|
Drupada
Drupada (), also known as Yajnasena (, ), is the king of the southern part of Panchala Kingdom, in the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is the father of Draupadi, the epic's lead female character. In the Kurukshetra War as the head of 1 akshauhini army, Drupada fought from the side of his sons-in-law, the Pandavas, and was killed by his childhood friend and rival, Drona. Early life and family According to the ''Mahabharata'', Drupada is the son of Prishata, the king of Panchala Kingdom and his birth name was Yajnasena. Some Puranic scriptures provide a contradictory genealogy, according to which Drupada is the son of Somaka and Prishata is Somaka’s great grandfather.Puranic Encyclopedia: a comprehensive dictionary with special reference to the epic and Puranic literature, Vettam Mani, Motilal Banarsidass, Delhi, 1975251/ref> Drupada's early life is narrated in the ''Adi Parva'' of the epic, according to which he goes to the hermitage of the sage Bharadvaja for education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draupadi
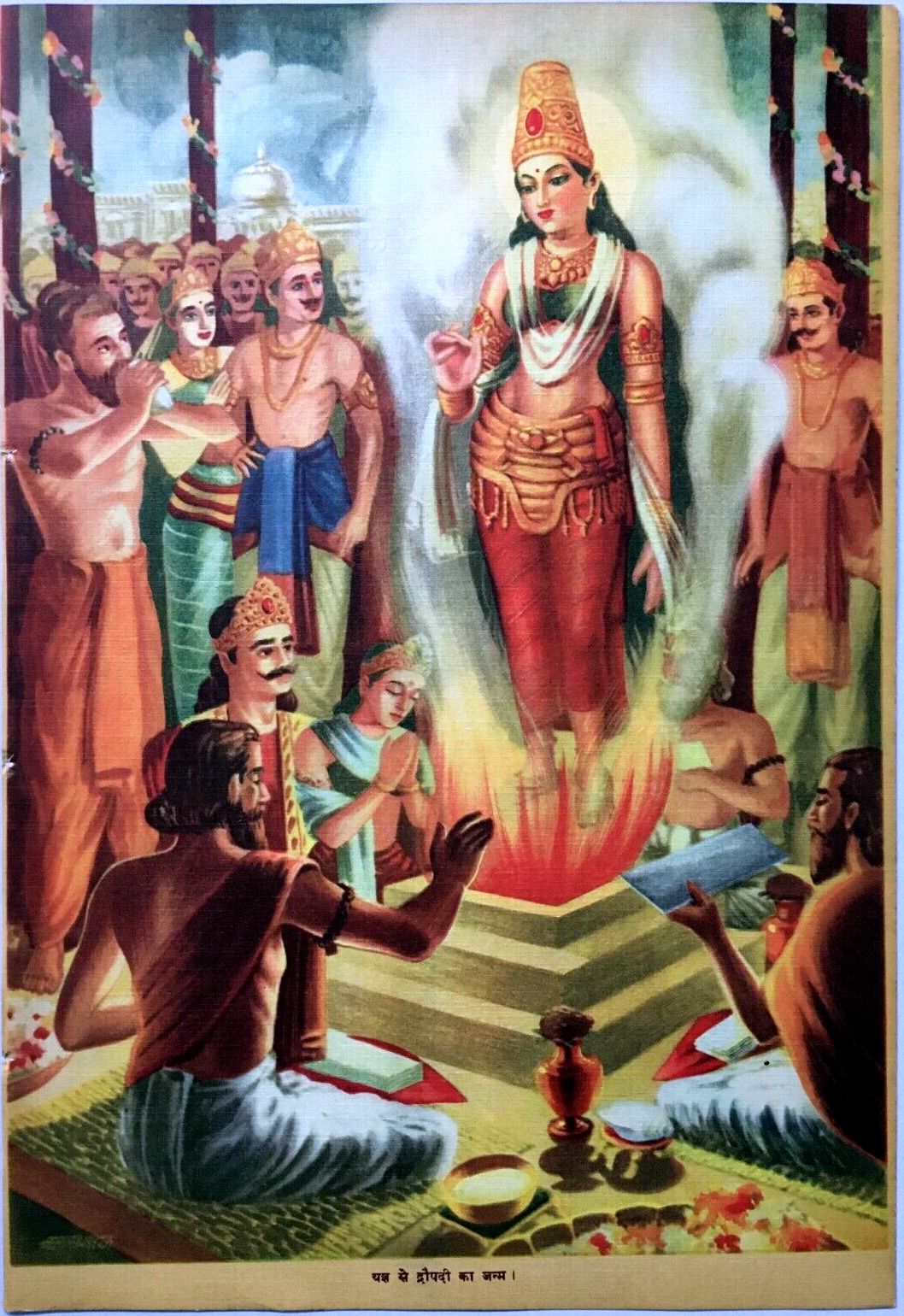
Draupadi (), also referred to as Krishnā, Panchali and Yajnaseni, is the central heroine of the Indian epic poetry, ancient Indian epic ''Mahabharata''. In the epic, she is the princess of Panchala Kingdom, who later becomes the empress of Kuru kingdom, Kuru Kingdom. She is the Polyandry, common wife of the five Pandava brothers—Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—and is renowned for her beauty, courage, devotion, intelligence and rhetorical skills. She is also described as ''sakhi''—a close friend—of the god Krishna. Draupadi, along with her twin brother Dhrishtadyumna, emerges fully grown from a ''yajna'' (fire sacrifice) organized by King Drupada of Panchala. Draupadi’s marriage is determined through a ''svayamvara'' (self-choice ceremony), structured as an archery contest of great difficulty. Arjuna succeeds in the challenge and wins her hand. However, their mother, Kunti, unknowingly instructs her sons to share whatever they had brought home, resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
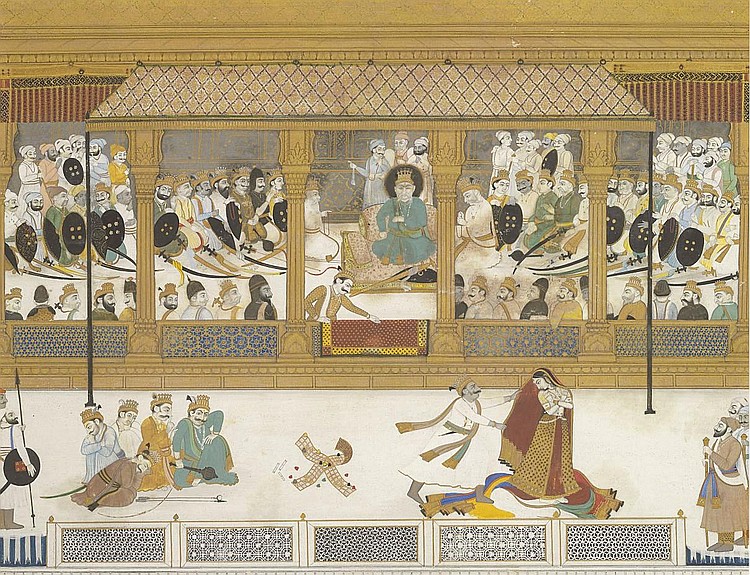
Drona And The Fire Of Friendship
Droṇa (, ), also referred to as Dronacharya (, ), is a major character of the Hindu epic Mahabharata. In the epic, he serves as the royal preceptor of the Kauravas and the Pandavas. He is one of the primary counsellors and warriors featured in the epic. Drona is the son of the sage Bharadvaja, and a descendant of the sage Angirasa. Despite being master of advanced military arts and the divine weapons known as astras, Drona initially chooses a life of poverty until he is humiliated by his friend Drupada, the king of Panchala. With the help of his students, he captures Drupada and takes away half of the kingdom. Drona serves as the second commander-in-chief of the Kaurava army, from the 11th day to the 15th day. The acharya fails four times in capturing Yudhishthira (the 11th day, 12th day, 14th day, and the 14th night). He was beheaded by Dhrishtadyumna—his student and son of Drupada—when he meditates to release his soul on the battlefield. Etymology Drona's name means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drona
Droṇa (, ), also referred to as Dronacharya (, ), is a major character of the Hindu epic Mahabharata. In the epic, he serves as the royal preceptor of the Kauravas and the Pandavas. He is one of the primary counsellors and warriors featured in the epic. Drona is the son of the sage Bharadvaja, and a descendant of the sage Angirasa. Despite being master of advanced military arts and the divine weapons known as astras, Drona initially chooses a life of poverty until he is humiliated by his friend Drupada, the king of Panchala. With the help of his students, he captures Drupada and takes away half of the kingdom. Drona serves as the second commander-in-chief of the Kaurava army, from the 11th day to the 15th day. The acharya fails four times in capturing Yudhishthira (the 11th day, 12th day, 14th day, and the 14th night). He was beheaded by Dhrishtadyumna—his student and son of Drupada—when he meditates to release his soul on the battlefield. Etymology Drona's name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhristadyumna
Dhrishtadyumna () is a pivotal character in the ancient Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is the son of Drupada—the king of the Panchala kingdom—and the brother of Draupadi—the wife of the five Pandavas. Dhrishtadyumna is born from a ''yajna'' (fire-sacrifice) organised by Drupada, who wanted a son capable of killing his enemy, Drona. When the Pandava prince Arjuna—disguised as a ''Brahmana''—won the hand of Draupadi in marriage, Dhrishtadyumna realised his identity. In the Kurukshetra War, Dhrishtadyumna joins the Pandavas, and becomes the supreme commander-in-chief of the Pandava forces. On the fifteenth day of the war, he beheads Drona, fulfilling the mission of his birth. Birth left, A Mughal painting by Bilal Habsi depicting the birth of Dhrishtadyumna. A folio of ''Razmnama'', the Persian translation of the epic Dhishtadyumna, along with Draupadi, is described as an "''ayonija''", one not born from a woman's womb. His birth is narrated in the ''Adi Parva'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikhandi
Shikhandi () is a character in the Hindu epic Mahabharata. Born as the daughter of Drupada, the King of Panchala, Shikhandi becomes male after agreeing to a sex exchange with a yaksha. He is the brother of Draupadi, the female protagonist of the epic, who is the common wife of the Pandavas. Shikhandi, whose natal female identity is sometimes rendered Shikhandini, is the reincarnation of Amba, a princess who was abducted by Bhishma at a svayamvara and later spurned by him. The prince fights in the Kurukshetra War on the side of his brothers-in-law, the Pandavas, and is instrumental in causing the death of Bhishma. He also engages in combat with great warriors like Ashwatthama, Kripa, and Kritavarma. In Javanese wayang tradition, Shikhandi is known as Srikandhi and is born as a male, and changes into a female. She becomes the second wife of the Pandava brother Arjuna, and Sembadra being the first. Legend Previous birth In the majority of the versions of the Mahabha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amba (Mahabharata)
Amba () is a character in the Hindu epic Mahabharata. She is the eldest and most beautiful daughter of Kashya, the King of Kashi, and the sister of Ambika and Ambalika. Amba, along with her sisters, were abducted by Bhishma during their svayamvara ceremony, as brides to marry Vichitravirya, the King of Hastinapura. Before the wedding ceremony, the princess approaches Bhishma, and informs him of her love for King Salva, upon which she is allowed to go to the latter and urge him to accept her as his wife. To her dismay, Salva rejects her, regarding her to have been customarily accepted by Bhishma as his wife. Despite her efforts, as well as those of Parashurama, Bhishma refuses to marry her. Amba holds Bhishma responsible for her misfortune, undertaking a penance, and is granted a boon by Shiva. She is reborn as Shikhandi, the child of King Drupada, and the sibling of the epic's female protagonist, Draupadi. Etymology Amba is a commonly used word in Sanskrit meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arjuna
Arjuna (, , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, [ɐɾd͡ʒun̪ə]) is one of the central characters of the ancient Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is the third of the five Pandava brothers, and is widely regarded as the most important and renowned among them. He is the son of Indra, the king of the Deva (Hinduism), gods, and Kunti, wife of King Pandu of Kuru kingdom, Kuru dynasty—making him a Demigod, divine-born hero. Arjuna is famed for his extraordinary prowess in archery and mastery over Astra (weapon), celestial weapons. Throughout the epic, Arjuna sustains a close friendship with his maternal cousin, Krishna, who serves as his spiritual guide. Arjuna is celebrated for numerous heroic exploits throughout the epic. From childhood, he emerges as an excellent pupil, studying under the warrior-sage Drona. In his youth, Arjuna wins the hand of Draupadi, the princess of the Pañcāla, Panchalas, by excelling in a formidable archery competition. Soon after, he goes on a journey during a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characters In The Mahabharata
The '' Mahabharata'' is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India composed by Veda Vyasa. At its heart lies the epic struggle between the Pandavas and the Kauravas. The central characters include the five Pandava brothers— Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—along with their wife Draupadi. On the opposing side, the hundred Kaurava brothers are led by the elder brother, Duryodhana. However, the ''Mahabharata'' is richly populated with other notable figures including Krishna, Bhishma, Drona, Karna, Kunti, Dushasana, Kripa, Dhritrashtra, Gandhari, Shakuni, Ashwatthama, Balarama, Subhadra, Vyasa, Abhimanyu, Pandu, Satyavati and Amba. The ''Mahabharata'' manuscripts exist in numerous versions, wherein the specifics and details of major characters and episodes vary, often significantly. Except for the sections containing the ''Bhagavad Gita'' which is remarkably consistent between the numerous manuscripts, the rest of the epic exists in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchala Kingdom (Mahabharata)
Panchala () was an ancient kingdom of northern India, located in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the Upper Gangetic plain which is identified as Kanyakubja or region around Kannauj. During Late Vedic times (c. 1100–500 BCE), it was one of the most powerful states of ancient India, closely allied with the Kuru Kingdom. By the c. 5th century BCE, it had become an oligarchic confederacy, considered one of the ''solasa'' (sixteen) mahajanapadas (major states) of the Indian subcontinent. After being absorbed into the Mauryan Empire (322–185 BCE), Panchala regained its independence until it was annexed by the Gupta Empire in the 4th century CE. Location The Pañcāla state was located to the west of the Gomti river, and the north of the Chambal River. Its western neighbours were the Sūrasenas and the Yakṛllomas, while in the north-west it was separated from the Gaṅgā and the Kurus by dense forests. The northern boundaries of Pañcāla were the forests around the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prishati
The ''Mahabharata'' is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India composed by Veda Vyasa. At its heart lies the epic struggle between the Pandavas and the Kauravas. The central characters include the five Pandava brothers—Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—along with their wife Draupadi. On the opposing side, the hundred Kaurava brothers are led by the elder brother, Duryodhana. However, the ''Mahabharata'' is richly populated with other notable figures including Krishna, Bhishma, Drona, Karna, Kunti, Dushasana, Kripa, Dhritrashtra, Gandhari, Shakuni, Ashwatthama, Balarama, Subhadra, Vyasa, Abhimanyu, Pandu, Satyavati and Amba. The ''Mahabharata'' manuscripts exist in numerous versions, wherein the specifics and details of major characters and episodes vary, often significantly. Except for the sections containing the ''Bhagavad Gita'' which is remarkably consistent between the numerous manuscripts, the rest of the epic exists in many ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchala (Mahabharata)
Panchala () was an ancient kingdom of northern India, located in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the Upper Gangetic plain which is identified as Kanyakubja or region around Kannauj. During Late Vedic times (c. 1100–500 BCE), it was one of the most powerful states of ancient India, closely allied with the Kuru Kingdom. By the c. 5th century BCE, it had become an oligarchic confederacy, considered one of the ''solasa'' (sixteen) mahajanapadas (major states) of the Indian subcontinent. After being absorbed into the Mauryan Empire (322–185 BCE), Panchala regained its independence until it was annexed by the Gupta Empire in the 4th century CE. Location The Pañcāla state was located to the west of the Gomti river, and the north of the Chambal River. Its western neighbours were the Sūrasenas and the Yakṛllomas, while in the north-west it was separated from the Gaṅgā and the Kurus by dense forests. The northern boundaries of Pañcāla were the forests around the regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |