|
Dos-à-dos (carriage)
A carriage is a two- or four-wheeled horse-drawn vehicle for passengers. In Europe they were a common mode of transport for the wealthy during the Roman Empire, and then again from around 1600 until they were replaced by the motor car around 1900. They were generally owned by the rich, but second-hand private carriages became common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping or, on those made in recent centuries, steel springs. There are numerous names for different types. Two-wheeled carriages are usually owner-driven. Coaches are a special category within carriages. They are carriages with four corner posts and a fixed roof. Two-wheeled war chariots and transport vehicles such as four-wheeled wagons and two-wheeled carts were forerunners of carriages. In the 21st century, horse-drawn carriages are occasionally used for public parades by royalty and for traditional formal ceremonies. Simplified modern version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Of Buckingham Palace, Londres Cropped Straightened
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a Domestication, domesticated, odd-toed ungulate, one-toed, ungulate, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two Extant taxon, extant subspecies of wild horse, ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolution of the horse, evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, ''Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 Common Era, BCE in Central Asia, and their domestication of the horse, domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, which are horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from equine anatomy, anatomy to life sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
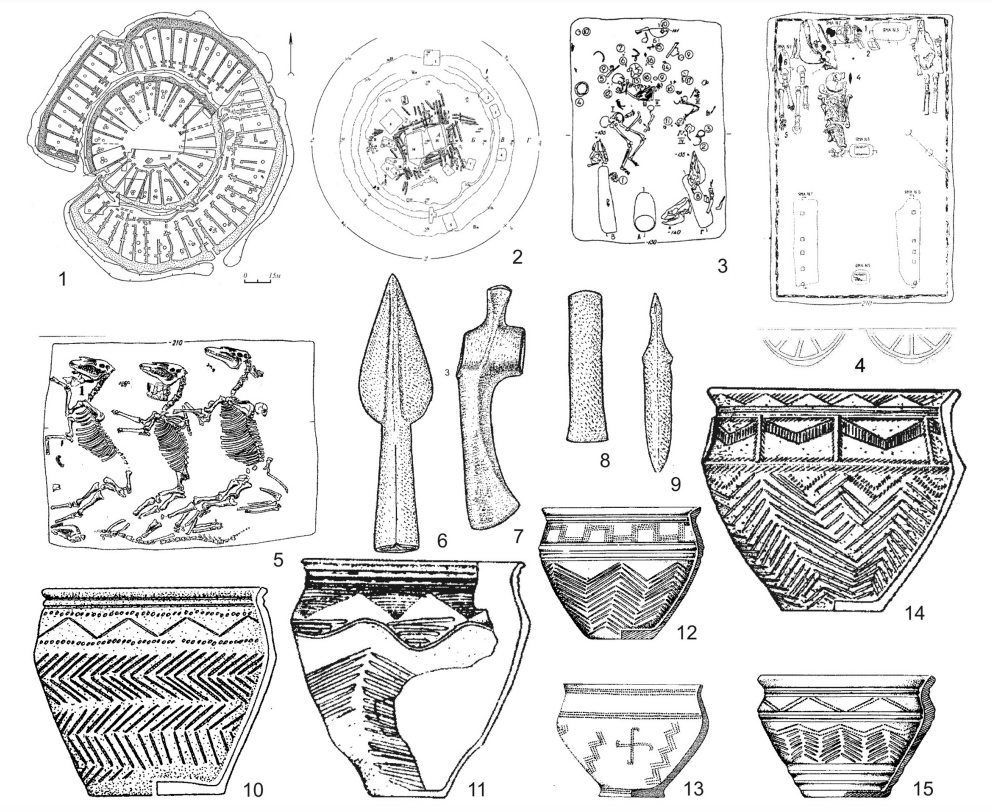
Bullock Cart
A bullock cart or ox cart (sometimes called a Carriage#Bullock carriage, bullock carriage when carrying people in particular) is a two-wheeled or four-wheeled vehicle pulled by oxen. It is a means of transportation used since ancient times in many parts of the world. They are still used today where modern vehicles are too expensive or less suitable for the local infrastructure. Used especially for carrying goods, the bullock cart is pulled by one or several oxen. The cart is attached to an ox team by a special chain attached to yokes, but a rope may also be used for one or two animals. The driver, and any other passengers, sit on the front of the cart, while load (if there is any) is placed in the back. Traditionally, the cargo has been agrarian goods and lumber. History The first indications of the use of a wagon (cart tracks, incisions, model wheels) are dated to around 4400 BC. The oldest wooden wheels usable for transport were found in southern Russia and dated to 3325 ± 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anyang
Anyang ( zh, s=安阳, t=安陽; ) is a prefecture-level city in Henan, China. Geographical coordinates are 35° 41'~ 36° 21' north latitude and 113° 38'~ 114° 59' east longitude. The northernmost city in Henan, Anyang borders Puyang to the east, Hebi and Xinxiang to the south, and the provinces of Shanxi and Hebei to its west and north respectively. Anyang had a total population of 5,477,614 as of the 2020 Chinese census, 2020 census, 2,675,523 of whom lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of four urban districts and Anyang and Tangyin counties, now largely agglomerated with the city proper. Anyang is the location of the ancient city of Yinxu, Yin, which was the capital of the Shang dynasty and the first stable capital of China. As the ancient capital of the Seven Dynasties and one of the birthplaces of Chinese civilization, Anyang is rich in historical and cultural resources and has a number of world-class and national historical sites. At the end of 1986, it was recogniz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henan
Henan; alternatively Honan is a province in Central China. Henan is home to many heritage sites, including Yinxu, the ruins of the final capital of the Shang dynasty () and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the historical capitals of China, Luoyang, Anyang, Kaifeng and Zhengzhou, are in Henan. While the province's name means 'south of the river', approximately a quarter of the province lies north of the Yellow River. With an area of , Henan covers a large part of the fertile and densely populated North China Plain. Its neighboring provinces are Shaanxi, Shanxi, Hebei, Shandong, Anhui, and Hubei. Henan is China's third-most populous province and the most populous among inland provinces, with a population of over 99 million as of 2020. It is also the world's seventh-most populous administrative division; if it were a country by itself, Henan would be the 17th-most populous in the world, behind Egypt and Vietnam. People from Henan often suffer from regional discrimination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Villa Boscoreale, many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, Pompeii offers a unique snapshot of Culture of ancient Rome, Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, as well as insight into ancient urban planning. It was a wealthy town of 10,000 to 20,000 residents at the time it was destroyed. It hosted many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and artworks, which were the main attractions for early excavators; subsequent excavations have found hundreds of private homes and businesses reflecting various architectural styles and social classes, as well as numerous public buildings. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latins (Italic tribe), Latin and Etruscan civilization, Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and List of Roman deities, its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by Roman Senate, a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconstruction Of A Roman Traveling Carriage Richly Decorated With Bronze Fittings, Romisch-Germanisches Museum, Cologne (8115675659)
Reconstruction may refer to: Politics, history, and sociology *Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company *''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Union political movement * Critical reconstruction, an architectural theory related to the reconstruction of Berlin after the end of the Berlin Wall *Economic reconstruction *Ministry of Reconstruction, a UK government department * *The Reconstruction era of the United States, the period after the American Civil War, 1865–1877 ** The Reconstruction Acts, or Military Reconstruction Acts, addressing requirements for Southern States to be readmitted to the Union *Reconstruction Finance Corporation, a United States government agency from 1932 to 1957 Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Reconstruction'' (1968 film), a Romanian tragicomedy * ''Reconstruction'' (2001 film), about the 1959 Ioanid Gang bank heist in Romania * ''Reconstruction'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 1950–1880 BC and are depicted on cylinder seals from Central Anatolia Region, Central Anatolia in Kültepe dated to c. 1900 BC. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The chariot was a fast, light, open, two-wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more Equidae, equids (usually horses) that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze Age, Bronze and Iron Age, Iron Ages, but after its military capabilities had been superseded by Light cavalry, light and Heavy cavalry, heavy cavalries, chariots continued to be used for travel and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanhudaro
Chanhu-daro , a shorter form of Chanhun-jo-daro which in Sindhi means "the mound of Chanhun", is an archaeological site belonging to the Indus Valley civilization. The site is located south of Mohenjo-daro, now in Sindh, Pakistan. The settlement was inhabited between 4000 and 1700 BCE, and is considered to have been a centre for manufacturing carnelian beads. This site is a group of three low mounds that excavations has shown were parts of a single settlement, approximately 7 hectares in size. Chanhudaro was first excavated by N. G. Majumdar in March, 1931, and again during winter field session of 1935-36 by the American School of Indic and Iranian Studies and the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston team led by Ernest John Henry Mackay. Prof. W. Norman Brown of the University of Pennsylvania was instrumental in enabling the funds for this project. After the independence of Pakistan, Mohammed Rafique Mughal also did exploratory work in the area. Since 2015 the archaeological exca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro (; , ; ) is an archaeological site in Larkana District, Sindh, Pakistan. Built 2500 BCE, it was one of the largest settlements of the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation, and one of the world's earliest major city, cities, contemporaneous with the civilisations of ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Minoan civilization, Minoan Crete, and Caral–Supe civilization, Norte Chico.Mohenjo-Daro (archaeological site, Pakistan) on Encyclopedia Britannica website Retrieved 25 November 2019 With an estimated population of at least 40,000 people, Mohenjo-daro prospered for several centuries, but by 1700 BCE had been abandoned, along with other large cities of the Indus Valley Civilisation. The site was rediscovered in the 1920s. Significant excavation has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harappa
Harappa () is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal, that takes its name from a modern village near the former course of the Ravi River, which now runs to the north. Harappa is the type site of the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilisation ("IVC"), as it was the first IVC site to be excavated by the Archaeological Survey of India during the British Raj, although its significance did not become manifest until the discovery of Mohenjo-daro some years later. For this reason, IVC is sometimes called the "Harappan civilisation," a term more commonly used by the Archaeological Survey of India after decolonization in 1947. The discovery of Harappa and, soon afterwards, Mohenjo-Daro, two major urban settlements of IVC, was the culmination of work that had begun after the founding of the Archaeological Survey of India in 1861. The city of Harappa is believed to have had as many as 23,500 residents and occupied about with clay brick houses at its greatest extent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |