|
Direct Air Capture
Direct air capture (DAC) is a process of capturing carbon dioxide () directly from the ambient air (as opposed to capturing from point sources, such as a cement factory or biomass power plant) and generating a concentrated stream of for sequestration or utilization or production of carbon-neutral fuel and windgas. Carbon dioxide removal is achieved when ambient air makes contact with chemical media, typically an aqueous alkaline solvent or sorbents. These chemical media are subsequently stripped of CO2 through the application of energy (namely heat), resulting in a CO2 stream that can undergo dehydration and compression, while simultaneously regenerating the chemical media for reuse. DAC was suggested in 1999 by Klaus S. Lackner and is still in development. Several commercial plants are planned or in operation in Europe and the US. Large-scale DAC deployment may be accelerated when connected with economical applications or policy incentives. In contrast to carbon captur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
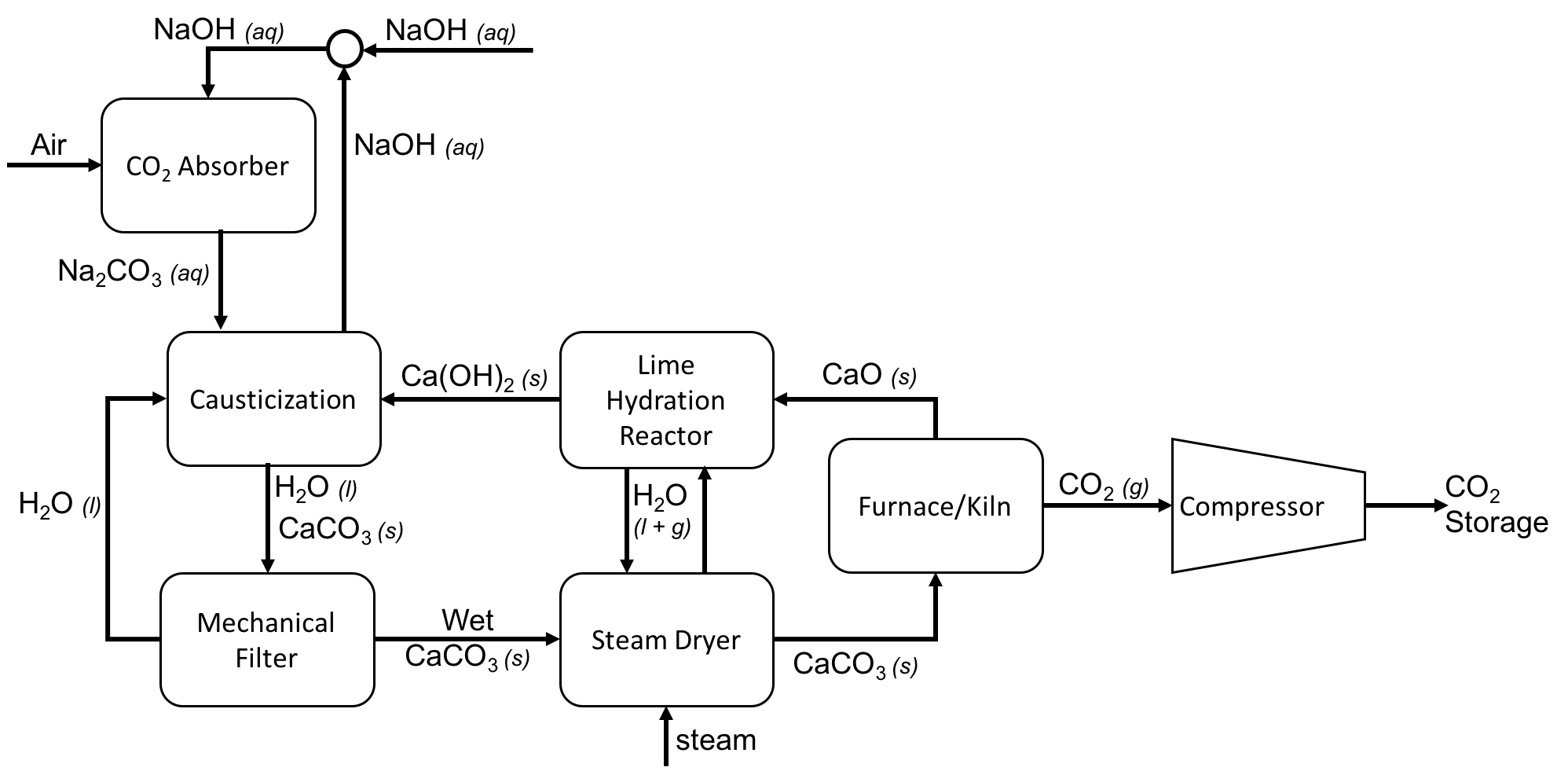
Direct Air Capture Process Flow Diagram Using Caustic Soda
Direct may refer to: Mathematics * Directed set, in order theory * Direct limit of (pre), sheaves * Direct sum of modules, a construction in abstract algebra which combines several vector spaces Computing * Direct access (other), a method of accessing data in a database * Direct connect (other), various methods of telecommunications and computer networking * Direct memory access, access to memory by hardware subsystems independently of the CPU Entertainment * Direct (Tower of Power album), ''Direct'' (Tower of Power album) * Direct (Vangelis album), ''Direct'' (Vangelis album) * Direct (EP), ''Direct'' (EP), by The 77s Other uses * Nintendo Direct, an online presentation frequently held by Nintendo * Mars Direct, a proposal for a crewed mission to Mars * DIRECT, a proposed space shuttle-derived launch vehicle * DirectX, a proprietary dynamic media platform * Direct current, a direct flow of electricity * Direct examination, the in-trial questioning of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010- Direct Air Capture - Global - International Energy Agency (IEA) - Bar Chart
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal–organic Framework
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are a class of compounds consisting of metal ions or clusters coordinated to organic ligands to form one-, two-, or three-dimensional structures. The organic ligands included are sometimes referred to as "struts" or "linkers", one example being 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (BDC). More formally, a metal–organic framework is a crystalline material with organic ligands containing potential voids. In most cases for MOFs, the pores are stable during the elimination of the guest molecules (often solvents) and could be refilled with other compounds. Because of this property, MOFs are of interest for the storage of gases such as hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Other possible applications of MOFs are in gas purification, in gas separation, in water remediation, in catalysis, as conducting solids and as supercapacitors. The synthesis and properties of MOFs constitute the primary focus of the discipline called (from Latin , "small net"). In contrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
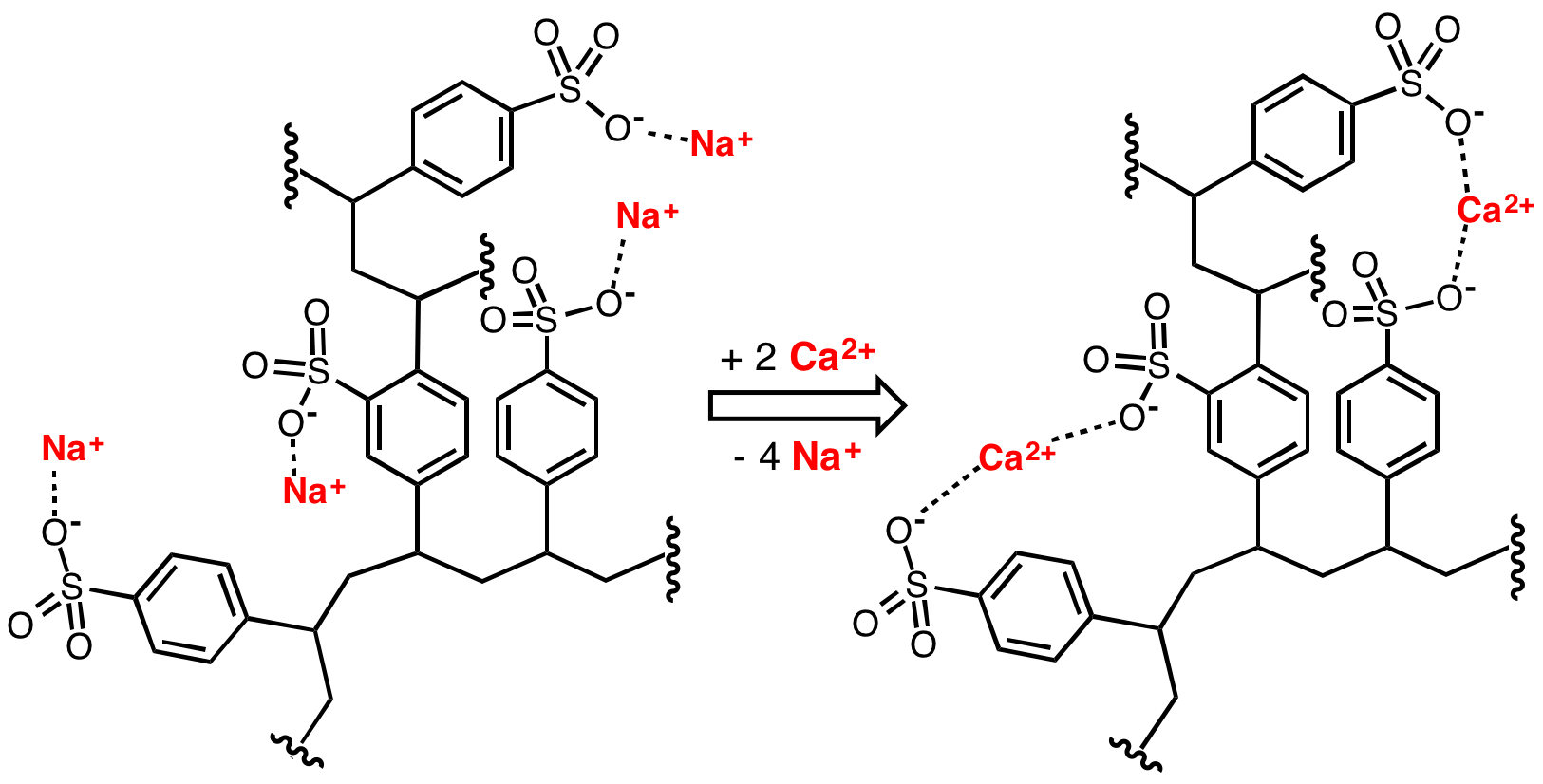
Ion-exchange Resin
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radius) microbeads, usually white or yellowish, fabricated from an organic polymer substrate. The beads are typically porous, providing a large surface area on and inside them where the trapping of ions occurs along with the accompanying release of other ions, and thus the process is called ion exchange. There are multiple types of ion-exchange resin. Most commercial resins are made of polystyrene sulfonate.François Dardel and Thomas V. Arden "Ion Exchangers" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2008, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Ion-exchange resins are widely used in different separation, purification, and decontamination processes. The most common examples are water softening and water purification. In many cases ion-exchange resins were introduced in such proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Negative Carbon Emissions
The Center for Negative Carbon Emissions (CNCE) is led by Director Matthew Green, and was founded by Klaus S. Lackner in the School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment (SSEBE) at Arizona State University in 2014. CNCE is advancing carbon management technologies that can capture directly from ambient air in an outdoor operating environment. CNCE aims to demonstrate systems that over time increase in scope, reliability and efficiency while lowering the cost of carbon dioxide capture from air. References Direct air capture {{US-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide Scrubber
A carbon dioxide scrubber is a piece of equipment that absorbs carbon dioxide (CO2). It is used to treat exhaust gases from industrial plants or from exhaled air in life support systems such as rebreathers or in spacecraft, submersible craft or airtight chambers. Carbon dioxide scrubbers are also used in controlled atmosphere (CA) storage. They have also been researched for carbon capture and storage as a means of combating climate change. Technologies Amine scrubbing The primary application for CO2 scrubbing is for removal of CO2 from the exhaust of coal- and gas-fired power plants. Virtually the only technology being seriously evaluated involves the use of various amines, e.g. monoethanolamine. Cold solutions of these organic compounds bind CO2, but the binding is reversed at higher temperatures: :CO2 + 2 ↔ + , this technology has only been lightly implemented because of capital costs of installing the facility and the operating costs of utilizing it. Minerals an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adsorbents
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid (the ''absorbate'') is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid (the ''absorbent''). Adsorption is a '' surface phenomenon'', while absorption involves the whole volume of the material, although adsorption does often precede absorption. The term ''sorption'' encompasses both processes, while ''desorption'' is the reverse of it. Like surface tension, adsorption is a consequence of surface energy. In a bulk material, all the bonding requirements (be they ionic, covalent or metallic) of the constituent atoms of the material are fulfilled by other atoms in the material. However, atoms on the surface of the adsorbent are not wholly surrounded by other adsorbent atoms and therefore can attract adsorbates. The exact nature of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonation
Carbonation is the chemical reaction of carbon dioxide to give carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbonic acid. In chemistry, the term is sometimes used in place of carboxylation, which refers to the formation of carboxylic acids. In inorganic chemistry and geology, carbonation is common. Metal hydroxides (MOH) and metal oxides (M'O) react with CO2 to give bicarbonates and carbonates: :MOH + CO2 → M(HCO3) :M'O + CO2 → M'CO3 In reinforced concrete, the chemical reaction between carbon dioxide in the air and calcium hydroxide and hydrated calcium silicate Calcium silicate is the chemical compound Ca2SiO4, also known as calcium orthosilicate and is sometimes formulated as 2CaO·SiO2. It is also referred to by the shortened trade name Cal-Sil or Calsil. It occurs naturally as the mineral larnite. ... in the concrete is known as Neutralization (chemistry), neutralisation. The similar reaction in which calcium hydroxide from cement reacts with carbon dioxide and for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemisorption
Chemisorption is a kind of adsorption which involves a chemical reaction between the surface and the adsorbate. New chemical bonds are generated at the adsorbent surface. Examples include macroscopic phenomena that can be very obvious, like corrosion, and subtler effects associated with heterogeneous catalysis, where the catalyst and reactants are in different phases. The strong interaction between the adsorbate and the substrate surface creates new types of electronic bonds. In contrast with chemisorption is physisorption, which leaves the chemical species of the adsorbate and surface intact. It is conventionally accepted that the energetic threshold separating the binding energy of "physisorption" from that of "chemisorption" is about 0.5 eV per adsorbed species. Due to specificity, the nature of chemisorption can greatly differ, depending on the chemical identity and the surface structural properties. The bond between the adsorbate and adsorbent in chemisorption is either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions . Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali that decomposes proteins at ordinary ambient temperatures and may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water, and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound. As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water and acidic hydrochloric acid to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students. Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the manufacture of pulp and paper, textiles, drinking water, soap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants growing in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process. Hydrates Sodium carbonate is obtained as three hydrates and as the anhydrous salt: * sodium carbonate decahydrate ( natron), Na2CO3·10H2O, which readily effloresces to form the monohydrate. * sodium carbonate heptahydrate (not known in mineral form), Na2CO3·7H2O. * sodium carbonate monohydrate ( thermonatrite), Na2CO3·H2O. Also known as crystal carbonate. * anhydrous sodium carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions . Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali that decomposes proteins at ordinary ambient temperatures and may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water, and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound. As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water and acidic hydrochloric acid to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students. Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the manufacture of pulp and paper, textiles, drinking water, soap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |