|
Década Perdida
"La Década Perdida" in Spanish or "A Década Perdida" in Portuguese ("The Lost Decade") of Latin America is a term used to describe the economic crisis suffered in Latin America during the 1980s, which continued for some countries into the 1990s. In general, the crisis was composed of unpayable external debts, taxes, and volatile inflation and exchange rates, which in the majority of the countries in the region were fixed. Overview During the 1970s, the rise in prices of raw materials (primarily oil) and the decrease in the value of the dollar caused US dollars to flow into Latin America, a region that then debated between an industrial model directed from the state or a market based model. In 1980, the decreased price of raw materials and the rise of interest rates in the industrialized countries generated a lack of resources, which provoked a massive depreciation of exchange rates, appreciating the real interest rate on the debt, a situation made worse by the presence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina Inflation
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human presenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Ecuador and Peru to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 departments and the Capital District of Bogotá, the country's largest city. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi), and has a population of 52 million. Colombia's cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a Spanish colony, fusing cultural elements brought by immigration from Europe and the Middle East, with those brought by enslaved Africans, as well as with those of the various Amerindian civilizations that predate colonization. Spanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1980s In Economic History
File:1980s replacement montage02.PNG, 420px, From left, clockwise: The first Space Shuttle, ''Space Shuttle Columbia, Columbia'', lifts off in 1981; US president Ronald Reagan and Soviet Union, Soviet General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, leader Mikhail Gorbachev ease tensions between the two superpowers, leading to the Cold War (1985–1991), end of the Cold War; The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 is considered to be one of the most momentous events of the 1980s; In 1981, the IBM Personal Computer is released; In 1985, the Live Aid concert is held in order to fund relief efforts for the 1983–1985 famine in Ethiopia, famine in Ethiopia during the time Mengistu Haile Mariam ruled the country; Pollution and ecological problems persisted when the Soviet Union and much of the world is filled with radioactive debris from the 1986 Chernobyl disaster, and in 1984, when thousands of people perished in Bhopal, India, Bhopal during a Bhopal disaster, gas leak from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation In Brazil
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of inflation is deflation, a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. As prices do not all increase at the same rate, the consumer price index (CPI) is often used for this purpose. The employment cost index is also used for wages in the United States. Most economists agree that high levels of inflation as well as hyperinflation—which have severely disruptive effects on the real economy—are caused by persistent excessive growth in the money supply. Views on low to moderate rates of inflation are more varied. Low or moderate inflation may be at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation In Argentina
The economy of Argentina is the second-largest national economy in South America, behind Brazil. Argentina is a developing country with a highly literate population, an export-oriented agricultural sector, and a diversified industrial base. Argentina benefits from rich natural resources. Argentina's economic performance has historically been very uneven, with high economic growth alternating with severe recessions, particularly since the late twentieth century. Income maldistribution and poverty have increased since this period. Early in the twentieth century, Argentina had one of the ten highest per capita GDP levels globally. It was on par with Canada and Australia, and had surpassed both France and Italy. Argentina's currency declined by about 50% in 2018 to more than 38 Argentine pesos per U.S. Dollar. As of that year, it is under a stand-by program from the International Monetary Fund. In 2019, the currency fell further by 25%. In 2020, it fell by 90%, in 2021, 68%, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Collapses
Economic collapse, also called economic meltdown, is any of a broad range of bad economic conditions, ranging from a severe, prolonged depression with high bankruptcy rates and high unemployment (such as the Great Depression of the 1930s), to a breakdown in normal commerce caused by hyperinflation (such as in Weimar Germany in the 1920s), or even an economically caused sharp rise in the death rate and perhaps even a decline in population (such as in countries of the former USSR in the 1990s). Often economic collapse is accompanied by social chaos, civil unrest and a breakdown of law and order. Cases There are few well documented cases of economic collapse. One of the best documented cases of collapse or near collapse is the Great Depression, the causes of which are still being debated. "To understand the Great Depression is the Holy Grail of macroeconomics." —Ben Bernanke (1995) Bernanke's comment addresses the difficulty of identifying specific causes when many factors may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic History Of Mexico
Since the colonial era, Mexico's economic history has been characterized by resource extraction, agriculture, and a relatively underdeveloped industrial sector. Economic elites in the colonial period were predominantly Spanish-born, active as transatlantic merchants and mine owners, and diversifying their investments with the landed estates. The largest population sector was indigenous subsistence farmers, which predominantly inhabited the center and south. New Spain was envisioned by the Spanish crown as a supplier of wealth to Iberia, which was accomplished through large silver mines and indigenous labor. A colonial economy to supply foodstuffs and products from ranching as well as a domestic textile industry meant that the economy provided much of its own needs, with international trade mainly conducted through colonial monopolies. Crown economic policies rattled American-born elites’ loyalty to Spain when in 1804, it instituted a policy to make mortgage holders pay immedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperinflation In Brazil
Hyperinflation in Brazil occurred between the first three months of 1990. The monthly inflation rates between January and March 1990 were 71.9%, 71.7% and 81.3% respectively. As accepted by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), hyperinflation is defined as a period of time in which the average price level of goods and services rise by more than 50% a month. Brazil experienced over a decade of very high inflation – often double-digit monthly inflation – preceding the hyperinflationary period. The nation sustained hyperinflation for less than half a year. This economic event was the culmination of a number of structural aspects of the Brazilian economy including, but not exclusive to, limited foreign trade and high external public debt as well as unsuccessful preventive measures. The Brazilian government responded to hyperinflation by using multiple periods of price freezes to artificially stop inflation. This was effective in managing hyperinflation for a few months. In July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
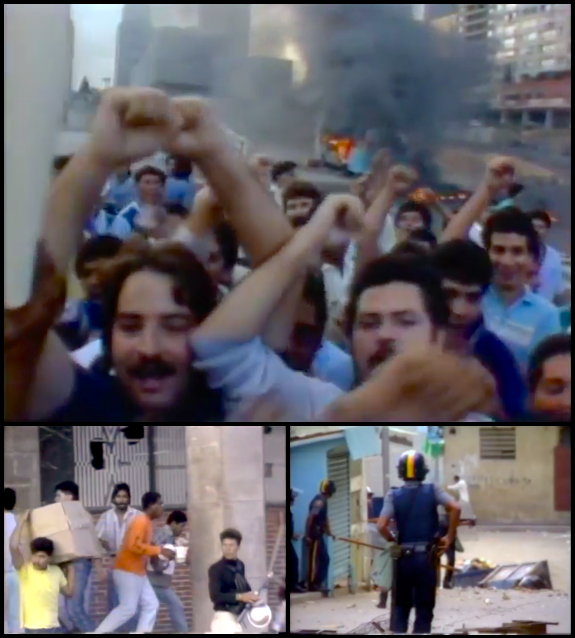
Caracazo
The ''Caracazo'' is the name given to the wave of protests, riots and looting. that started on 27 February 1989 in Guarenas, spreading to Caracas and surrounding towns. The weeklong clashes resulted in the deaths of hundreds of people, thousands by some accounts, mostly at the hands of security forces and the military. Amnesty International, March 1990, Reports of Arbitrary Killings and Torture:, February/March 1989, AI Index: AMR 53/02/90, https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/amr53/002/1991/en/ The riots and the protests began mainly in response to the government's economic reforms and the resulting increase in the price of gasoline and transportation. Etymology The term, “Caracazo,” stems from the city’s name, Caracas, and “-azo,” which stems from another historic event, the Bogotazo, was a massive riot in Bogotá, recognized as having a crucial role in Colombia’s history. “Caracazo” is technically defined as the “Caracas smash” or “the big one in Carac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-shaped Recession
Recession shapes or recovery shapes are used by economists to describe different types of recessions and their subsequent recoveries. There is no specific academic theory or classification system for recession shapes; rather the terminology is used as an informal shorthand to characterize recessions and their recoveries. The most commonly used terms are V-shaped (with variations of square-root shaped, and Nike-swoosh shaped), U-shaped, W-shaped (also known as a double-dip recession), and L-shaped recessions, with the COVID-19 pandemic leading to the K-shaped recession (also known as a two-stage recession). The names derive from the shape the economic data – particularly GDP – takes during the recession and recovery. V-shaped In a V-shaped recession, the economy suffers a sharp but brief period of economic decline with a clearly defined trough, followed by a strong recovery. V-shapes are the normal shape for a recession, as the strength of the economic recovery is typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin American Debt Crisis
The Latin American debt crisis ( es, Crisis de la deuda latinoamericana; pt, Crise da dívida latino-americana) was a financial crisis that originated in the early 1980s (and for some countries starting in the 1970s), often known as ''La Década Perdida'' (The Lost Decade), when Latin American countries reached a point where their foreign debt exceeded their earning power, and they were not able to repay it. Origins In the 1960s and 1970s, many Latin American countries, notably Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico, borrowed huge sums of money from international creditors for industrialization, especially infrastructure programs. These countries had soaring economies at the time, so the creditors were happy to provide loans. Initially, developing countries typically garnered loans through public routes like the World Bank. After 1973, private banks had an influx of funds from oil-rich countries which believed that sovereign debt was a safe investment. Mexico borrowed against fut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Of 1982
Growth rate of Chile's GDP (orange) and Latin America (blue) between 1971 and 2007 The Crisis of 1982 was a major economic crisis suffered in Chile during the military government of Chile (1973–1990). La transformación económica de chilena entre 1973-2003'. Memoria Chilena. Chile's GDP fell 14.3%, and unemployment rose to 23.7%. Background After the socialist reorientation of the economy during the presidency of Salvador Allende, economic sabotage by the Nixon presidency, and the subsequent Chilean economic crisis which reached its zenith during 1973,''Historia contemporánea de Chile III. La economía: mercados empresarios y trabajadores.'' 2002. Gabriel Salazar and Julio Pinto. pp. 35–62. the Armed Forces following the orders of the military junta and with the support of the United States government made a Coup d'état and demobilized the forces loyal to Allende like the Revolutionary Left Movement. They closed down the congress, imposed censorship, limited civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)