|
Drop Tube
In physics and materials science, a drop tower or drop tube is a structure used to produce a controlled period of weightlessness for an object under study. Air bags, polystyrene pellets, and magnetic or mechanical brakes are sometimes used to arrest the fall of the experimental payload. In other cases, high-speed impact with a substrate at the bottom of the tower is an intentional part of the experimental protocol. Not all such facilities are towers: NASA Glenn's Zero Gravity Research Facility is based on a vertical shaft, extending to below ground level. Typical operation For a typical materials science experiment, a sample of the material under study is loaded into the top of the drop tube, which is filled with inert gas or evacuated to create a low-pressure environment. Following any desired preprocessing (e.g. induction heating to melt a metal alloy), the sample is released to fall to the bottom of the tube. During its flight or upon impact the sample can be charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomit Comet
A reduced-gravity aircraft is a type of fixed-wing aircraft that provides brief near-weightless environments for training astronauts, conducting research, and making gravity-free movie shots. Versions of such airplanes were operated by the NASA Reduced Gravity Research Program, and one is currently operated by the Human Spaceflight and Robotic Exploration Programmes of the European Space Agency. The unofficial nickname "vomit comet" became popular among those who experienced their operation. History Parabolic flight as a way of simulating weightlessness was first proposed by the German aerospace engineer Fritz Haber and his brother, physicist Heinz Haber in 1950. Both had been brought to the US after World War II as part of Operation Paperclip. As well, Shih-Chun Wang studied nausea in astronauts for NASA, which helped lead to the creation of the vomit comet. Parabolic flights are sometimes used to examine the effects of weightlessness on a living organism. While humans a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Shot
Shot is a collective term for small spheres or pellets, often made of lead. These have been projected from slings since ancient times and were the original projectiles for shotguns and are still fired primarily from shotguns and grenade launchers, while they are less commonly used in riot guns. Shot shells are also available in many handgun calibers in a configuration known as " birdshot", " rat shot", or " snake shot". Lead shot is also used for a variety of other purposes such as filling cavities with dense material for weight and/or balance. Some versions may be plated with other metals. Lead shot was originally made by pouring molten lead through screens into water, forming what was known as "swan shot", and, later, more economically mass-produced at higher quality using a shot tower. The ''Bliemeister method'' has supplanted the shot tower method since the early 1960s. Manufacture Producing lead shot from a shot tower was pioneered in the late 18th century by Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shot Tower
A shot tower is a tower designed for the production of small-diameter shot balls by free fall of molten lead, which is then caught in a water basin. The shot is primarily used for projectiles in shotguns, and for ballast, radiation shielding, and other applications for which small lead balls are useful. Shot making Process In a shot tower, lead is heated until molten, then dropped through a copper sieve high in the tower. The liquid lead forms tiny spherical balls by surface tension, and solidifies as it falls. The partially cooled balls are caught at the floor of the tower in a water-filled basin.. The now fully cooled balls are checked for roundness and sorted by size; those that are "out of round" are remelted. A slightly inclined table is used for checking roundness. To make larger shot sizes, a copper sieve with larger holes is used. The maximum size is limited by the height of the tower, because larger shot sizes must fall farther to solidify. A shot tower with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo's Leaning Tower Of Pisa Experiment
Between 1589 and 1592, the Italian scientist Galileo Galilei (then professor of mathematics at the University of Pisa) is said to have dropped "unequal weights of the same material" from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to demonstrate that their time of descent was independent of their mass, according to a biography by Galileo's pupil Vincenzo Viviani, composed in 1654 and published in 1717. Vincenzo Viviani (1717), ''Racconto istorico della vita di Galileo Galilei'', p. 606: [...dimostrando ciò con replicate esperienze, fatte dall'altezza del Campanile di Pisa con l'intervento delli altri lettori e filosofi e di tutta la scolaresca... [...Galileo showed this [all bodies, whatever their weights, fall with equal speeds] by repeated experiments made from the height of the Leaning Tower of Pisa in the presence of other professors and all the students...]. The basic premise had already been demonstrated by Italian experimenters a few decades earlier. According to the story, Galileo discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaning Tower Of Pisa
The Leaning Tower of Pisa ( ), or simply the Tower of Pisa (), is the , or freestanding bell tower, of Pisa Cathedral. It is known for its nearly four-degree lean, the result of an unstable Foundation (engineering), foundation. The tower is one of three structures in Pisa's Cathedral Square (), which includes the cathedral and Pisa Baptistery, Pisa Baptistry. Over time, the tower has become one of the most visited tourist attractions in the world as well as an architectural icon of Italy, receiving over 5 million visitors each year. The height of the tower is from the ground on the low side and on the high side. The width of the walls at the base is . Its weight is estimated at . The tower has 296 or 294 steps; the seventh floor has two fewer steps on the north-facing staircase. The tower began to lean during construction in the 12th century, due to soft ground which could not properly support the structure's weight. It worsened through the completion of construction in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the father of observational astronomy, modern-era classical physics, the scientific method, and modern science. Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of the pendulum and " hydrostatic balances". He was one of the earliest Renaissance developers of the thermoscope and the inventor of various military compasses. With an improved telescope he built, he observed the stars of the Milky Way, the phases of Venus, the four largest satellites of Jupiter, Saturn's rings, lunar craters and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
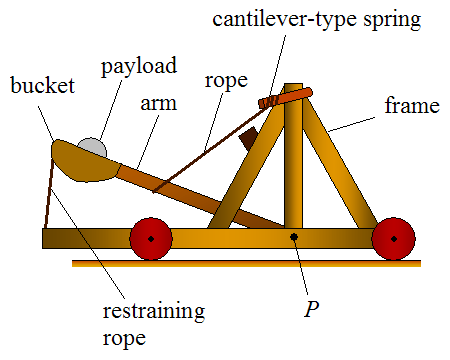
Catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored potential energy to propel its payload. Most convert Tension (mechanics), tension or Torsion (mechanics), torsion energy that was more slowly and manually built up within the device before release, via springs, bows, twisted rope, elastic, or any of numerous other materials and mechanisms which allow the catapult to launch a projectile such as rocks, cannon balls, or debris. During wars in the ancient times, the catapult was usually known to be the strongest heavy weaponry. In modern times the term can apply to devices ranging from a simple hand-held implement (also called a "slingshot") to a mechanism for Aircraft catapult, launching aircraft from a ship. The earliest catapults date to at least the 7th century BC, with Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Bremen
The University of Bremen () is a public university in Bremen, Germany, with approximately 18,400 students from 117 countries. Its 12 faculties offer more than 100 degree programs. The University of Bremen has been among the top 50 European research universities for more than 50 years and focuses its research on 5 high-profile areas. It is one of 11 institutions which were successful in the category "Institutional Strategies" of the Excellence Initiative launched by the Federal Government and the Federal States in 2012. The university was also successful in the categories "Graduate Schools" and "Clusters of Excellence" of the initiative. Some of the paths that were taken in the early days of the university, also referred to as the "Bremen model", have since become characteristics of modern universities, such as interdisciplinary, explorative learning, social relevance to practice-oriented project studies which enjoy a high reputation in the academic world as well as in business a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fallturm Bremen
Fallturm Bremen is a drop tower at the Center of Applied Space Technology and Microgravity at the University of Bremen in Bremen. It was built between 1988 and 1990, and includes a 122-metre-high drop tube (actual drop distance is 110 m), in which for 4.74 seconds (with release of the drop capsule), or for over 9 seconds (with the use of a catapult, installed in 2004) weightlessness can be produced. The entire tower, formed out of a reinforced concrete shank, is 146 metres high. The 122-metre drop tube is free-standing within the concrete shell, in order to prevent the transmission of wind-induced vibrations, which could otherwise result in the airtight drop capsule hitting the walls. The drop tube is pumped down prior to every free-fall experiment to about 10 Pa (~ 1/10 000 atmosphere). Evacuation takes about 1.5 hours. In 2021, German and French scientists at the drop tube managed to produce and record the lowest temperature ever measured. Using quantum gas, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall Space Flight Center
Marshall Space Flight Center (officially the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center; MSFC), located in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama (Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville postal address), is the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government's civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. As the largest NASA center, MSFC's first mission was developing the Saturn (rocket family), Saturn launch vehicles for the Apollo program. Marshall has been the lead center for the Space Shuttle main propulsion and Space Shuttle external tank, external tank; payloads and related crew training; International Space Station (ISS) design and assembly; computers, networks, and information management; and the Space Launch System. Located on the Redstone Arsenal near Huntsville, MSFC is named in honor of General of the Army (United States), General of the Army George C. Marshall. The center contains the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC), also known as the International Space S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |