|
Denis Alexander
Dr. Denis Alexander has spent 40 years in the biomedical research community. He is an Emeritus Fellow of St. Edmund’s College, Cambridge and an Emeritus Director of the Faraday Institute for Science and Religion, Cambridge which he co-founded with Bob White in 2006. Scientific work Alexander was an Open Scholar at St Peter's College, Oxford, where he studied Biochemistry under the late Arthur Peacocke. He studied for a PhD in Neurochemistry at the Institute of Psychiatry, where he analysed the molecular structure of the sodium-potassium pump. He spent 15 years in various university departments and laboratories outside the United Kingdom (1971-1986), including a post at Hacettepe University (1972-1974) and the Middle East Technical University (1974-1980) in Ankara, Turkey, where he set up a neurochemistry laboratory in the newly formed Biological Sciences Department. From 1981-1986 he held the post of Associate Professor of Biochemistry at the American University of Bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denis Alexander 2012 Cropped
Denis may refer to: People * Saint Denis of Paris, 3rd-century Christian martyr and first bishop of Paris * Denis the Areopagite, Biblical figure * Denis, son of Ampud (died 1236), baron in the Kingdom of Hungary * Denis the Carthusian (1402–1471), theologian and mystic * Denis of Hungary (c. 1210–1272), Hungarian-born Aragonese knight * Denis of Portugal (1261–1325), king of Portugal * Denis, Lord of Cifuentes (1354–1397) * Denis the Little (c. 470 – c. 544), Scythian monk * Denis Handlin (born 1951), Australian entrepreneur and business executive * Denis, Palatine of Hungary, lord in the Kingdom of Hungary * Denis (harpsichord makers), French harpsichord makers * Denis Perera (1930-2013), general, Commander of the Sri Lanka Army from 1977-1981 * Louis Juchereau de St. Denis (1676–1744), French-Canadian explorer of French Louisiana and Spanish Texas * Denis Villeneuve (born 1967), Canadian filmmaker Other uses * Denis (given name) * Denis (surname) * "Denis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creationism
Creationism is the religious belief that nature, and aspects such as the universe, Earth, life, and humans, originated with supernatural acts of divine creation. Gunn 2004, p. 9, "The ''Concise Oxford Dictionary'' says that creationism is 'the belief that the universe and living organisms originated from specific acts of divine creation.'" In its broadest sense, creationism includes a continuum of religious views, Haarsma 2010, p. 168, "Some Christians, often called 'Young Earth creationists,' reject evolution in order to maintain a semi-literal interpretation of certain biblical passages. Other Christians, called 'progressive creationists,' accept the scientific evidence for some evolution over a long history of the earth, but also insist that God must have performed some miracles during that history to create new life-forms. Intelligent design, as it is promoted in North America is a form of progressive creation. Still other Christians, called theistic evolutionists' or 'e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Andrews University
(Aien aristeuein) , motto_lang = grc , mottoeng = Ever to ExcelorEver to be the Best , established = , type = Public research university Ancient university , endowment = £117.7 million (2021) , budget = £286.6 million (2020–21) , chancellor = The Lord Campbell of Pittenweem , rector = Leyla Hussein , principal = Sally Mapstone , academic_staff = 1,230 (2020) , administrative_staff = 1,576 , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , doctoral = , other = , city = St Andrews , state = , country = Scotland , coordinates = , campus = College town , colours = United College, St Andrews St Mary's College School of Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gifford Lectures
The Gifford Lectures () are an annual series of lectures which were established in 1887 by the will of Adam Gifford, Lord Gifford. Their purpose is to "promote and diffuse the study of natural theology in the widest sense of the term – in other words, the knowledge of God." A Gifford lectures appointment is one of the most prestigious honours in Scottish academia. The lectures are given at four Scottish universities: University of St Andrews, University of Glasgow, University of Aberdeen and University of Edinburgh. University calendars record that at the four Scottish universities, the Gifford Lectures are to be "public and popular, open not only to students of the university, but the whole community (for a tuition fee) without matriculation. Besides a general audience, the Lecturer may form a special class of students for the study of the subject, which will be conducted in the usual way, and tested by examination and thesis, written and oral". In 1889, those attending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Templeton Foundation
The John Templeton Foundation (Templeton Foundation) is a philanthropic organization that reflects the ideas of its founder, John Templeton, who became wealthy via a career as a contrarian investor, and wanted to support progress in religious and spiritual knowledge, especially at the intersection of religion and science. He also sought to fund research on methods to promote and develop moral character, intelligence, and creativity in people, and to promote free markets. In 2008, the foundation was awarded the National Humanities Medal. In 2016 ''Inside Philanthropy'' called it "the oddest—or most interesting—big foundation around." Templeton founded the organization in 1987 and headed it as chairman until his death in 2008. Templeton's son, John Templeton Jr., served as its president from its founding until his death in 2015, at which point Templeton Jr.'s daughter, Heather Templeton Dill, became president. The foundation administers the annual Templeton Prize for achievem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Society For Science And Religion
The International Society for Science and Religion (ISSR) is a learned society established in 2001 for the purpose of the promotion of education through the support of inter-disciplinary learning and research in the fields of science and religion conducted where possible in an international and multi-faith context. The Society took shape after a four-day conference in Granada, Spain. Membership Membership is available to all interested persons. However, Fellowship is only attained through nomination by existing Fellows only. There were 97 founding members, including five Fellows of the Royal Society. Varieties of faith tradition Although many of the founders of the ISSR are Christians, the society actively welcomes members from other faith traditions. The book ''Why the Science and Religion Dialogue Matters'' produced by the society has major contributions from: * John Polkinghorne, George Ellis, Holmes Rolston III and Fraser Watts (who are Christians), on why the science and reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Christian Belief
''Science and Christian Belief'' is a biannual peer-reviewed academic journal published by Christians in Science and the Victoria Institute. The editors-in-chief are Keith R Fox and Meric Srokosz. The journal was established in 1989, with Oliver Barclay and A. Brian Robins as co-editors-in-chief. It is abstracted and indexed in ''New Testament Abstracts'', '' Religion Index One: Periodicals'', and '' Religious & Theological Abstracts'', and is distributed by EBSCO Information Services as part of Academic Search and other collections. The journal is free to members of Christians in Science. The Victoria Institute (also known as the Philosophical Society of Great Britain) published the ''Journal of the Transactions of The Victoria Institute'', which was established in 1866; it was renamed ''Faith and Thought'' in 1958, and then merged with the (informal) ''CIS Bulletin'' in 1989, obtaining its current name, ''Faith and Thought''.''Faith & Though'' (formerly ''Faith and Thought New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Montefiore
Hugh William Montefiore (born Hugh William Sebag-Montefiore; 12 May 1920 – 13 May 2005) was an English Anglican bishop and academic, who served as Bishop of Kingston from 1970 to 1978 and Bishop of Birmingham from 1978 to 1987. Early life and family Montefiore was born in London, a member of a famous Jewish family. His parents were Charles Sebag-Montefiore (great-great-nephew of Moses Montefiore) and his wife Muriel Alice Ruth de Pass.Charles Mosley, editor, ''Burke's Peerage, Baronetage & Knightage, 107th edition, 3 volumes'' (Wilmington, Delaware, U.S.A.: Burke's Peerage (Genealogical Books) Ltd, 2003), volume 1, page 507. On 1 December 1945 he married Elisabeth Mary MacDonald Paton (13 October 1919 – 14 November 1999), sister of William D.M. Paton, and daughter of William Paton and his wife Grace Mackenzie. The couple had three daughters: Teresa, Jan (wife of the journalist Patrick Cockburn), and Catherine. Career Montefiore was educated at Rugby School, where he unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Edmund's College, Cambridge
St Edmund's College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in England. Founded in 1896, it is the second-oldest of the four Cambridge colleges oriented to mature students, which accept only students reading for postgraduate degrees or for undergraduate degrees if aged 21 years or older. Named after St Edmund of Abingdon (1175–1240), who was the first known Oxford Master of Arts and Archbishop of Canterbury from 1234 to 1240, the college has traditionally Roman Catholic roots. Its founders were Henry Fitzalan-Howard, 15th Duke of Norfolk, and Baron Anatole von Hügel (1854–1928), the first Catholic to take a Cambridge degree since the deposition of King James II in 1688. The Visitor is the Archbishop of Westminster (at present Cardinal Vincent Nichols). The college is located on Mount Pleasant, northwest of the centre of Cambridge, near Lucy Cavendish College, Murray Edwards College and Fitzwilliam College. Its campus consists of a garden setting on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
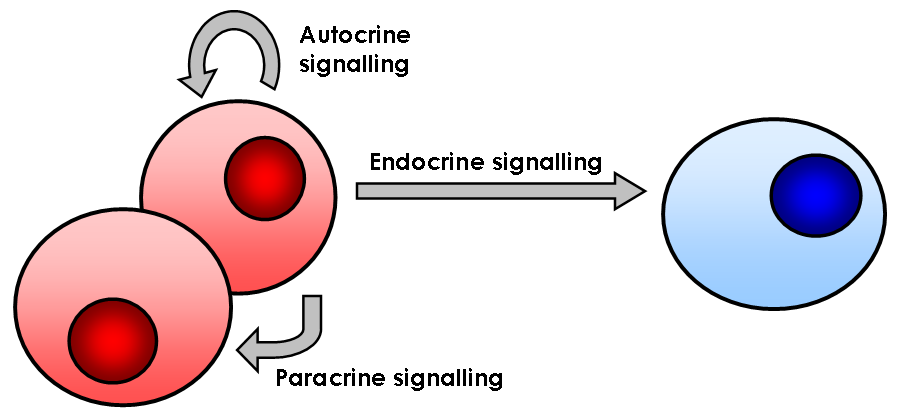
Signaling Pathway
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTPN11
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) also known as protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D (PTP-1D), Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-2 (SHP-2), or protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2C (PTP-2C) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTPN11'' gene. PTPN11 is a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) Shp2. PTPN11 is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP contains two tandem Src homology-2 domains, which function as phospho-tyrosine binding domains and mediate the interaction of this PTP with its substrates. This PTP is widely expressed in most tissues and plays a regulatory role in various cell signaling events that are important for a diversity of cell functions, such as mitogenic activation, metabolic control, transcription regulation, and cell migrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |