|
Drehovian
The Dregoviches, also called the ''Dregovichi'', were an East Slavic tribal union. They inhabited the territories along the lower Pripyat River and the northern parts of the right bank of the Dnieper River (more exact extents of the tribe's domain are still unknown). Etymology The name of the tribe most probably derives from the Proto-Slavic word "*drъgъva" (found only in Southern Belarusian as "dregva" and Northern Ukrainian as "dragva, dryagva", which is a loanword from Baltic languages "dreguva" meaning 'swamp'), because the Dregoviches used to live in the marshlands. Linguists consider that they are "undoubtedly" related to a South Slavic tribe with a similar name, Drougoubitai.Трубачев О. Н. Ранние славянские этнонимы — свидетели миграции славян // Вопр. языкознания. 1974. № 6. С. 52-53 History The first known reference to the Dregoviches is in the ''Primary Chronicle''(c. 1113), where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jewellery Dregoviches GIM
Jewellery (or jewelry in American English) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a western perspective, the term is restricted to durable ornaments, excluding flowers for example. For many centuries metal such as gold often combined with gemstones, has been the normal material for jewellery, but other materials such as glass, shells and other plant materials may be used. Jewellery is one of the oldest types of archaeological artefact – with 100,000-year-old beads made from ''Nassarius'' shells thought to be the oldest known jewellery. The basic forms of jewellery vary between cultures but are often extremely long-lived; in European cultures the most common forms of jewellery listed above have persisted since ancient times, while other forms such as adornments for the nose or ankle, important in other cultures, are muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Primary Chronicle
The ''Primary Chronicle'', shortened from the common ''Russian Primary Chronicle'' (, commonly transcribed ''Povest' vremennykh let'' (PVL), ), is a Rus' chronicle, chronicle of Kievan Rus' from about 850 to 1110. It is believed to have been originally compiled in or near Kiev in the 1110s. Tradition ascribed its compilation to the monk Nestor the Chronicler, Nestor (''Nestor's Chronicle'') beginning in the 12th century, but this is no longer believed to have been the case. The title of the work, ("Tale of Bygone Years") comes from the opening sentence of the Laurentian Codex, ''Laurentian'' text: "These are the narratives of bygone years regarding the origin of the land of Rus', the first princes of Kiev, and from what source the land of Rus' had its beginning". The work is considered a fundamental source for the earliest history of the East Slavs. The content of the chronicle is known today from the several surviving versions and codices, revised over the years, slightly var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
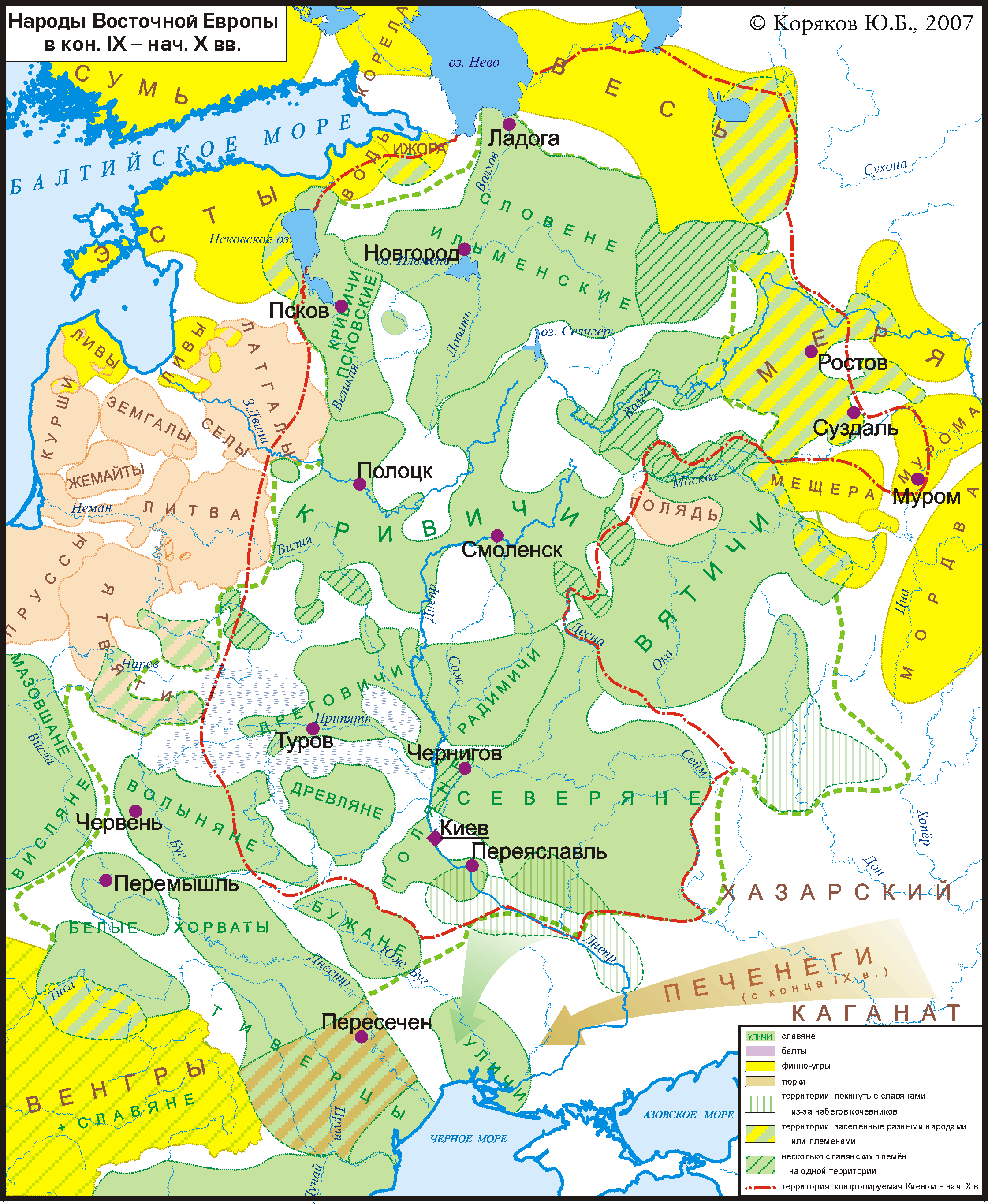
List Of Early Slavic Peoples
This is a list of early Slavic peoples reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500. Ancestors *Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers) ** Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of Balts and Slavs) (Proto-Balto-Slavic speakers) ***Proto-Slavs (Proto-Slavic speakers) Antiquity * Sporoi (also known as Vistula Veneti): common ancestors of all Slavs, Proto-Slavs, and the West-Slavic Veneti. It is hypothesized that Proto-Slavs had their origin in the area of present-day western Ukraine - west of the Dnieper, east of the Vistula, south of the Pripyat Marshes and north of the Carpathian Mountains and the Dniester, to the northwest of the Pontic Eurasian Steppes and south of the Baltic peoples, especially West Baltic peoples, with whom they have common ancestors, the Balto-Slavs. Proto-Slavs are mainly associated with the Zarubintsy culture that had possible links to the ancient peoples of the Vistula basin (Przeworsk culture). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polotsk Principality
The Principality of Polotsk (obsolete spelling: ''Polock''; ; ), also known as the Duchy of Polotsk or Polotskian Rus', was a medieval principality. The origin and date of the establishment of the state are uncertain. Chronicles of Kievan Rus' mention Polotsk being conquered by Vladimir the Great, and thereafter it became associated with Kievan Rus' and its ruling Rurik dynasty. The principality was supposedly established around the town of Polotsk (now in Belarus) by the tribal union of Krivichs. In the second half of the 10th century, Polotsk was governed by its own dynasty; its first ruler mentioned in the chronicles was the semi-legendary Rogvolod (?–978), better known as the father of Rogneda of Polotsk, Rogneda. The principality was heavily involved in several succession crises of the 11th–12th centuries and a war with the Novgorod Land. By the 13th century, it was integrated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. At the time of its greatest extent, the principality stret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Turov Principality
The Principality of Turov, later called the Principality of Turov and Pinsk (; ; ), also known as Turovian Rus', was a medieval principality of Kievan Rus' from the 10th century on the territory of modern-day Belarus and northern Ukraine. The princes of Turov often served as grand princes early in 10th and 11th centuries. Its capital was Turov (Turaŭ), and other important cities included Pinsk, Mazyr, Slutsk, Lutsk, Brest, and Volodymyr. Until the 12th century, the principality was very closely associated with the principalities of Kiev and Volhynia. Later for a short period time until the Mongol invasion it enjoyed a wide degree of autonomy when it was annexed to the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. In the 14th century, it became part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. History The Principality of Turov originated mainly from the Dregovich tribe and partially the Drevlyans. While circumstances of its creation are not clearly known, the Principality as mentioned in the Primary Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Turaŭ
Turov or Turaw is a town in Zhytkavichy District, Gomel Region, Belarus. As of 2025, it has a population of 2,761. It served as the capital of the Principality of Turov during the Middle Ages. History Turov was an ancient capital of the Dregovich tribe - one of the three Eastern Slavic tribes that are considered ancestors of the modern Belarusian people (the others being Krivichs and Drevlians). Turov was first mentioned in the '' Tale of Bygone Years'' from 980. It is located in the southern part of Belarus, in the historical region of Polesia. According to legend, the city was founded at the crossing of Yazda and Strumen rivers by Duke Tur - hence the name Turov. Other etymology draws the name from ''Tur'', the Slavic name of the Aurochs. Both rivers join with the Pripyat river, which in turn flows into the Dnieper and then leads to the Black Sea. This river route was known to Vikings, who used it extensively for communication and during their frequent raids to Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". In a related sense, now not commonly used, all more or less sovereign rulers over a state, including kings, were "princes" in the language of international politics. They normally had another title, for example king or duke. Many of these were Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, ), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the '' princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chronicle
A chronicle (, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events, the purpose being the recording of events that occurred, seen from the perspective of the chronicler. A chronicle which traces world history is a universal chronicle. This is in contrast to a narrative or history, in which an author chooses events to interpret and analyze and excludes those the author does not consider important or relevant. The information sources for chronicles vary. Some are written from the chronicler's direct knowledge, others from witnesses or participants in events, still others are accounts passed down from generation to generation by oral tradition.Elisabeth M. C. Van Houts, ''Memory and Gender in Medieval Europe: 900–1200'' (Toronto; Buffalo: University of Toronto Press, 1999), pp. 19–20. Some used writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Krivichians
The Krivichs or Kryvichs ( rus, кри́вичи, p=ˈkrʲivʲɪtɕɪ, krivichi, links=y; , ) were a tribal union of Early East Slavs between the 6th and the 12th centuries. It is suggested that originally the Krivichi were native to the area around Pskov. They migrated to the mostly Finnic areas in the upper reaches of the Volga, Dnieper, Dvina, areas south of the lower reaches of river Velikaya and parts of the Neman basin. Etymology According to Max Vasmer, the name of the tribe probably stems from that of their legendary forefather Kriv.WORD: кри́вичи from ''Этимологический словарь Фасмер ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Severians
The Severians, also Severyans, Siverians, or Siverianians (; ; ; ) were a tribe or tribal confederation of early East Slavs occupying areas to the east of the middle Dnieper River and southeast of the Danube River. They are mentioned by the Bavarian Geographer (9th century), Emperor Constantine VII (956–959), the Khazar ruler Joseph (c. 955), and in the Primary Chronicle (1113). Ethnonym The etymology of the name "Severian" is uncertain. The name of the Severia region originated from the Slavic tribes. One theory proposes derivation from the Slavic word for "north" (''sěver''; men of the north), but the Severians never were the northernmost tribe of Slavs. Another theory proposes an Iranic derivation, from the name of the Sarmatian ''Seuer'' tribe (''seu'' meaning "black"). Some scholars have argued that Jews called this tribe the ''Sawarta,'' based on the '' Kievan Letter'' (c. 930), written in Hebrew as ''SWRTH'' (read either as ''Sur'ata'' or ''Sever'ata''), derived from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,. * was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.14–16. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavs, East Slavic, Norsemen, Norse, and Finnic peoples, Finnic, it was ruled by the Rurik dynasty, founded by the Varangians, Varangian prince Rurik.Kievan Rus , Encyclopædia Britannica Online. The name was coined by Russian historians in the 19th century to describe the period when Kiev was preeminent. At its greatest extent in the mid-11th century, Kievan Rus' stretched from the White Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south and from the River source, headwaters of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Constantine Porphyrogenitus
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Byzantine emperor of the Macedonian dynasty, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Karbonopsina, and the nephew of his predecessor Alexander. Most of his reign was dominated by co-regents: from 913 until 919 he was under the regency of his mother, while from 920 until 945 he shared the throne with Romanos Lekapenos, whose daughter Helena he married, and his sons. Constantine VII is best known for the '' Geoponika'' (τά γεοπονικά), an important agronomic treatise compiled during his reign, and three, perhaps four, books; (bearing in Greek the heading Πρὸς τὸν ἴδιον υἱὸν Ῥωμανόν), (Περὶ τῆς Βασιλείου Τάξεως), '' De Thematibus'' (Περὶ θεμάτων Άνατολῆς καὶ Δύσεως), and '' Vita Basilii'' (Βίος Βασιλείου), though his authorship of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |