|
Delivery After Previous Caesarean Section
In case of a previous caesarean section a subsequent pregnancy can be planned beforehand to be childbirth, delivered by either of the following two main methods: * Vaginal birth after caesarean section (VBAC) * Elective surgery, Elective repeat caesarean section (ERCS) Both have higher risks than a vaginal birth with no previous caesarean section. There are many issues which affect the decision for planned vaginal or planned abdominal delivery. There is a slightly higher risk for uterine rupture and perinatal death of the child with VBAC than ERCS, but the absolute increased risk of these complications is small, especially with only one previous low transverse caesarean section. 60–80% of women planning VBAC will achieve a successful vaginal delivery, although there are more risks to the mother and baby from an unplanned caesarean section than from an ERCS. Successful VBAC also reduces the risk of complications in future pregnancies more than ERCS. Technique Where the woman is la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
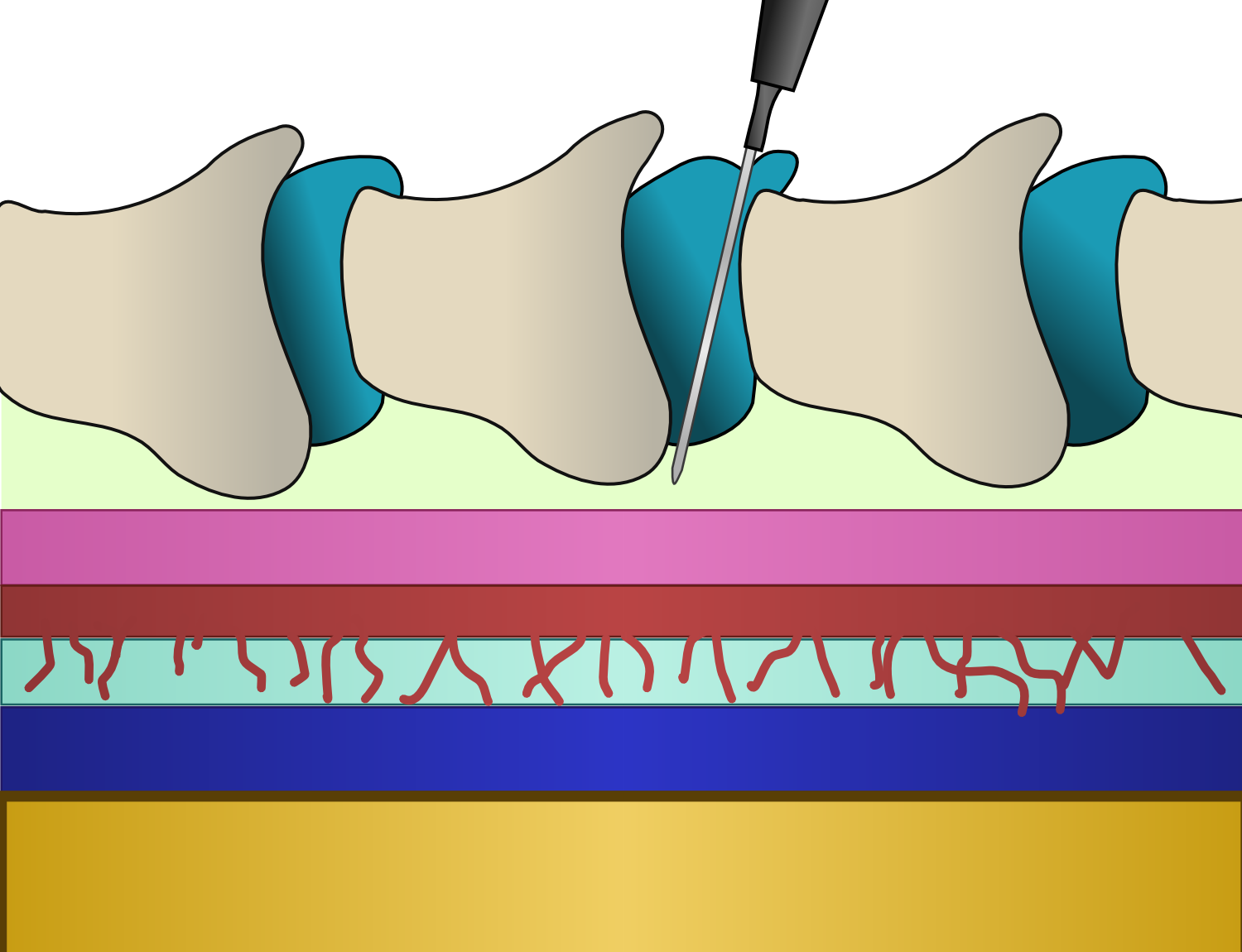
Caesarean Section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk. Reasons for the operation include obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, breech birth, and problems with the placenta or umbilical cord. A caesarean delivery may be performed based upon the shape of the mother's pelvis or history of a previous C-section. A trial of vaginal birth after C-section may be possible. The World Health Organization recommends that caesarean section be performed only when medically necessary. Most C-sections are performed without a medical reason, upon request by someone, usually the mother. A C-section typically takes 45 minutes to an hour. It may be done with a spinal block, where the woman is awake, or under general anesthesia. A urinary catheter is used to drain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive. Often the cause is unknown. Causes may include pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and birth complications, problems with the placenta or umbilical cord, birth defects, infections such as malaria and syphilis, and poor health in the mother. Risk factors include a mother's age over 35, smoking, drug use, use of assisted reproductive technology, and first pregnancy. Stillbirth may be suspected when no fetal movement is felt. Confirmation is by ultrasound. Worldwide prevention of most stillbirths is possible with improved health systems. Around half of stillbirths occur durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta Accreta
Placenta accreta occurs when all or part of the placenta attaches abnormally to the ''myometrium'' (the muscular layer of the uterine wall). Three grades of abnormal placental attachment are defined according to the depth of attachment and invasion into the muscular layers of the uterus: # ''Accreta – chorionic villi'' attached to the myometrium, rather than being restricted within the ''decidua basalis''. # ''Increta – chorionic villi'' invaded into the ''myometrium''. # ''Percreta – chorionic villi'' invaded through the '' perimetrium'' (uterine serosa). Because of abnormal attachment to the myometrium, placenta accreta is associated with an increased risk of heavy bleeding at the time of attempted vaginal delivery. The need for transfusion of blood products is frequent, and surgical removal of the uterus ( hysterectomy) is sometimes required to control life-threatening bleeding. Rates of placenta accreta are increasing. As of 2016, placenta accreta affects an estimated 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Maternal Age
Advanced maternal age, in a broad sense, is the instance of a woman being of an older age at a stage of reproduction, although there are various definitions of specific age and stage of reproduction.Effect of advanced age on fertility and pregnancy in women at . Author: Ruth C Fretts. Section Editor: Louise Wilkins-Haug. Deputy Editor: Vanessa A Barss. This topic last updated: 3 December 2012. The variability in definitions is in part explained by the effects of increasing age occurring as a |
Cervical Dilation
Cervical dilation (or cervical dilatation) is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery. Cervical dilation may occur naturally, or may be induced surgically or medically. In childbirth In the later stages of pregnancy, the cervix may already have opened up to 1–3 cm (or more in rarer circumstances), but during labor, repeated uterine contractions lead to further widening of the cervix to about 6 centimeters. From that point, pressure from the presenting part (head in vertex births or bottom in breech births), along with uterine contractions, will dilate the cervix to 10 centimeters, which is "complete." Cervical dilation is accompanied by effacement, the thinning of the cervix. General guidelines for cervical dilation: * Latent phase: 0–3 centimeters * Active Labor: 4–7 centimeters * Transition: 8–10 centimeters * Complete: 10 centimeters. Delivery of the infant takes place sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidural Anaesthesia
Epidural administration (from Ancient Greek ἐπί, , upon" + ''dura mater'') is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians and nurse anesthetists to administer local anesthetic agents, analgesics, diagnostic medicines such as radiocontrast agents, and other medicines such as glucocorticoids. Epidural administration involves the placement of a catheter into the epidural space, which may remain in place for the duration of the treatment. The technique of intentional epidural administration of medication was first described in 1921 by Spanish military surgeon Fidel Pagés. In the United States, over 50% of childbirths involve the use of epidural anesthesia. Epidural anaesthesia causes a loss of sensation, including pain, by blocking the transmission of signals through nerve fibres in or near the spinal cord. For this reason, epidurals are commonly used for pain cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstructed Labour
Obstructed labour, also known as labour dystocia, is the baby not exiting the pelvis because it is physically block during childbirth although the uterus contracts normally. Complications for the baby include not getting enough oxygen which may result in death. It increases the risk of the mother getting an infection, having uterine rupture, or having post-partum bleeding. Long-term complications for the mother include obstetrical fistula. Obstructed labour is said to result in prolonged labour, when the active phase of labour is longer than 12 hours. The main causes of obstructed labour include a large or abnormally positioned baby, a small pelvis, and problems with the birth canal. Abnormal positioning includes shoulder dystocia where the anterior shoulder does not pass easily below the pubic bone. Risk factors for a small pelvis include malnutrition and a lack of exposure to sunlight causing vitamin D deficiency. It is also more common in adolescence as the pelvis may not ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Mass Index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and height in metres. The BMI may be determined using a table or chart which displays BMI as a function of mass and height using contour lines or colours for different BMI categories, and which may use other units of measurement (converted to metric units for the calculation). The BMI is a convenient rule of thumb used to broadly categorize a person as ''underweight'', ''normal weight'', ''overweight'', or ''obese'' based on tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) and height. Major adult BMI classifications are underweight (under 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5 to 24.9), overweight (25 to 29.9), and obese (30 or more). When used to predict an individual's health, rather than as a statistical measurement for groups, the BMI has limitations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labor Induction
Labor induction is the process or treatment that stimulates childbirth and delivery. Inducing (starting) labor can be accomplished with pharmaceutical or non-pharmaceutical methods. In Western countries, it is estimated that one-quarter of pregnant women have their labor medically induced with drug treatment. Inductions are most often performed either with prostaglandin drug treatment alone, or with a combination of prostaglandin and intravenous oxytocin treatment. Medical uses Commonly accepted medical reasons for induction include: * Postterm pregnancy, i.e. if the pregnancy has gone past the end of the 42nd week. * Intrauterine fetal growth restriction (IUGR). * There are health risks to the woman in continuing the pregnancy (e.g. she has pre-eclampsia). * Premature rupture of the membranes (PROM); this is when the membranes have ruptured, but labor does not start within a specific amount of time. * Premature termination of the pregnancy (abortion). * Fetal death in utero and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic () is a nonprofit American academic medical center focused on integrated health care, education, and research. It employs over 4,500 physicians and scientists, along with another 58,400 administrative and allied health staff, across three major campuses: Rochester, Minnesota; Jacksonville, Florida; and Phoenix/Scottsdale, Arizona. The practice specializes in treating difficult cases through tertiary care and destination medicine. It is home to the top-15 ranked Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine in addition to many of the highest regarded residency education programs in the United States. It spends over $660 million a year on research and has more than 3,000 full-time research personnel. William Worrall Mayo settled his family in Rochester in 1864 and opened a sole proprietorship medical practice that evolved under his sons, Will and Charlie Mayo, along with practice partners Stinchfield, Graham, Plummer, Millet, Judd, and Balfour, into Mayo Clinic. Toda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Infantile respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS), also called respiratory distress syndrome of newborn, or increasingly surfactant deficiency disorder (SDD), and previously called hyaline membrane disease (HMD), is a syndrome in premature infants caused by developmental insufficiency of pulmonary surfactant production and structural immaturity in the lungs. It can also be a consequence of neonatal infection and can result from a genetic problem with the production of surfactant-associated proteins. IRDS affects about 1% of newborns and is the leading cause of death in preterm infants. Data has shown the choice of elective caesarean sections to strikingly increase the incidence of respiratory distress in term infants; dating back to 1995, the UK first documented 2,000 annual caesarean section births requiring neonatal admission for respiratory distress. The incidence decreases with advancing gestational age, from about 50% in babies born at 26–28 weeks to about 25% at 30–31 weeks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxic Ischaemic Encephalopathy
Cerebral hypoxia is a form of hypoxia (reduced supply of oxygen), specifically involving the brain; when the brain is completely deprived of oxygen, it is called ''cerebral anoxia''. There are four categories of cerebral hypoxia; they are, in order of increasing severity: diffuse cerebral hypoxia (DCH), focal cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction, and global cerebral ischemia. Prolonged hypoxia induces neuronal cell death via apoptosis, resulting in a hypoxic brain injury. Cases of total oxygen deprivation are termed "anoxia", which can be hypoxic in origin (reduced oxygen availability) or ischemic in origin (oxygen deprivation due to a disruption in blood flow). Brain injury as a result of oxygen deprivation either due to hypoxic or anoxic mechanisms are generally termed hypoxic/anoxic injuries (HAI). Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a condition that occurs when the entire brain is deprived of an adequate oxygen supply, but the deprivation is not total. While HIE is ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |