revolt. Modern railways were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrocarriles Nacionales De México
Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México (better known as N de M and especially in its final years as FNM) was Mexico's state owned railroad company from 1938 to 1998, and prior to 1938 (dating from the regime of Porfirio Díaz), a major railroad controlled by the government that linked Mexico City to the major cities of Ciudad Juárez, Nuevo Laredo and Matamoros on the U.S. border. The first trains to Nuevo Laredo from Mexico City began operating in 1903. History The beginnings of rail transport in Mexico date back to the concessions granted by Maximilian I of Mexico, mostly to foreign companies, and continued by Benito Juárez. In 1898, José Yves Limantour proposed a system of concessions of the railway companies on the future lines to be built from 1900. That same year the Secretariat of the Treasury promulgated the first General Railway Law. This law established a system whereby concessions would be granted to companies to lay railway lines only when they satisfied the econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMD FT
The EMD FT is a diesel-electric locomotive that was produced between March 1939 and November 1945, by General Motors' Electro-Motive Corporation (EMC), later known as GM Electro-Motive Division (EMD). The "F" stood for Fourteen Hundred (1400) horsepower (rounded from 1350) and the "T" for Twin, as it came standard in a two-unit set. The design was developed from the TA model built for the C,RI&P in 1937, and was similar in cylinder count, axle count, length, and layout. All told 555 cab-equipped ”A” units were built, along with 541 cabless booster or ”B” units, for a grand total of 1,096 units. The locomotives were all sold to customers in the United States. It was the first model in EMD's very successful F-unit series of cab unit freight diesels and was the locomotive that convinced many U.S. railroads that the diesel-electric freight locomotive was the future. Many rail historians consider the FT one of the most important locomotive models of all time. Design an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago & North Western Railway
The Chicago and North Western was a Class I railroad in the Midwestern United States. It was also known as the "North Western". The railroad operated more than of track at the turn of the 20th century, and over of track in seven states before retrenchment in the late 1970s. Until 1972, when the employees purchased the company, it was named the Chicago and North Western Railway (or Chicago and North Western Railway Company). The C&NW became one of the longest railroads in the United States as a result of mergers with other railroads, such as the Chicago Great Western Railway, Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway and others. By 1995, track sales and abandonment had reduced the total mileage to about 5,000. The majority of the abandoned and sold lines were lightly trafficked branches in Iowa, Illinois, Minnesota, South Dakota and Wisconsin. Large line sales, such as those that resulted in the Dakota, Minnesota and Eastern Railroad, further helped reduce the railroad to a mainline c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cab Unit
In North American railroad terminology, a cab unit is a railroad " locomotive" with its own cab and controls. "Carbody unit" is a related term, which may be either a cabless booster unit controlled from a linked cab unit, or a cab unit that contains its own controls. Characteristics With both body styles, a bridge-truss design framework is used to make the body a structural element of the locomotive. The body extends the full width and length of the locomotive. The service walkways are inside the body. Carbody units, gaining rigidity from the body trusswork, require less structural weight to achieve rigidity than do locomotives with non-structural bodies. For that reason, carbody construction was favored to increase the power-to-weight ratio for early diesel locomotives, before the power available with diesel technology was increased. Recent years have seen carbody construction revived in the quest for greater fuel efficiency with passenger locomotives. The full-width bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMD F-unit
EMD F-units are a line of diesel-electric locomotives produced between November 1939 and November 1960 by General Motors Electro-Motive Division and General Motors-Diesel Division. Final assembly for all F-units was at the GM-EMD plant at La Grange, Illinois, and the GMDD plant in London, Ontario. They were sold to railroads throughout the United States, Canada and Mexico, and a few were exported to Saudi Arabia. The term ''F-unit'' refers to the model numbers given to each successive type (i.e. F3, F7, etc.), all of which began with the letter ''F''. The ''F'' originally meant "fourteen", as in , not "freight". Longer EMD E-units for passenger service had twin diesel engines (called " prime movers" in that type of application). The ''E'' meant "eighteen" as in . Similarly, for early model EMD switchers, ''S'' meant "six hundred" and ''N'' meant "nine hundred horsepower" ( respectively). F-units were originally designed for freight service, although many without steam generato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)