|
Dushara
Dushara (Nabataean Arabic: 𐢅𐢈𐢝𐢛𐢀 ''dwšrʾ''), also transliterated as Dusares or Dhu Shara, is a pre-Islamic Arabian god worshipped by the Nabataeans at Petra and Madain Saleh (of which city he was the patron). Safaitic inscriptions imply he was the son of the goddess Al-Lat, and that he assembled in the heavens with other deities. He is called "Dushara from Petra" in one inscription. Dushara was expected to bring justice if called by the correct ritual. Etymology Dushara is known first from epigraphic Nabataean sources who invariably spell the name ''dwšrʾ'', the Nabataean script denoting only consonants. He appears in Classical Greek sources as Δουσάρης (''Dousárēs'') and in Latin as ''Dusares''. The original meaning is disputed, but early Muslim historian Hisham ibn al-Kalbi in his " Book of Idols" explains the name as ''Dhū l-Šarā'' (), "etymologically probably 'the one of the Shara (mountains north of Petra)'", referring to a mountain rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataeans
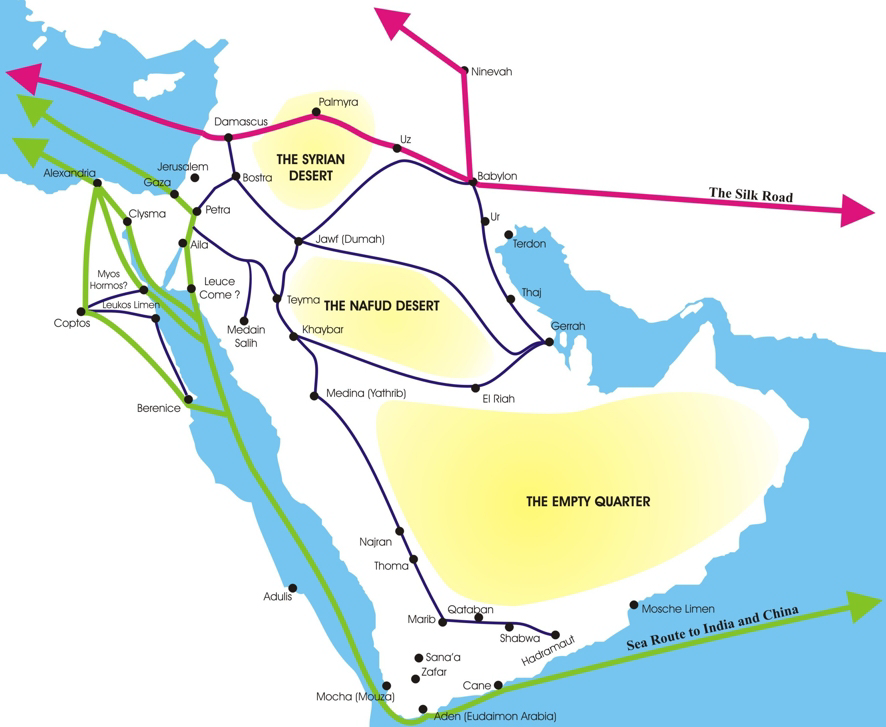
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ) were an ancient Arabs, Arab people who inhabited northern Arabian Peninsula, Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' () to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BC, with Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed into the Roman Empire by Emperor Trajan in 106 AD. Nabataeans' individual culture, easily identified by their characteristic finely potted painted ceramics, was adopted into the larger Greco-Roman culture. They converted to Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhushara
Dushara (Nabataean Arabic: 𐢅𐢈𐢝𐢛𐢀 ''dwšrʾ''), also transliterated as Dusares or Dhu Shara, is a pre-Islamic Arabian god worshipped by the Nabataeans at Petra and Madain Saleh (of which city he was the patron). Safaitic inscriptions imply he was the son of the goddess Al-Lat, and that he assembled in the heavens with other deities. He is called "Dushara from Petra" in one inscription. Dushara was expected to bring justice if called by the correct ritual. Etymology Dushara is known first from epigraphic Nabataean sources who invariably spell the name ''dwšrʾ'', the Nabataean script denoting only consonants. He appears in Classical Greek sources as Δουσάρης (''Dousárēs'') and in Latin as ''Dusares''. The original meaning is disputed, but early Muslim historian Hisham ibn al-Kalbi in his "Book of Idols" explains the name as ''Dhū l-Šarā'' (), "etymologically probably 'the one of the Shara (mountains north of Petra)'", referring to a mountain range sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Lat
Al-Lat (, ), also spelled Allat, Allatu, and Alilat, is a pre-Islamic Arabian goddess, at one time worshipped under various associations throughout the entire Arabian Peninsula, including Mecca, where she was worshipped alongside Al-Uzza and Manat as one of the daughters of Allah. The word ''Allat'' or Elat has been used to refer to various goddesses in the ancient Near East, including the goddess Asherah-Athirat. She also is associated with the Great Goddess. The worship of al-Lat is attested in South Arabian inscriptions as Lat and Latan, but she had more prominence in north Arabia and the Hejaz, and her cult reached as far as Syria. The writers of the Safaitic script frequently invoked al-Lat in their inscriptions. She was also worshipped by the Nabataeans and was associated with al-'Uzza. The presence of her cult was attested in both Palmyra and Hatra. Under Greco-Roman influence, her iconography began to show the attributes of Athena, the Greek goddess of war, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Gods
Deities formed a part of the polytheistic religious beliefs in pre-Islamic Arabia, with many of the deities' names known. Up until about the time between the fourth century AD and the emergence of Islam, polytheism was the dominant form of religion in Arabia. Deities represented the forces of nature, love, death, and so on, and were interacted with by a variety of rituals. Formal pantheons are more noticeable at the level of kingdoms, of variable sizes, ranging from simple city-states to collections of tribes.Robin, Christian Julien, "South Arabia, Religions in Pre-Islamic", in The Kaaba alone was said to have contained 360 idols of many deities. Tribes, towns, clans, lineages and families had their own cults too. Christian Julien Robin suggests that this structure of the divine world reflected the society of the time. Many deities did not have proper names and were referred to by titles indicating a quality, a family relationship, or a locale preceded by "he who" or "she who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Pre-Islamic Arabia
In pre-Islamic Arabia, the dominant religious practice was that of Arab polytheism, which was based on the veneration of various deities and spirits, such as the god Hubal and the goddesses al-Lāt, al-‘Uzzā, and Manāt. Worship was centred around local shrines and temples, most notably including the Kaaba in Mecca. Deities were venerated and invoked through pilgrimages, divination, and ritual sacrifice, among other traditions. Different theories have been proposed regarding the role of "Allah" (a word in Arabic that is now chiefly associated with God in Islam) in the Meccan religion. Many of the physical descriptions of the pre-Islamic gods and goddesses are traced to idols, especially near the Kaaba, which is said to have contained up to 360 of them. Other religions—namely Christianity, Judaism, and Zoroastrianism—were also represented in the region. The influence of the Roman Empire and the Kingdom of Aksum enabled the nurturing of Christianity in pre-Islamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
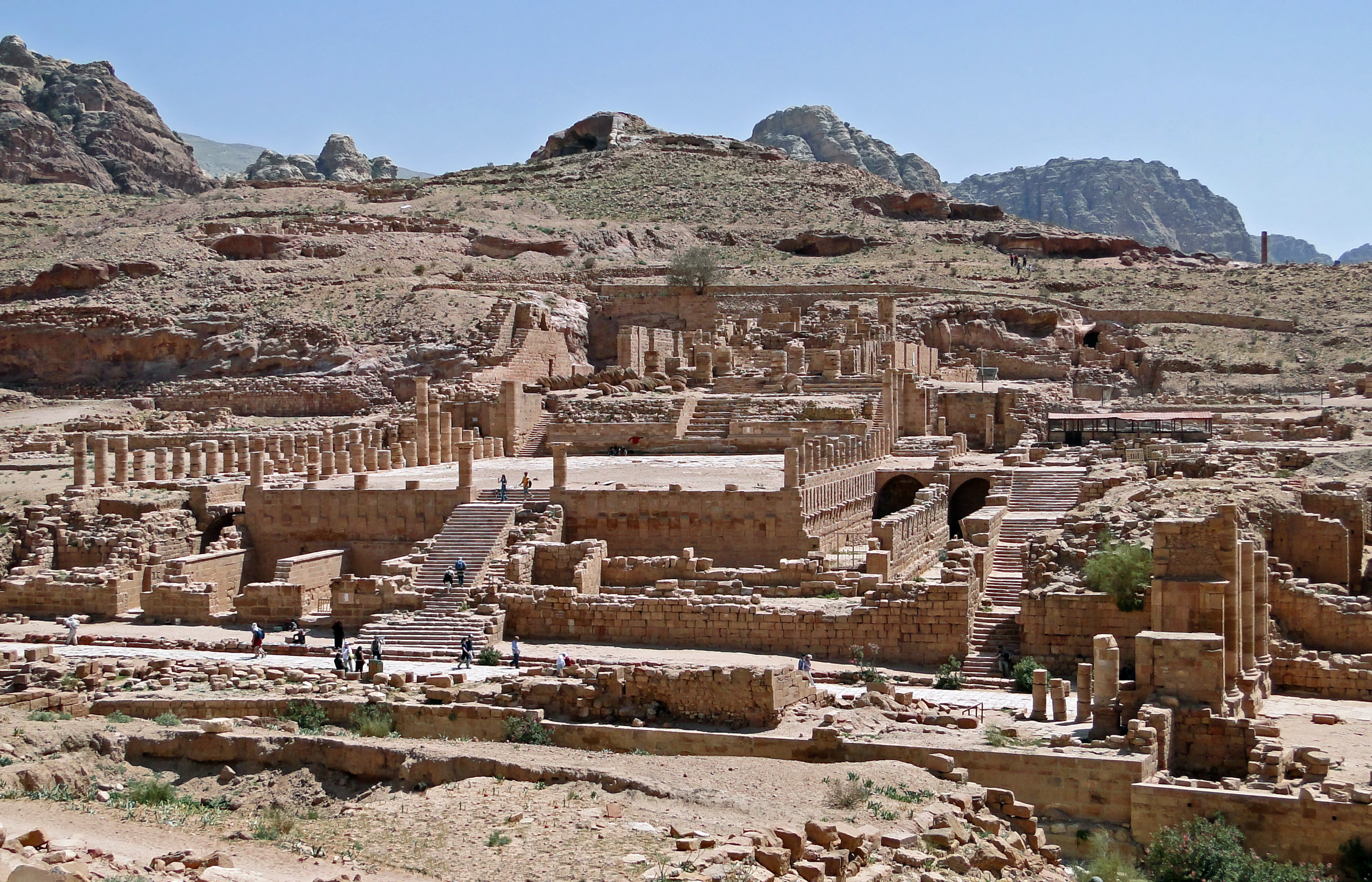
Petra
Petra (; "Rock"), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu (Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: or , *''Raqēmō''), is an ancient city and archaeological site in southern Jordan. Famous for its rock-cut architecture and water conduit systems, Petra is also called the "Rose City" because of the colour of the sandstone from which it is carved. The city is one of the New 7 Wonders of the World and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The area around Petra has been inhabited from as early as 7000 BC, and was settled by the Nabataeans, a nomadic Arab people, in the 4th century BC. Petra would later become the capital city of the Nabataean Kingdom in the second century BC. The Nabataeans invested in Petra's proximity to the incense trade routes by establishing it as a major regional trading hub, which gained them considerable revenue. Unlike their enemies, the Nabataeans were accustomed to living in the barren deserts and thus were able to defend their kingdom. They were particularly sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Idols
The ''Book of Idols'' ('), written by the Arab scholar Hisham ibn al-Kalbi (737–819), is the most popular Islamic work about the religion in pre-Islamic Arabia. Arabian religion before Muhammad is described as polytheistic and idolatrous. Ibn al-Kalbi portrays this state of religion as a degradation from the pure monotheism introduced by Abraham and his son Ishmael, only restored by the coming of Islam. Ibn al-Kalbi relied on Arab oral tradition to write his work. Historians agree that the Book of Idols is not a reliable source for Arabian religion before Islam. Overview The ''Book of Idols'' is essentially an itemized list of short descriptions of idols and sanctuaries in pre-Islamic Arabia. For each idol, he describes their geography and tribe. Sometimes Ibn al-Kalbi offers additional information, such as how the idol was destroyed in the Islamic era. In the primary manuscript, the text is 56 pages and each page contains 12 lines. The longest entry is about the goddess al-Uz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuntillet Ajrud Inscriptions
The Kuntillet Ajrud inscriptions refers to a set of pithos, pithoi and plaster inscriptions, stone incisions, and art discovered at the site of Kuntillet Ajrud. They were discovered at a unique Judean crossroads location, which featured an unusual number and variety of vessels and other inscriptions. They date to the late 9th century BC in the Sinai Peninsula. The finds were discovered during excavations in 1975–1976, during the Israeli occupation of the Sinai Peninsula, but were not published in first edition until 2012. The "shocking" and "exceedingly controversial" inscriptions have been called "the pithoi that launched a thousand articles" due to their influence on the fields of Ancient Near East studies, Ancient Near East and Biblical studies, raising and answering many questions about the relationship of Yahweh and Asherah. Description The most famousSchmidt, Brian B., "The Iron Age Pithoi Drawings from Ḥorvat Teman or Kuntillet ʿAjrud: Some New Proposals", '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataea
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea () was a political state of the Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Tihamah into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it to Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several formerly nomadic Arab tribes that roamed (later settled) the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. The origin of the specific tribe of Arab nomads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shara (god)
Shara ( Sumerian: 𒀭𒁈, '' dšara2'') was a Mesopotamian god associated with the city of Umma and other nearby settlements. He was chiefly regarded as the tutelary deity of this area, responsible for agriculture, animal husbandry, and irrigation, but he could also be characterized as a divine warrior. In the third millennium BCE, his wife was Ninura, associated with the same area, but later, in the Old Babylonian period, her cult faded into obscurity, and Shara was instead associated with Usaḫara or Kumulmul. An association between him and Inanna is well attested. In Umma, he was regarded as the son of Inanna of Zabalam and an unknown father, while in the myth ''Inanna's Descent to the Underworld,'' he is one of the servants mourning her temporary death. He also appears in the myth of Anzû, in which he is one of the three gods who refuse to fight the eponymous monster. Character While the original etymology of Shara's name is unknown, according to Fabienne Huber Vuillet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaabou
According to the early Christian bishop Epiphanius of Salamis (c. 315–403), Chaabou or Kaabu (; ) was a goddess in the Nabataean pantheon—a virgin who gave birth to the god Dusares. However, a few modern scholars claim without proof that Epiphanius may have mistaken the word ''kaʿbu'' ("cube", etymologically identical to the name of the Kaaba), referring to the stone blocks used by the Nabateans to represent Dusares and possibly other deities, for the proper name of a goddess. His report that Chaabou was a virgin was likely influenced by his desire to find a parallel to the Christian belief in the virgin birth of Jesus, and by the similarity of the words ''ka'bah'' and ''ka'ibah'' ("virgin") in Arabic, the native tongue of the Nabataeans. See also *al-Lat *Kaaba The Kaaba (), also spelled Kaba, Kabah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaba al-Musharrafa (), is a stone building at the center of Islam's most important mosque and Holiest sites in Islam, holiest site, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |