|
DARPin
DARPins (an acronym for designed ankyrin repeat proteins) are genetically engineered antibody mimetic proteins typically exhibiting highly specific and high-affinity target protein binding. They are derived from natural ankyrin repeat proteins, one of the most common classes of binding proteins in nature, which are responsible for diverse functions such as cell signaling, regulation and structural integrity of the cell. DARPins consist of at least three, repeat motifs or modules, of which the most N- and the most C-terminal modules are referred to as "caps", since they shield the hydrophobic core of the protein. The number of internal modules is indicated as number (e.g. N1C, N2C, N3C, ...) while the caps are indicated with "N" or "C", respectively. The molecular mass of e.g. 14 or 18 kDa (kilodaltons) for four- (N2C) or five- (N3C) repeat DARPins is rather small for a biologic (ca 10% of the size of an IgG). DARPins constitute a new class of potent, specific and versatile s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Partners
Molecular Partners AG is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company based in Zürich, Switzerland. The company is developing a new class of potent, specific and versatile small-protein therapies called DARPins, with potential clinical applications in a range of disease areas including oncology, immuno-oncology, ophthalmology, and infectious diseases. Molecular Partners currently has two DARPin molecules in clinical development, and a broad pipeline of molecules in preclinical development.Molecular Partners Interim Management Statement Q1 2021 History Researchers at the |
Andreas Plückthun
Andreas Plückthun (born May 7, 1956) is a scientist whose research is focused on the field of protein engineering. Andreas Plückthun is the director of the department of biochemistry at the University of Zurich. Plückthun was appointed to the faculty of the University of Zurich as a Full professor of biochemistry in 1993. Plückthun was group leader at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry , Germany (1985-1993). He was elected to the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) in 1992, and named a member of the German National Academy of Science (Leopoldina) in 2003. He is cofounder of the biotechnology companies Morphosys (Martinsried, Germany) Molecular Partners AG (Zürich-Schlieren, Switzerland) and G7 Therapeutics. (Zürich-Schlieren, Switzerland). Plückthun is a member of the board directors of the Antibody Society. His work is highly cited in the field of antibody engineering. He has been honoured by a number of international awards. Biography Andreas Pl� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody Mimetic
Antibody mimetics are organic compounds that, like antibodies, can specifically bind antigens, but that are not structurally related to antibodies. They are usually artificial peptides or proteins with a molar mass of about 3 to 20 kDa. (Antibodies are ~150 kDa.) Nucleic acids and small molecules are sometimes considered antibody mimetics as well, but not artificial antibodies, antibody fragments and fusion proteins composed from these. Common advantages over antibodies are better solubility, tissue penetration, stability towards heat and enzymes, and comparatively low production costs. Antibody mimetics are being developed as therapeutic and diagnostic Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine "cause and effect". In systems enginee ... agents. Examples See also * Protein mimetic * Optimer Ligand Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
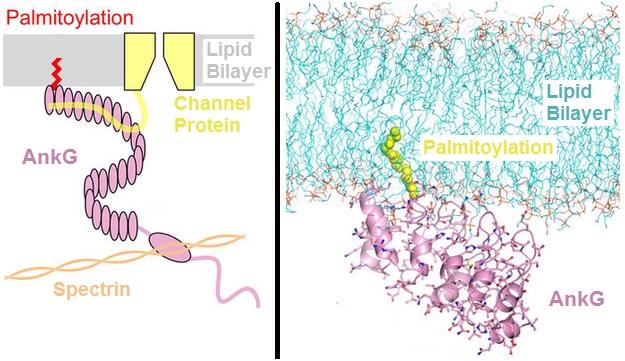
Ankyrin
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that mediate the attachment of integral membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin based membrane cytoskeleton. Ankyrins have binding sites for the beta subunit of spectrin and at least 12 families of integral membrane proteins. This linkage is required to maintain the integrity of the plasma membranes and to anchor specific ion channels, ion exchangers and ion transporters in the plasma membrane. The name is derived from the Greek word ἄγκυρα (''ankyra'') for "anchor". Structure Ankyrins contain four functional domains: an N-terminal domain that contains 24 tandem ankyrin repeats, a central domain that binds to spectrin, a death domain that binds to proteins involved in apoptosis, and a C-terminal regulatory domain that is highly variable between different ankyrin proteins. Membrane protein recognition The 24 tandem ankyrin repeats are responsible for the recognition of a wide range of membrane proteins. These 24 repeats contain 3 str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankyrin Repeat
The ankyrin repeat is a 33-residue motif in proteins consisting of two alpha helices separated by loops, first discovered in signaling proteins in yeast Cdc10 and ''Drosophila'' Notch. Domains consisting of ankyrin tandem repeats mediate protein–protein interactions and are among the most common structural motifs in known proteins. They appear in bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic proteins, but are far more common in eukaryotes. Ankyrin repeat proteins, though absent in most viruses, are common among poxviruses. Most proteins that contain the motif have four to six repeats, although its namesake ankyrin contains 24, and the largest known number of repeats is 34, predicted in a protein expressed by ''Giardia lamblia''. Ankyrin repeats typically fold together to form a single, linear solenoid structure called ankyrin repeat domains. These domains are one of the most common protein–protein interaction platforms in nature. They occur in a large number of functionally divers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library (biology)
In molecular biology, a library is a collection of DNA fragments that is stored and propagated in a population of micro-organisms through the process of molecular cloning. There are different types of DNA libraries, including cDNA libraries (formed from reverse-transcribed RNA), genomic libraries (formed from genomic DNA) and randomized mutant libraries (formed by de novo gene synthesis where alternative nucleotides or codons are incorporated). DNA library technology is a mainstay of current molecular biology, genetic engineering, and protein engineering, and the applications of these libraries depend on the source of the original DNA fragments. There are differences in the cloning vectors and techniques used in library preparation, but in general each DNA fragment is uniquely inserted into a cloning vector and the pool of recombinant DNA molecules is then transferred into a population of bacteria (a Bacterial Artificial Chromosome or BAC library) or yeast such that each o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome. Recombinant DNA is the general name for a piece of DNA that has been created by combining at least two fragments from two different sources. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure, and differ only in the nucleotide sequence within that identical overall structure. Recombinant DNA molecules are sometimes called chimeric DNA, because they can be made of material from two different species, like the mythical chimera. R-DNA technology uses palindromic sequences and leads to the production of sticky and blunt ends. The DNA sequences used in the construction of recombinant DNA molecules can originate from any species. For example, plant DNA may be joined to ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Structures
Biomolecular structure is the intricate folded, three-dimensional shape that is formed by a molecule of protein, DNA, or RNA, and that is important to its function. The structure of these molecules may be considered at any of several length scales ranging from the level of individual atoms to the relationships among entire protein subunits. This useful distinction among scales is often expressed as a decomposition of molecular structure into four levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The scaffold for this multiscale organization of the molecule arises at the secondary level, where the fundamental structural elements are the molecule's various hydrogen bonds. This leads to several recognizable ''domains'' of protein structure and nucleic acid structure, including such secondary-structure features as alpha helixes and beta sheets for proteins, and hairpin loops, bulges, and internal loops for nucleic acids. The terms ''primary'', ''secondary'', ''tertiary'', and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome Display
Ribosome display is a technique used to perform ''in vitro'' protein evolution to create proteins that can bind to a desired ligand. The process results in translated proteins that are associated with their mRNA progenitor which is used, as a complex, to bind to an immobilized ligand in a selection step. The mRNA-protein hybrids that bind well are then reverse transcribed to cDNA and their sequence amplified via PCR. The result is a nucleotide sequence that can be used to create tightly binding proteins. Ribosome display process Ribosome display begins with a native library of DNA sequences coding for polypeptides. Each sequence is transcribed, and then translated ''in vitro'' into polypeptide. However, the DNA library coding for a particular library of binding proteins is genetically fused to a spacer sequence lacking a stop codon before its end. The lack of a stop codon prevents release factors from binding and triggering the disassembly of the translational complex. So, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,000,000,000,000
This list contains selected positive numbers in increasing order, including counts of things, dimensionless quantity, dimensionless quantities and probability, probabilities. Each number is given a name in the Long and short scales, short scale, which is used in English-speaking countries, as well as a name in the long and short scales, long scale, which is used in some of the countries that do not have English as their national language. Smaller than (one googolth) * ''Mathematics – random selections:'' Approximately is a rough first estimate of the probability that a typing "monkey", or an English-illiterate typing robot, when Infinite monkey theorem, placed in front of a typewriter, will type out William Shakespeare's play ''Hamlet'' as its first set of inputs, on the precondition it typed the needed number of characters. However, demanding correct punctuation, capitalization, and spacing, the probability falls to around 10−360,783. * ''Computing:'' 2.2 is appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity (pharmacology)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |