|
Drogue
A drogue or storm drogue is a device trailed behind a boat on a long line attached to the stern. A drogue is used to slow the boat down in a storm and to prevent the hull (watercraft), hull from becoming side-on to the water waves, waves. A boat that has deployed a drogue should not overspeed down the slope of a wave and crash into the next one, nor will the vessel Broach (sailing), broach. By slowing the vessel, the drogue makes the vessel easier to control in heavy weather and will help to prevent wikt:pitchpole, pitchpoling. A drogue works by providing substantial Drag (physics), resistance when dragged through the water. An alternative device is the sea anchor which is streamed from the bows. The advantage of the sea anchor is that the bows of a yacht are invariably finer for breaking through waves than the stern, thereby giving a safer and more comfortable experience in a storm. Both drogues and sea anchors will have ''tripping lines'' to aid recovery of the drogue after d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Anchor
A sea anchor (also known as a parachute anchor, drift anchor, drift sock, para-anchor or boat brake) is a device that is streamed from a boat in heavy weather. Its purpose is to stabilize the vessel and to limit progress through the water. Rather than tethering the boat to the seabed with a conventional anchor, a sea anchor provides hydrodynamic drag (physics), drag, thereby acting as a brake. Normally attached to a vessel's Bow (ship), bows, a sea anchor can prevent the vessel from turning broadside to the waves and being overwhelmed by them. Early sea anchors were crude devices, but today most take the form of a drogue parachute. Larger sea anchors are so efficient that they need a tripping line to collapse the parachute for retrieval. Being made of fabric, a sea parachute may be bagged and easily stowed when not in use. A similar device to the sea anchor is the much smaller drogue, which is streamed from a vessel's stern in strong winds so as to slow the boat to prevent pitch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Refuelling
Aerial refueling ( en-us), or aerial refuelling ( en-gb), also referred to as air refueling, in-flight refueling (IFR), air-to-air refueling (AAR), and tanking, is the process of transferring aviation fuel from one aircraft (the tanker) to another (the receiver) while both aircraft are in flight. The two main refueling systems are '' probe-and-drogue'', which is simpler to adapt to existing aircraft and the '' flying boom'', which offers faster fuel transfer, but requires a dedicated boom operator station. The procedure allows the receiving aircraft to remain airborne longer, extending its range or loiter time. A series of air refuelings can give range limited only by crew fatigue/physical needs and engineering factors such as engine oil consumption. Because the receiver aircraft is topped-off with extra fuel in the air, air refueling can allow a takeoff with a greater payload which could be weapons, cargo, or personnel: the maximum takeoff weight is maintained by carrying l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heaving To
In sailing, heaving to (to heave to and to be hove to) is a way of slowing a sailing vessel's forward progress, as well as fixing the helm and sail positions so that the vessel does not have to be steered. It is commonly used for a "break"; this may be to wait for the tide before proceeding, or to wait out a strong or contrary wind. For a solo or shorthanded sailor it can provide time to go below deck, to attend to issues elsewhere on the boat or to take a meal break.www.sailingusa.info/points_of_sail.htm Heaving to can make reefing a lot easier, especially in traditional vessels with several sails. It is also used as a storm tactic. A sailing vessel that is hove to is still, for the purposes of the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoy
A buoy (; ) is a buoyancy, floating device that can have many purposes. It can be anchored (stationary) or allowed to drift with ocean currents. History The ultimate origin of buoys is unknown, but by 1295 a seaman's manual referred to navigation buoys in the Guadalquivir River in Spain. To the north there are early medieval mentions of the French / Belgian River Meuse, Maas being buoyed. Such early buoys were probably just timber beams or rafts, but in 1358 there is a record of a barrel buoy in the Dutch Maasmond (also known as the Maas Sluis or Maasgat). The simple barrel was difficult to secure to the seabed, and so a conical ''tonne'' was developed. They had a solid plug at the narrow end through which a mooring ring could be attached. By 1790 the older conical tonne was being replaced by a ''nun'' buoy. This had the same conical section below the waterline as the tonne buoy, but at the waterline a barrel shape was used to allow a truncated cone to be above the water. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
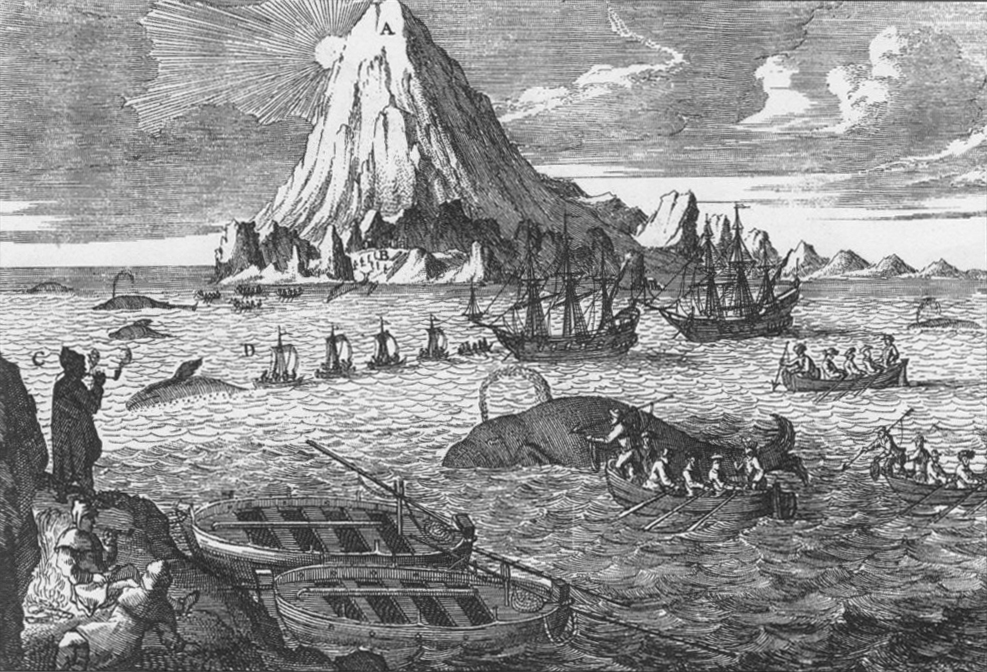
Whaling
Whaling is the hunting of whales for their products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that was important in the Industrial Revolution. Whaling was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16th century, it had become the principal industry in the Basque coastal regions of Spain and France. The whaling industry spread throughout the world and became very profitable in terms of trade and resources. Some regions of the world's oceans, along the animals' migration routes, had a particularly dense whale population and became targets for large concentrations of whaling ships, and the industry continued to grow well into the 20th century. The depletion of some whale species to near extinction led to the banning of whaling in many countries by 1969 and to an international cessation of whaling as an industry in the late 1980s. Archaeological evidence suggests the earliest known forms of whaling date to at least 3000 BC, practiced by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Melville
Herman Melville (Name change, born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance (literature), American Renaissance period. Among his best-known works are ''Moby-Dick'' (1851); ''Typee'' (1846), a romanticized account of his experiences in Polynesia; and ''Billy Budd, Billy Budd, Sailor'', a posthumously published novella. At the time of his death Melville was not well known to the public, but 1919, the centennial of his birth, was the starting point of a #Melville revival and Melville studies, Melville revival. ''Moby-Dick'' would eventually be considered one of the great American novels. Melville was born in New York City, the third child of a prosperous merchant whose death in 1832 left the family in dire financial straits. He took to sea in 1839 as a common sailor on the merchant ship ''St. Lawrence'' and then, in 1841, on the whaler ''Acushnet'', but he jumped ship in the Marquesas I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moby-Dick
''Moby-Dick; or, The Whale'' is an 1851 Epic (genre), epic novel by American writer Herman Melville. The book is centered on the sailor Ishmael (Moby-Dick), Ishmael's narrative of the maniacal quest of Captain Ahab, Ahab, captain of the whaler, whaling ship ''Pequod (Moby-Dick), Pequod'', for vengeance against Moby Dick (whale), Moby Dick, the giant white sperm whale that bit off his leg on the ship's previous voyage. A contribution to the literature of the American Renaissance (literature), American Renaissance, ''Moby-Dick'' was published to mixed reviews, was a commercial failure, and was out of print at the time of the author's death in 1891. Its reputation as a Great American Novel was established only in the 20th century, after the 1919 centennial of its author's birth. William Faulkner said he wished he had written the book himself, and D. H. Lawrence called it "one of the strangest and most wonderful books in the world" and "the greatest book of the sea ever written". It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
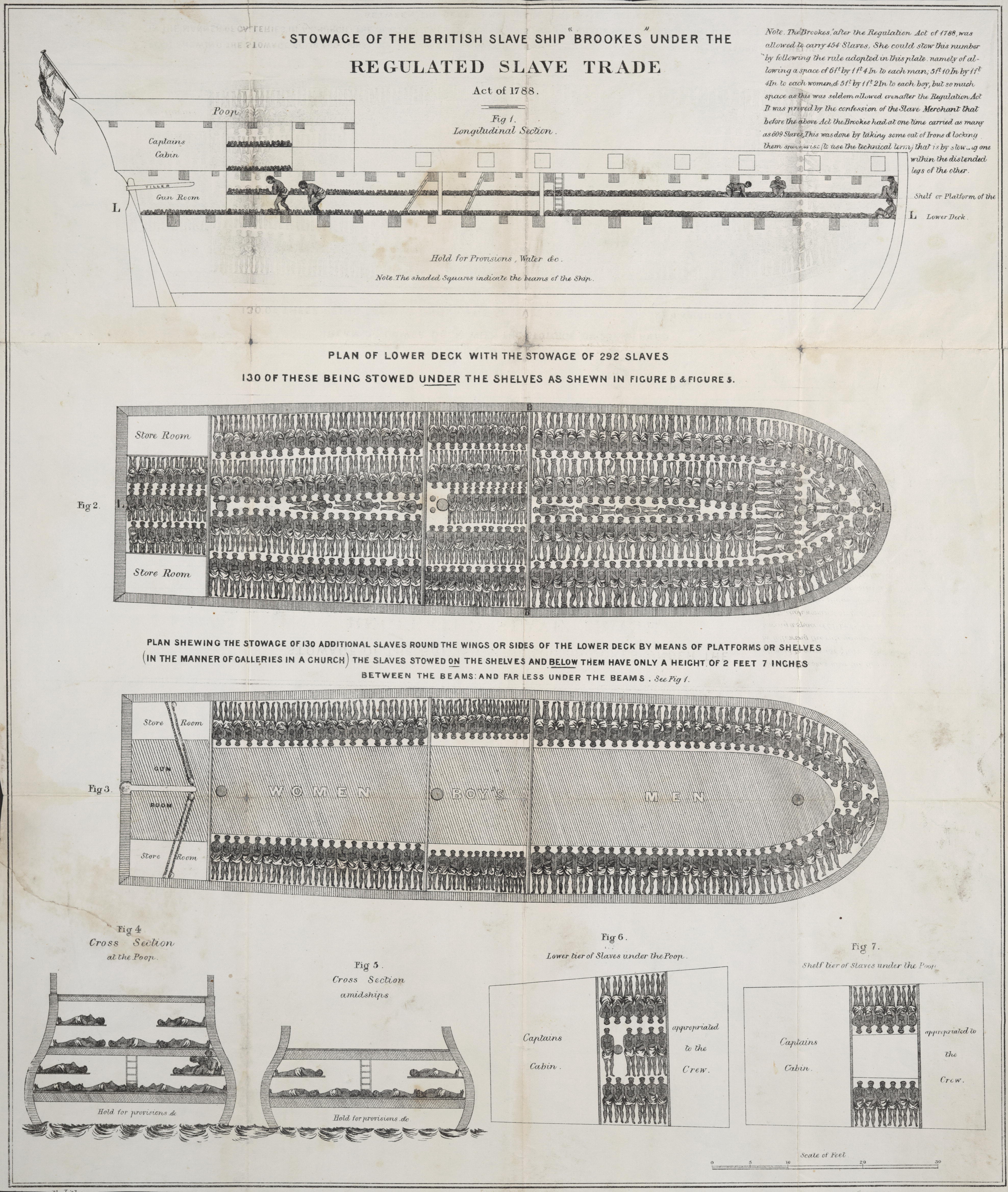
Slave Ship
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting Slavery, slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea (region), Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 17th century, more than a century after the arrival of European emigration, Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure Profit (accounting), profitability, the owners of the ships divided their Hull (watercraft), hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery, and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often, the ships carried hundreds of sla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornblower In The West Indies
''Hornblower in the West Indies'', or alternately ''Admiral Hornblower in the West Indies'', is one of the novels in the series that C. S. Forester wrote about fictional Royal Navy officer Horatio Hornblower. All the other novels in the series take place during the wars with revolutionary and Napoleonic France; this one, however, takes place when Britain is at peace, May 1821 – October 1823. Hornblower has been promoted rear-admiral and named in command of the West Indies Station (in the Caribbean) with a squadron consisting of three frigates and fourteen brigs and schooners. It is the last Hornblower novel chronologically, although the short story (" The Last Encounter") is set later. The book's five long, titled chapters can be read as independent novellas, much as the ten titled chapters of '' Mr. Midshipman Hornblower'' are a sequence of largely independent short stories. Plot summary St. Elizabeth of Hungary Hornblower raises his flag in the schooner HMS ''Crab'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basket Case MOD 45147014
A basket is a container that is traditionally constructed from stiff fibers, and can be made from a range of materials, including wood splints, runners, and cane. While most baskets are made from plant materials, other materials such as horsehair, baleen, or metal wire can be used. Baskets are generally woven by hand. Some baskets are fitted with a lid, while others are left open on top. Uses Baskets serve utilitarian as well as aesthetic purposes. Some baskets are ceremonial, that is religious, in nature. While baskets are usually used for harvesting, storage and transport, specialized baskets are used as sieves for a variety of purposes, including cooking, processing seeds or grains, tossing gambling pieces, rattles, fans, fish traps, and laundry. History Prior to the invention of woven baskets, people used tree bark to make simple containers. These containers could be used to transport gathered food and other items, but crumbled after only a few uses. Weaving strips of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
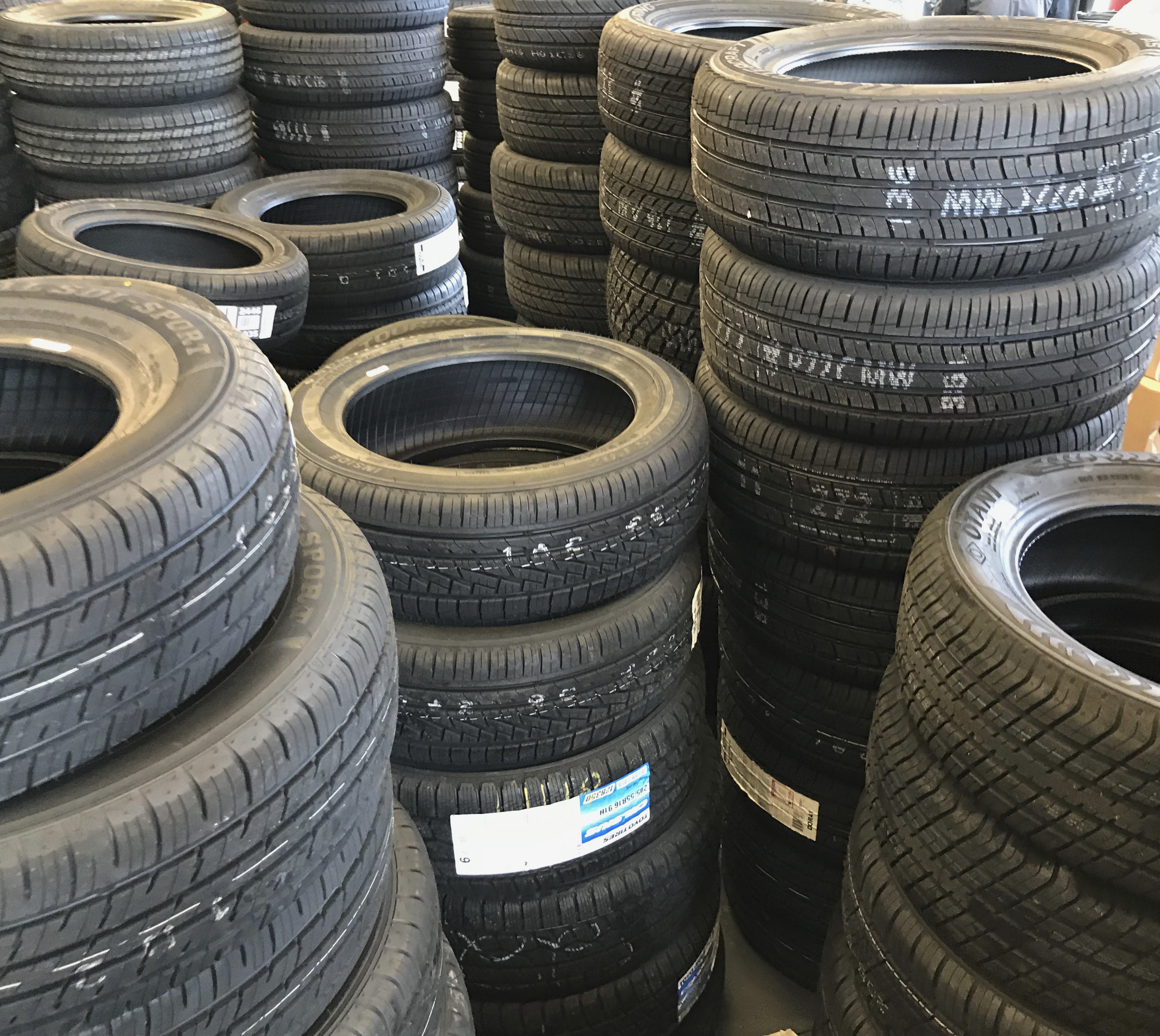
Tires
A tire (North American English) or tyre (Commonwealth English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, providing a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, designed to match the vehicle's weight and the bearing on the surface that it rolls over by exerting a pressure that will avoid deforming the surface. The materials of modern pneumatic tires are synthetic rubber, natural rubber, fabric, and wire, along with carbon black and other chemical compounds. They consist of a tread and a body. The tread provides traction while the body provides containment for a quantity of compressed air. Before rubber was developed, tires wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |